
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134110646
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 57EAP
In FIGUREP11.57, a block of mass m slides along a frictionless track with speed vm. It collides with a stationary block of mass M. Find an expression for the minimum value of vmthat will allow the second block to circle the loop-the-loop without falling off if the collision is (a) perfectly inelastic or (b) perfectly elastic.
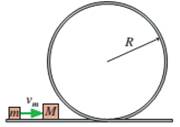
FIGURE P11.57
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
need help part d
A cab driver heads south with a steady speed of v₁ = 20.0 m/s for t₁ = 3.00 min, then makes a right turn and travels at v₂ = 25.0 m/s for t₂ = 2.80 min, and then drives northwest at v3 = 30.0 m/s for t3 = 1.00 min. For this 6.80-min trip, calculate the following.
Assume +x is in the eastward direction.
(a) total vector displacement (Enter the magnitude in m and the direction in degrees south of west.)
magnitude
direction
For each straight-line movement, model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the starting point be the origin of your coordinate system. Use the relationship
speed = distance/time to find the distances traveled during each segment. Write the displacement vector, and calculate its magnitude and direction. Don't forget to convert min to s! m
Model the car as a particle under constant velocity, and draw a diagram of the displacements, labeling the distances and angles. Let the…
î
A proton is projected in the positive x direction into a region of uniform electric field E = (-5.50 x 105) i N/C at t = 0. The
proton travels 7.20 cm as it comes to rest.
(a) Determine the acceleration of the proton.
magnitude 5.27e13
direction -X
m/s²
(b) Determine the initial speed of the proton.
8.71e-6
magnitude The electric field is constant, so the force is constant, which means the acceleration will be constant.
m/s
direction +X
(c) Determine the time interval over which the proton comes to rest.
1.65e-7
Review you equations for constant accelerated motion. s
Chapter 11 Solutions
Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol 1. (Chs 1-21)
Ch. 11 - Prob. 1CQCh. 11 - Prob. 2CQCh. 11 - \A 2 kg object is moving to the right with a speed...Ch. 11 - Prob. 4CQCh. 11 - Prob. 5CQCh. 11 - Angie, Brad, and Carlos are discussing a physics...Ch. 11 - Prob. 7CQCh. 11 - Automobiles are designed with “crumple zones”...Ch. 11 - A golf club continues forward after hitting the...Ch. 11 - Suppose a rubber ball collides head-on with a more...
Ch. 11 - Two particles collide, one of which was initially...Ch. 11 - Two ice skaters, Paula and Ricardo, push off from...Ch. 11 - Prob. 13CQCh. 11 - At what speed do a bicycle and its rider, with a...Ch. 11 - What is the magnitude of the momentum of A 3000 kg...Ch. 11 - What impulse does the force shown in FIGURE EX11.3...Ch. 11 - What is the impulse on a 3.0 kg particle that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 6EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 11 - A sled slides along a horizontal surface on which...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 11 - A g air-track glider collides with a spring at one...Ch. 11 - A 250 g ball collides with a wall. FIGURE EX11.13...Ch. 11 - A 5000 kg open train car is rolling on...Ch. 11 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 11 - Three identical train cars, coupled together, are...Ch. 11 - A 300 g bird flying along at 6.0 m/s sees a 10 g...Ch. 11 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 11 - A 1500 kg car is rolling at 2.0 m/s. You would...Ch. 11 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 11 - A 50 g marble moving at 2.0 m/s strikes a 20 g...Ch. 11 - A proton is traveling to the right at 2.0 × 107...Ch. 11 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 11 - Two particles collide and bounce apart. FIGURE...Ch. 11 - An object at rest explodes into three fragments....Ch. 11 - A 20 g ball of clay traveling east at 3.0 m/s...Ch. 11 - 34. At the center of a 50-m-diameter circular ice...Ch. 11 - A small rocket with 15 kN thrust burns 250 kg of...Ch. 11 - A rocket in deep space has an empty mass of 150 kg...Ch. 11 - A rocket in deep space has an exhaust-gas speed of...Ch. 11 - A tennis player swings her 1000 g racket with a...Ch. 11 - A 60 g tennis ball with an initial speed of 32 m/s...Ch. 11 - A 500 g cart is released from rest 1.00 m from the...Ch. 11 - A 200 g ball is dropped from a height of 2.0 m,...Ch. 11 - The flowers of the bunchberry plant open with...Ch. 11 - A particle of mass in is at rest at t = 0. Its...Ch. 11 - Air-track gliders with masses 300 g, 400 g, and...Ch. 11 - Most geologists believe that the dinosaurs became...Ch. 11 - Squids rely on jet propulsion to move around. A...Ch. 11 - A firecracker in a coconut blows the coconut into...Ch. 11 - One billiard ball is shot east at 2.0 m/s. A...Ch. 11 - a. A bullet of mass m is fired into a block of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 11 - An object at rest on a flat, horizontal surface...Ch. 11 - A 1500 kg weather rocket accelerates upward at 10...Ch. 11 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 11 - Two 5 g blocks of wood are 2.0 m apart on a...Ch. 11 - A 100 g granite cube slides down a 40°...Ch. 11 - You have been asked to design a “ballistic spring...Ch. 11 - In FIGUREP11.57, a block of mass m slides along a...Ch. 11 - The stoplight had just changed and a 2000 kg...Ch. 11 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 11 - Force Fx= (10 N) sin (2pt/4.0 s) is exerted on a...Ch. 11 - A 500 g particle has velocity vx=5.0 m/s at t = 2...Ch. 11 - 30 ton rail car and a 90 ton rail car, initially...Ch. 11 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 11 - Old naval ships fired 10 kg cannon balls from a...Ch. 11 - A proton (mass 1 u) is shot toward an unknown...Ch. 11 - The nucleus of the polonium isotope 214Po (mass...Ch. 11 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 11 - A 20 g ball of clay traveling east at 2.0 m/s...Ch. 11 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 11 - a. To understand why rockets often have multiple...