
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (Chs 1-42) Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition)
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780133953145
Author: Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus)
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 4EAP
What is the impulse on a 3.0 kg particle that experiences the force shown in FIGURE EX11.4?
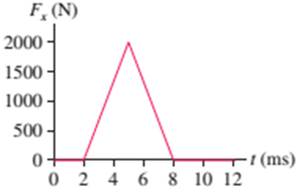
FIGURE EX11.4
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:09
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
A positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The
charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net
electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this
line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of
the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is
the other?
A charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a
particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed
of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel
before its speed is zero?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (Chs 1-42) Plus Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (4th Edition)
Ch. 11 - Prob. 1CQCh. 11 - Prob. 2CQCh. 11 - \A 2 kg object is moving to the right with a speed...Ch. 11 - Prob. 4CQCh. 11 - Prob. 5CQCh. 11 - Angie, Brad, and Carlos are discussing a physics...Ch. 11 - Prob. 7CQCh. 11 - Automobiles are designed with “crumple zones”...Ch. 11 - A golf club continues forward after hitting the...Ch. 11 - Suppose a rubber ball collides head-on with a more...
Ch. 11 - Two particles collide, one of which was initially...Ch. 11 - Two ice skaters, Paula and Ricardo, push off from...Ch. 11 - Prob. 13CQCh. 11 - At what speed do a bicycle and its rider, with a...Ch. 11 - What is the magnitude of the momentum of A 3000 kg...Ch. 11 - What impulse does the force shown in FIGURE EX11.3...Ch. 11 - What is the impulse on a 3.0 kg particle that...Ch. 11 - Prob. 5EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 6EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 7EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 8EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 9EAPCh. 11 - A sled slides along a horizontal surface on which...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11EAPCh. 11 - A g air-track glider collides with a spring at one...Ch. 11 - A 250 g ball collides with a wall. FIGURE EX11.13...Ch. 11 - A 5000 kg open train car is rolling on...Ch. 11 - Prob. 15EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 16EAPCh. 11 - Three identical train cars, coupled together, are...Ch. 11 - A 300 g bird flying along at 6.0 m/s sees a 10 g...Ch. 11 - Prob. 19EAPCh. 11 - A 1500 kg car is rolling at 2.0 m/s. You would...Ch. 11 - Prob. 21EAPCh. 11 - A 50 g marble moving at 2.0 m/s strikes a 20 g...Ch. 11 - A proton is traveling to the right at 2.0 × 107...Ch. 11 - Prob. 24EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 25EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 26EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 27EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 28EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 29EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 30EAPCh. 11 - Two particles collide and bounce apart. FIGURE...Ch. 11 - An object at rest explodes into three fragments....Ch. 11 - A 20 g ball of clay traveling east at 3.0 m/s...Ch. 11 - 34. At the center of a 50-m-diameter circular ice...Ch. 11 - A small rocket with 15 kN thrust burns 250 kg of...Ch. 11 - A rocket in deep space has an empty mass of 150 kg...Ch. 11 - A rocket in deep space has an exhaust-gas speed of...Ch. 11 - A tennis player swings her 1000 g racket with a...Ch. 11 - A 60 g tennis ball with an initial speed of 32 m/s...Ch. 11 - A 500 g cart is released from rest 1.00 m from the...Ch. 11 - A 200 g ball is dropped from a height of 2.0 m,...Ch. 11 - The flowers of the bunchberry plant open with...Ch. 11 - A particle of mass in is at rest at t = 0. Its...Ch. 11 - Air-track gliders with masses 300 g, 400 g, and...Ch. 11 - Most geologists believe that the dinosaurs became...Ch. 11 - Squids rely on jet propulsion to move around. A...Ch. 11 - A firecracker in a coconut blows the coconut into...Ch. 11 - One billiard ball is shot east at 2.0 m/s. A...Ch. 11 - a. A bullet of mass m is fired into a block of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 50EAPCh. 11 - An object at rest on a flat, horizontal surface...Ch. 11 - A 1500 kg weather rocket accelerates upward at 10...Ch. 11 - Prob. 53EAPCh. 11 - Two 5 g blocks of wood are 2.0 m apart on a...Ch. 11 - A 100 g granite cube slides down a 40°...Ch. 11 - You have been asked to design a “ballistic spring...Ch. 11 - In FIGUREP11.57, a block of mass m slides along a...Ch. 11 - The stoplight had just changed and a 2000 kg...Ch. 11 - Prob. 59EAPCh. 11 - Force Fx= (10 N) sin (2pt/4.0 s) is exerted on a...Ch. 11 - A 500 g particle has velocity vx=5.0 m/s at t = 2...Ch. 11 - 30 ton rail car and a 90 ton rail car, initially...Ch. 11 - Prob. 63EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 64EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 65EAPCh. 11 - Old naval ships fired 10 kg cannon balls from a...Ch. 11 - A proton (mass 1 u) is shot toward an unknown...Ch. 11 - The nucleus of the polonium isotope 214Po (mass...Ch. 11 - Prob. 69EAPCh. 11 - A 20 g ball of clay traveling east at 2.0 m/s...Ch. 11 - Prob. 71EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 72EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 73EAPCh. 11 - a. To understand why rockets often have multiple...Ch. 11 - Prob. 75EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 76EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 77EAPCh. 11 - In Problems 75 through 78 you are given the...Ch. 11 - A 1000 kg cart is rolling to the right at 5.0 m/s....Ch. 11 - Prob. 80EAPCh. 11 - Prob. 81EAPCh. 11 - A two-stage rocket is traveling at 1200 m/s with...Ch. 11 - 83. The air-track carts in FIGURE P11.83 are...Ch. 11 - Section 11.6 found an equation for vmaxof a rocket...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
When you rub your cold hands together, the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands. Why doe...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
12.1 Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
a. CH3-CH2-OH
b.
