
(a)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
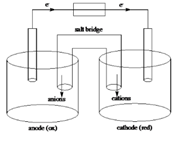
Values of
Explanation of Solution
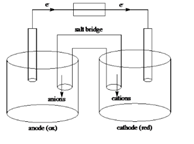
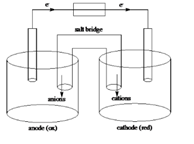
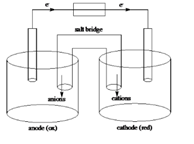
Below is a sketch of a galvanic cell where electrons flow from anode to cathode with a salt bridge between two to supply the required ions and complete the circuit. Cations will always flow to the anode and anions will always flow to the cathode.
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cr has +3 oxidation state and Cl has 0 oxidation state and in products Cr has +6 oxidation state and Cl has -1 oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Cr, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred.
Cr has lost three electrons because Cr atom has gone from +3 to +6. Add six electrons to the products. The half reaction is now change balanced as well.
It has been converted to
Each Cl atom required one electron because they have gone from 0 to -1, thus add two electrons in reactants for a change balance.
Add two half reactions together and cancel out the electrons to determine overall process. Because Cr half reaction has six electrons multiply Cl half reaction by three before adding two together.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(b)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Cu has +2 oxidation state and Mg has 0 oxidation state and in products Cu has 0 oxidation state and Mg has +2oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Mg, it is oxidized. This means that Mg is at the anode. For Cu oxidation number decreased, it was reduced. This means that
Add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons determine overall process.
Determine the standard reduction potential from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(c)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(c)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determine which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction I has +5 oxidation state and Fe has +2 oxidation state and in products I has 0 oxidation state and Fe has +3oxidation state. Oxidation number increased for Fe, it is oxidized. This means that
Determine actual half reactions that have occurred
Each I atom has gone from +5 to 0 oxidation state, thus it has gained five electrons. Add ten electrons to reactants. Half-reaction is now charge balanced as well.
To determine overall process add two half reactions together and cancel out electrons. Because I half-reaction has ten electrons, multiply Fe half-reaction by ten before adding two together.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
(d)
Interpretation: The galvanic cells based on given overall reaction needs to be sketched and the value of
Concept Introduction: A galvanic cell is an electro chemical cell that drives electrical energy from chemical reactions taking place within a particular cell.
In a galvanic cell the oxidation and the reduction half cells are separated by a connecting wire so that electrons can flow through the wire.
(d)
Answer to Problem 19E
Sketch of a galvanic cell is as follows:
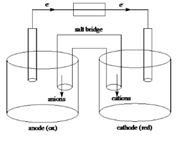
Values of
Explanation of Solution
By examining oxidation number of atoms in the reaction determines which compound is oxidized and which being reduced.
In above reaction Ag has +1 oxidation state and Zn has 0 oxidation state and in products Ag has 0 oxidation state and Zn has +2 oxidation state. This means Zn is at anode. Because oxidation number decrease for Ag. It is reduced. This means that
Determine actual-half reactions that have occurred. Zn has only been converted to
Zn loses two electrons so add two electrons to products to charge balance half-reaction.
Determine standard reduction potentials from reference table to calculate
Add these values together to give
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- How many chiral centers are there in the following molecule? HO 0 1 ○ 2 ♡ 4 'N'arrow_forwardThe following chemical structure represents a molecule of what molecular formula?arrow_forwardWhich region(s) of the following phospholipid is/are hydrophobic? RO I hydro-water phobic-dislikes = Hydrophobic dislikes water ○ I only Il only I and III only II and IV only O II, III, and IV only III || IVarrow_forward
- Given the following data, determine the order of the reaction with respect to H2. H2(g) + 21Cl(g) → I2(g) + 2HCl(g) Experiment [H2] (torr) [ICI] (torr) Rate (M/s) 1 250 325 0.266 2 250 81 0.0665 3 50 325 0.266arrow_forwardWhich one of the following molecules is chiral? H- NH₂ H3C དང་།་ OH H HO H₂N HO- -H CHO -OH H HO- OH H- -H CH₂OH OHarrow_forwardThe structure of an unsaturated phospholipid is shown below. Which region of the molecule is most hydrophilic ? H₂N-CH₂ H₂C IV CH3 CH3 hydro-water philic-likes = Hydrophilic likes water ○ IV All regions are equally hydrophilic. IIIarrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning