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 76EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 77EAPCh. 11 - In Problems 75 through 78 you are given the...Ch. 11 - A 1000 kg cart is rolling to the right at 5.0 m/s....Ch. 11 - Prob. 80EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 81EAPCh. 11 - A two-stage rocket is traveling at 1200 m/s with...Ch. 11 - 83. The air-track carts in FIGURE P11.83 are...Ch. 11 - Section 11.6 found an equation for vmaxof a rocket...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three charged particles are at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure below. (Let q = 2.00 μC, and L = 0.750 m.) y 7.00 με 60.0° L 9 -4.00 μC x (a) Calculate the electric field at the position of charge q due to the 7.00-μC and -4.00-μC charges. 112 Once you calculate the magnitude of the field contribution from each charge you need to add these as vectors. KN/CI + 64 × Think carefully about the direction of the field due to the 7.00-μC charge. KN/Cĵ (b) Use your answer to part (a) to determine the force on charge q. 240.0 If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mN Î + 194.0 × If you know the electric field at a particular point, how do you find the force that acts on a charge at that point? mNarrow_forwardIn the Donkey Kong Country video games you often get around by shooting yourself out of barrel cannons. Donkey Kong wants to launch out of one barrel and land in a different one that is a distance in x of 9.28 m away. To do so he launches himself at a velocity of 22.6 m/s at an angle of 30.0°. At what height does the 2nd barrel need to be for Donkey Kong to land in it? (measure from the height of barrel 1, aka y0=0)arrow_forwardFor which value of θ is the range of a projectile fired from ground level a maximum? 90° above the horizontal 45° above the horizontal 55° above the horizontal 30° above the horizontal 60° above the horizontalarrow_forward
- A map from The Legend of Zelda: The Breath of the Wild shows that Zora's Domain is 7.55 km in a direction 25.0° north of east from Gerudo Town. The same map shows that the Korok Forest is 3.13 km in a direction 55.0° west of north from Zora's Domain. The figure below shows the location of these three places. Modeling Hyrule as flat, use this information to find the displacement from Gerudo Town to Korok Forest. What is the magnitude of the displacement? Find the angle of the displacement. Measure the angle in degrees north of east of Gerudo Town.arrow_forwardRace car driver is cruising down the street at a constant speed of 28.9 m/s (~65 mph; he has a “lead” foot) when the traffic light in front of him turns red. a) If the driver’s reaction time is 160 ms, how far does he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he begins to slow down? b) If the driver’s combined reaction and movement time is 750 ms, how far do he and his car travel down the road from the instant he sees the light change to the instant he slams on her brakes and car begins to slow down? c) If the driver’s average rate of acceleration is -9.5 m/s2 as he slows down, how long does it take him to come to a stop (use information about his speed of 28.9 m/s but do NOT use his reaction and movement time in this computation)? Please answer parts a-c. Show all work. For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.arrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Answer questions a-d. a) What was the total race time for each team, in seconds? b) Which team won the race? What was the difference in the teams’ times? c) What was the average speed for each team for the whole race? (provide answer to 3 decimal places). d) Calculate the average speed for each swimmer and report the results in a table like the one above. Remember to show the calculation steps. (provide answer to 3 decimal places). PLEASE SHOW ALL WORK AND STEPS.arrow_forward
- Need complete solution Pleasearrow_forwardBelow you will find 100 m split times for the American and France men’s 4x100 meter free style relay race during the 2008 Beijing Summer Olympics). Fill out the chart below. Calculate average speed per split (m/s). Show all work.arrow_forwardThe magnitude of vector →A i s 261. m and points in the direction 349.° counterclockwise from the positive x-axis. Calculate the x-component of this vector . Calculate the y-component of this vector.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Impulse Derivation and Demonstration; Author: Flipping Physics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9rwkTnTOB0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY