
Concept explainers
Interpretation: A real estate firm wishes to open four new offices in Boston area and they are having six potential sites available. Based on the number of employees in each office and the location of the properties that each employee will manage, the firm estimated the total travel time in hours per day for each office and each location. The optimal assignment of offices to sites to minimize employee travel time needs to be determined.
| Offices | |||||
| A | B | C | D | ||
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | |
| Sites | 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
Concept Introduction: A discrete facility location problem is considered, when a balance has to be achieved between the minimum and maximum number of customers, wherein there is a difference that arises between the allocation of these customers made to every plant.
Answer to Problem 46AP
The optimal travel time has been derived as 17.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
| Offices | |||||
| A | B | C | D | ||
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | |
| Sites | 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
When there are no inter-departmental interactions and a discrete set of alternative locations could be considered, then assignment problems can be considered to be appropriate. Following are the procedure for solution for assignment problems:
- The smallest number in row 1 needs to be identified and it should be subtracted from all the entries in that row. This procedure needs to be repeated for all the rows in cost matrix.
- Similarly, the smallest number in column 1 needs to be identified and it should be subtracted from all the entries in column 1. This procedure needs to be repeated for all the columns in cost matrix.
- At a certain point, each column and each row will have at least a zero. If there is possibility for making a zero assignment, then the same can be done, which in turn will be the optimal solution, and if not, then proceed to the next step.
- The maximum number of zero cost assignments needs to be determined, which will be equal to smallest number of lines adequate to cover all zeros. These lines are not necessarily unique and are found by inspection. The number of lines drawn should be less than the maximum number of zero cost assignments.
- The smallest uncovered number should be identified and proceed with the following steps:
- Subtract smallest uncovered number from all the other uncovered numbers.
- Add this to the step at the point where the line crosses.
- Return back to step 3
Step 1: The below shown matrix, not being a square matrix, dummy rows to balance the sites and offices are added.
| Offices | ||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D |
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 |
| 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 |
By adding the dummy rows the matrix has been modified as shown below:
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 13 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 12 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 14 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 17 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Step 2: The row reducing matrix needs to be performed by subtracting the smallest number from each row. Since in this case, the resultant zero assignment has been achieved for each office, further column reduction matrix is not performed.
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Step 3: From each site identifying of the zero assignment gives the following matrix
| Offices | ||||||
| Sites | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| 3 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 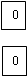 | 0 |
| 4 | 4 | 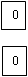 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 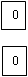 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 2 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 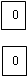 |
Thus the optimal solution for travel time will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS ANALYSIS
- Women who ask for what they want in negotiation are less well-liked than women who do not self-advocate. However, nonassertive, other-advocating women suffer a leadership backlash and are regarded as less competent because their behavior is regarded to be _____ and _____. A. high-negative feminine; low-positive masculine B. high-positive feminine; high-positive masculine C. high-negative masculine; low-negative feminine D. low-positive masculine; low-positive femininearrow_forwardThere are five most recognized personality traits that can reliably be measured and predict negotiator behavior in a number of different situations. All of the following are one of those "Big 5" personality traits except _____. A. conscientiousness B. introversion C. agreeableness D. openness to experiencearrow_forwardWith regard to reputation in negotiation, negotiators who use adversarial, stubborn, and ethically questionable behavior often have the effect of _____. A. improving their business relationships B. decreasing their effectiveness as a negotiator C. improving their business relationships D. decreasing their group statusarrow_forward
- When it comes to assertiveness, there is only a modest link between negotiators' self-views and how the counterparty sees them. Many negotiators come away from a negotiation thinking they came on too strong with the counterparty. The _____ refers to the fact that negotiators believe they are coming on too strong with the counterparty, but they actually are not. A. Collective trap illusion B. Attribution error C. Aggressive anchoring bias D. Line-crossing illusionarrow_forwardAs you think about the issue of using chatbots in contract negotiations, consider whether other facets and concepts of negotiations that we have discussed and whether they would be adequately addressed.arrow_forwardWhile I am not a fan of AI as of yet, I do understand the endless possibilities. Based on the research, it is clear that AI has great potential for negotiation (Yang, 2025). Herold et al. (2025) suggested that AI can flag potential risks and liabilities, allowing negotiators to address them and mitigate potential problems proactively. AI can draft new contract templates by examining industry standards and past contracts, and AI technology can help lawyers spot errors and inconsistencies in contract drafts. In relation to risk management, AI can flag possible risks and liabilities, allowing negotiators to proactively address them and lessen potential problems, which can speed up the negotiation process, making the negotiation efficient because AI can industrialize tasks like document review, redlining, and finding potential issues, significantly reducing negotiation time. Lastly, AI can analyze vast amounts of data and identify errors, inconsistencies, and irregularities in…arrow_forward
- What is a main thought on using AI in contract negotiations?arrow_forwardWhat are some people thoughts on using AI in contract negotiations?arrow_forward3. Develop a high-level or summary: a. Risk Management Plan Focus on specific, actionable steps for each risk and mitigation strategy.Provide detailed timelines for procurement, stakeholder engagement, and risk monitoring.Avoid over-simplifying and add more technical details in areas like quality assurance and financial control measures. Add a risk prioritization method and mention how risks will be monitored and reviewed throughout the project lifecycle. Overall, it is well organized andc overs key risks.arrow_forward
- 3. Develop a high-level or summary: Human Resource Management Plan Provide more concrete timelines and actionable steps for human resource management.Include more detailed risk management strategies and link them more explicitly to the overall project plan.Expand on how training and development will be evaluated and tracked.Also, the overall length is good, but some sections could be condensed by eliminating repetition (e.g., you discuss stakeholder communication and engagement in two sections without adding new information).Try not to repeat the same risk management ideas (e.g., resource sharing and stakeholder concerns) in multiple sections without adding value.arrow_forwardBased on the U.S. Department of Transporation's publication on the number of inrternatioal passengers that come through New York airport (JFK) in 2012, how would I estimate the passenger volume for the coming year?arrow_forwardWhat are the role of trends and seasonality based on the Department of Transportation publication of the number of international passengers that come through New York (JFK) in 2012?arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Management, Loose-Leaf VersionManagementISBN:9781305969308Author:Richard L. DaftPublisher:South-Western College Pub