c.
d.
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
In rabbits, chocolate-colored fur (w+) is dominant to white fur (w), straight fur (c+) is dominant to curly fur...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Flask A contains yeast cells in glucose-minimal salts broth incubated at 30C with aeration. Flask B contains ye...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Which of the following factors would tend to increase membrane fluidity? A. a greater proportion of unsaturated...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
8. A human maintaining a vegan diet (containing no animal products) would be a:
a. producer
b. primary consume...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- a) What is the minimum tension in N that the cable must be able to support without breaking? Assume the cable is massless. T = b) If the cable can only support a tension of 10,000 N what is the highest mass the ball can have in kg? mm =arrow_forwardCurve Fitter CURVE FITTER Open Update Fit Save New Exclusion Rules Select Validation Data Polynomial Exponential Logarithmic Auto Fourier Fit Fit Duplicate Data Manual FILE DATA FIT TYPE FIT Harmonic Motion X us 0.45 mi ce 0.4 0.35 0.3 0.25 0.2 Residuals Plot Contour Plot Plot Prediction Bounds None VISUALIZATION Colormap Export PREFERENCES EXPORT Fit Options COA Fourier Equation Fit Plot x vs. t -Harmonic Motion a0+ a1*cos(x*w) + b1*sin(x*w) Number of terms Center and scale 1 ▸ Advanced Options Read about fit options Results Value Lower Upper 0.15 a0 0.1586 0.1551 0.1620 a1 0.0163 0.0115 0.0211 0.1 b1 0.0011 -0.0093 0.0115 W 1.0473 0.9880 1.1066 2 8 10 t 12 14 16 18 20 Goodness of Fit Value Table of Fits SSE 0.2671 Fit State Fit name Data Harmonic Motion x vs. t Fit type fourier1 R-square 0.13345 SSE DFE 0.26712 296 Adj R-sq 0.12467 RMSE 0.030041 # Coeff Valic R-square 0.1335 4 DFE 296.0000 Adj R-sq 0.1247 RMSE 0.0300arrow_forwardWhat point on the spring or different masses should be the place to measure the displacement of the spring? For instance, should you measure to the bottom of the hanging masses?arrow_forward
- Let's assume that the brightness of a field-emission electron gun is given by β = 4iB π² d²α² a) Assuming a gun brightness of 5x108 A/(cm²sr), if we want to have an electron beam with a semi-convergence angle of 5 milliradian and a probe current of 1 nA, What will be the effective source size? (5 points) b) For the same electron gun, plot the dependence of the probe current on the parameter (dpa) for α = 2, 5, and 10 milliradian, respectively. Hint: use nm as the unit for the electron probe size and display the three plots on the same graph. (10 points)arrow_forwardi need step by step clear answers with the free body diagram clearlyarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- Review the data in Data Table 1 and examine the standard deviations and 95% Margin of Error calculations from Analysis Questions 3 and 4 for the Acceleration of the 1st Based on this information, explain whether Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Equation 1, was verified for your 1st Angle. Equation: SF=ma Please help with explaining the information I collected from a lab and how it relates to the equation and Newton's Second Law. This will help with additional tables in the lab. Thanks!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer the problem step by step with explanations along side each step stating what's been done correctly please. Thank you!! ( preferably type out everything)arrow_forwardAnswer thisarrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote instantarrow_forwardKirchoff's Laws. A circuit contains 3 known resistors, 2 known batteries, and 3 unknown currents as shown. Assume the current flows through the circuit as shown (this is our initial guess, the actual currents may be reverse). Use the sign convention that a potential drop is negative and a potential gain is positive. E₂ = 8V R₁₁ = 50 R₂ = 80 b с w 11 www 12 13 E₁ = 6V R3 = 20 a) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop abefa in the clockwise direction starting at point a. (2 pt). b) Apply Kirchoff's Loop Rule around loop bcdeb in the clockwise direction starting at point b. (2 pt). c) Apply Kirchoff's Junction Rule at junction b (1 pt). d) Solve the above 3 equations for the unknown currents I1, 12, and 13 and specify the direction of the current around each loop. (5 pts) I1 = A 12 = A 13 = A Direction of current around loop abef Direction of current around loop bcde (CW or CCW) (CW or CCW)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Impulse Derivation and Demonstration; Author: Flipping Physics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9rwkTnTOB0s;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY