
(a)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(a)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is0.27 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram of cell is shown below:
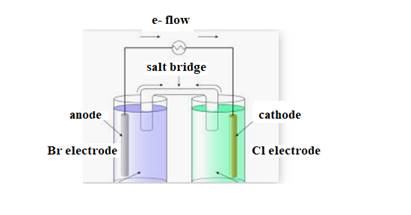
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The cell representation is shown below:
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.36 − (-1.09)
= 0.27 V
(b)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(b)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 0.09 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
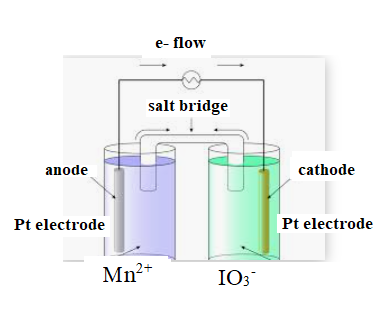
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.60 − 1.51
= 0.09 V
(c)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(c)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 1.10 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
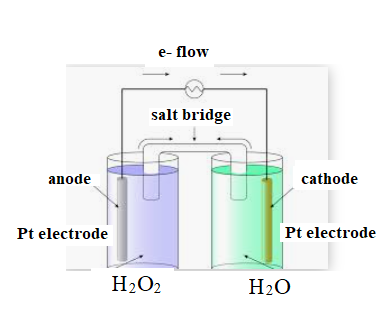
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= 1.78 − 0.68
= 1.10 V
(d)
Interpretation:
The sketch of galvanic cell along with cathode and anode and the direction of electron flow, the direction of flow of ions through salt bridge, the balanced chemical equation and the E0cell should be predicted.
Concept Introduction:
In galvanic cell chemical energy converted into electrical energy.
At anode oxidation takes place which means loss of electrons.
At cathode reduction takes place which means gain of electrons.
(d)
Answer to Problem 21E
The E0cell is 1.14 V
Reaction at anode:
Reaction at cathode:
Overall reaction:
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The diagram is shown below:
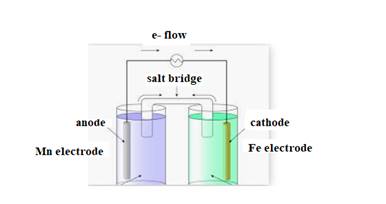
The direction of flow of electrons is from anode to cathode.
Negative ions flow towards anode.
At anode oxidation takes place
At cathode reduction takes place.
The oxidation half-cell reaction is shown below:
The reduction half-cell reaction is shown below:
The overall reaction is shown below:
The calculation of E0cell is shown below:
E0cell = E0cathode − E0anode
= - 0.036- (-1.18)
= 1.14 V
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Chemical Principles
- Concentration Trial1 Concentration of iodide solution (mA) 255.8 Concentration of thiosulfate solution (mM) 47.0 Concentration of hydrogen peroxide solution (mM) 110.1 Temperature of iodide solution ('C) 25.0 Volume of iodide solution (1) used (mL) 10.0 Volume of thiosulfate solution (5:03) used (mL) Volume of DI water used (mL) Volume of hydrogen peroxide solution (H₂O₂) used (mL) 1.0 2.5 7.5 Time (s) 16.9 Dark blue Observations Initial concentration of iodide in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of thiosulfate in reaction (mA) Initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide in reaction (mA) Initial Rate (mA's)arrow_forwardDraw the condensed or line-angle structure for an alkene with the formula C5H10. Note: Avoid selecting cis-/trans- isomers in this exercise. Draw two additional condensed or line-angle structures for alkenes with the formula C5H10. Record the name of the isomers in Data Table 1. Repeat steps for 2 cyclic isomers of C5H10arrow_forwardExplain why the following names of the structures are incorrect. CH2CH3 CH3-C=CH-CH2-CH3 a. 2-ethyl-2-pentene CH3 | CH3-CH-CH2-CH=CH2 b. 2-methyl-4-pentenearrow_forward
- Draw the line-angle formula of cis-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene. Then, draw the line-angle formula of trans-2,3-dichloro-2-pentene below. Draw the dash-wedge formula of cis-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane. Then, draw the dash-wedge formula of trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane below.arrow_forwardRecord the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. Dicyclopentadiene measured in volume Cyclopentadiene measured in grams 0 Measured Calculated Mol Yield Mass (g) or Volume (mL) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) 0.6 2.955 Part 2 Measurements and Results Record the amounts measured and calculate the percent yield for Part 2 in the table below. 0.588 0.0044 2.868 0.0434 N/A Table view List view Measured Calculated Mol $ Yield Melting Point (C) Mass (g) or Volume (ml) Mass (g) or Volume (ml.) Cyclopentadiene 0.1 0.08 0.001189 measured in volume Maleic Anhydride 0.196 N/A cis-norbornene-5,6-endo- dicarboxylic anhydride 0.041 0.0002467 N/A N/A N/A 0.002 N/A N/A 128arrow_forwardDraw the condensed structural formula and line-angle formula for each: 2,3-dimethylheptane 3-bromo-2-pentanol 3-isopropyl-2-hexene 4-chlorobutanoic acidarrow_forward
- Record the IUPAC names for each of the structures shown below. a) b) c) OH d) OH e)arrow_forwardA solution of 14 g of a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte compound in 0.10 kg of benzene boils at 81.7°C. If the BP of pure benzene is 80.2°C and the K, of benzene is 2.53°C/m, calculate the molar mass of the unknown compound. AT₁ = Km (14)arrow_forwardPlease help me answer the following questions. My answers weren't good enough. Need to know whyy the following chemicals were not used in this experiment related to the melting points and kf values. For lab notebook not a graded assignments.arrow_forward
- Draw the arrow pushing reaction mechanism. DO NOT ANSWER IF YOU WONT DRAW IT. Do not use chat gpt.arrow_forwardComplete the following esterification reaction by drawing the structural formula of the product formed. HOH HO i catalyst catalyst OH HO (product has rum flavor) (product has orange flavor)arrow_forwardThe statements in the tables below are about two different chemical equilibria. The symbols have their usual meaning, for example AG stands for the standard Gibbs free energy of reaction and K stands for the equilibrium constant. In each table, there may be one statement that is faise because it contradicts the other three statements. If you find a false statement, check the box next to t Otherwise, check the "no false statements" box under the table. statement false? AG"1 no false statements: statement false? AG-0 0 InK-0 0 K-1 0 AH-TAS no false statements 2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning





