
Concept explainers
The BOMs for products A & B and data from the inventory records are shown in Figure 11.41. Data from the inventory records are shown in Table 11.10. In the MPS for product A, the MPS start row has 85 units in week 2 and 200 in week 4 and 50 in week 8. In the MPS for product B, the MPS start row has 65 units in week 3 and 50 in week 4 and 50 in week 5 and 75 in week 8.
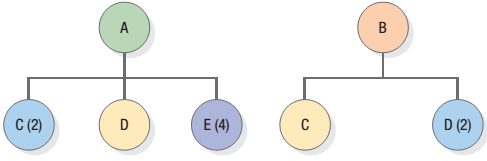
- Develop the material requirements plan for the next 8 weeks for items C, D, and E. Note any difficulties you observe in the inventory records.
- Can the difficulties noted in part (a) be rectified by expediting any
Scheduled Receipts?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains, Student Value Edition Plus MyLab Operations Management with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (12th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Macroeconomics
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Essentials of MIS (13th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting, The Financial Chapters (Book & Access Card)
- 1) View the video What is Operations Management (14.01 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapters 1 and/or 2) after watching this video. (https://www.viddler.com/embed/d01189e1) Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) View the video What McDonald’s is serving up at its new CosMc’s Chain (3.42 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and answer the following questions: (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k7ojpUzE8q4) i) From a strategic perspective, why do you think McDonald’s is opting for this new chain rather than trying to launch the new menu in its existing restaurants? ii) What factors do you think in McDonald’s external and internal environments are driving its decision to open the CosMc’s locations? iii) How do you think this format will improve McDonald’s profit margin as compared to its regular fast-food restaurants? Note: As a…arrow_forwardSince the end of World War II, globalization has steadily increased with rapid expansion around the turn of the 21st century. What are some of the forces driving globalization and international business? What are some of the challenges of engaging in international business compared to doing business in your home country?arrow_forwardPS.53 Brother I.D. Ricks is a faculty member at BYU-Idaho whose grandchildren live in Oklahoma and California. He and his wife would like to visit their grandchildren at least once a year in these states. They currently have one vehicle with well over 100,000 miles on it, so they want to buy a newer vehicle with fewer miles and that gets better gas mileage. They are considering two options: (1) a new subcompact car that would cost $18,750 to purchase or (2) a used sedan that would cost $12,750.They anticipate that the new subcompact would get 37 miles per gallon (combined highway and around town driving) while the sedan would get 26 miles per gallon. Based on their road tripping history they expect to drive 13,000 miles per year. For the purposes of their analysis they are assuming that gas will cost $2.93 per gallon.Question: How many miles would the Ricks need to drive before the cost of these two options would be the same? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) (Hint:…arrow_forward
- Choose one major approach to job design, and then discuss how best that approach can be utilized in either your current or previous employer, including a discussion of its strengths and weaknesses.arrow_forwardThe results of your four plans will provide an indicative EOQ value. State this value and discuss in a precise manner, why it is not the exact, true value. Additional calculations in the form of plans E, F etc. may also assist your explanation of the EOQ and can be includedarrow_forwardi). Complete the table assuming a Level production plan. ii) Comment on your results and explain whether at this stage, you consider a Level plan is a suitable approach for this particular business. Your comment should include reference to a calculated ‘fill rate’.arrow_forward
- In the following sawtooth inventory profile diagram, two inventory plans with different order quantities (Q) and different frequencies of delivery are shown; order quantity for Plan A = 200 units and Plan B = 50 units. i). Total demand (D) is 350 units, the holding cost per unit (Ch) is equal to (£0.8) and the ordering cost per order (Co) is (£12.5). Calculate the total costs for each plan and state which one is more preferable along with the reason why. ii). There is a stark difference in the composition of the total costs of Plans A and B. Explain this difference and why it occurs. Use the breakdown of costs for each plan to help illustrate your answer.arrow_forwardi). Complete the table for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible. You should support your answer with numerical data derived from Table 3. In comparing the costs, state any other assumptions made.arrow_forwardi). Complete for a Chase production plan. ii). Explain whether a Level or Chase plan is more suitable for the demand pattern experienced by this particular business, which incidentally relies on highly skilled workers in the production process. Assume a starting workforce of 7 and that fractional workers are permissible.arrow_forward
- Complete the table for a Chase production plan.arrow_forwardHow much can the garden centre expect to sell during each quarter of next year (Year 3) accounting for seasonality? Your forecast must make use of seasonal indices. All workings must be shown in full. (NOTE: Please round your calculations to three decimal places).arrow_forwardPS.53 Brother I.D. Ricks is a faculty member at BYU-Idaho whose grandchildren live in Oklahoma and California. He and his wife would like to visit their grandchildren at least once a year in these states. They currently have one vehicle with well over 100,000 miles on it, so they want to buy a newer vehicle with fewer miles and that gets better gas mileage. They are considering two options: (1) a new subcompact car that would cost $18,750 to purchase or (2) a used sedan that would cost $12,750.They anticipate that the new subcompact would get 37 miles per gallon (combined highway and around town driving) while the sedan would get 26 miles per gallon. Based on their road tripping history they expect to drive 13,000 miles per year. For the purposes of their analysis they are assuming that gas will cost $2.93 per gallon.Question: How many miles would the Ricks need to drive before the cost of these two options would be the same? (Display your answer to the nearest whole number.) (Hint:…arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage LearningMarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning





