1 Units, Physical Quantities, And Vectors 2 Motion Along A Straight Line 3 Motion In Two Or Three Dimensions 4 Newton’s Laws Of Motion 5 Applying Newton’s Laws 6 Work And Kinetic Energy 7 Potential Energy And Energy Conservation 8 Momentum, Impulse, And Collisions 9 Rotation Of Rigid Bodies 10 Dynamics Of Rotational Motion 11 Equilibrium And Elasticity 12 Fluid Mechanics 13 Gravitation 14 Periodic Motion 15 Mechanical Waves 16 Sound And Hearing 17 Temperature And Heat 18 Thermal Properties Of Matter 19 The First Law Of Thermodynamics 20 The Second Law Of Thermodynamics 21 Electric Charge And Electric Field 22 Gauss’s Law 23 Electric Potential 24 Capacitance And Dielectrics 25 Current, Resistance, And Electromotive Force 26 Direct-current Circuits 27 Magnetic Field And Magnetic Forces 28 Sources Of Magnetic Field 29 Electromagnetic Induction 30 Inductance 31 Alternating Current 32 Electromagnetic Waves 33 The Nature And Propagation Of Light 34 Geometric Optics 35 Interference 36 Diffraction 37 Relativity 38 Photons: Light Waves Behaving As Particles 39 Particles Behaving As Waves 40 Quantum Mechanics I: Wave Functions 41 Quantum Mechanics Ii: Atomic Structure 42 Molecules And Condensed Matter 43 Nuclear Physics 44 Particle Physics And Cosmology expand_more
11.1 Conditions For Equilibrium 11.2 Center Of Gravity 11.3 Solving Rigid-body Equilibrium Problems 11.4 Stress, Strain, And Elastic Moduli 11.5 Elasticity And Plasticity Chapter Questions expand_more
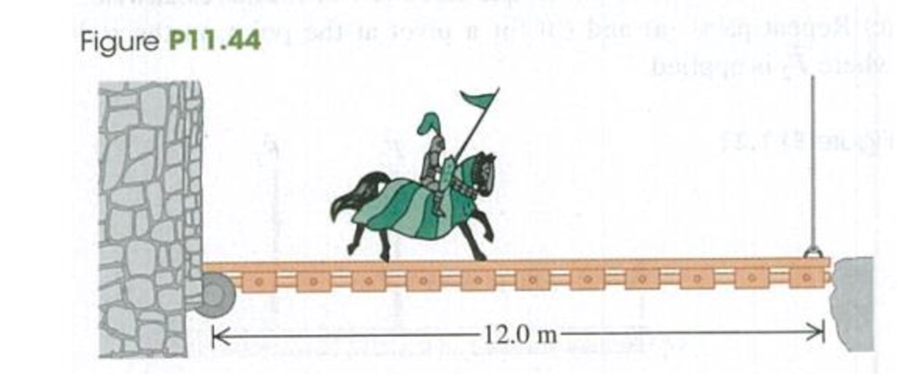
Problem 11.1DQ: Does a rigid object in uniform rotation about a fixed axis satisfy the first and second conditions... Problem 11.2DQ: (a) Is it possible for an object to be in translational equilibrium (the first condition) but not in... Problem 11.3DQ Problem 11.4DQ: Does the center of gravity of a solid body always be within the material of the body? If not, give a... Problem 11.5DQ Problem 11.6DQ: You are balancing a wrench by suspending it at a single point. Is the equilibrium stable, unstable,... Problem 11.7DQ: You can probably stand flatfooted on the floor and then rise up and balance on your tiptoes. Why are... Problem 11.8DQ Problem 11.9DQ: An object consists of a ball of weight W glued to the end of a uniform bar also of weight W. If you... Problem 11.10DQ Problem 11.11DQ Problem 11.12DQ: In pioneer days, when a Conestoga wagon was stuck in the mud, people would grasp the wheel spokes... Problem 11.13DQ: The mighty Zimbo claims to have leg muscles so strong that he can stand flat on his feet and lean... Problem 11.14DQ: Why is it easier to hold a 10-kg dumbbell in your hand at your side than it is to hold it with your... Problem 11.15DQ: Certain features of a person, such as height and mass, are fixed (at least over relatively long... Problem 11.16DQ: During pregnancy, women often develop back pains from leaning backward while walking. Why do they... Problem 11.17DQ: Why is a tapered water glass with a narrow base easier to tip over than a glass with straight sides?... Problem 11.18DQ Problem 11.19DQ: A uniform beam is suspended horizontally and attached to a wall by a small hinge (Fig. Q11.19). What... Problem 11.20DQ: If a metal wire has its length doubled and its diameter tripled, by what factor does its Youngs... Problem 11.21DQ: A metal wire of diameter D stretches by 0.100 mm when supporting a weight W. If the same-length wire... Problem 11.22DQ Problem 11.23DQ: The material in human bones and elephant bones is essentially the same, but an elephant has much... Problem 11.24DQ: There is a small bui appreciable amount of elastic hysteresis in the large tendon at the back of a... Problem 11.25DQ: When rubber mounting blocks are used to absorb machine vibrations through elastic hysteresis, as... Problem 11.1E: A 0.120-kg. 50.0-cm-long uniform bar has a small 0.055-kg mass glued to its left end and a small... Problem 11.2E Problem 11.3E: A uniform rod is 2.00 m long and has mass 1.80 kg. A 2.40-kg clamp is attached to the rod. How far... Problem 11.4E: A uniform 300-N trapdoor in a floor is hinged at one side. Find the net upward force needed to begin... Problem 11.5E: Raising a Ladder. A ladder carried by a fire truck is 20.0 m long. The ladder weighs 3400 N and its... Problem 11.6E: Two people are carrying a uniform wooden board that is 3.00 m long and weighs 160 N. If one person... Problem 11.7E: Two people carry a heavy electric motor by placing it on a light board 2.00 in long. One person... Problem 11.8E: A 60.0-cm. uniform. 50.0-N shelf is supported horizontally by two vertical wires attached (o the... Problem 11.9E: A 350-N, uniform. 1.50-m bar is suspended horizontally by two vertical cables at each end. Cable A... Problem 11.10E: A uniform ladder 5.0 m long rests against a frictionless, vertical wall with its lower end 3.0 m... Problem 11.11E: A diving board 3.00 m long is supported at a point 1.00 m from the end, and a diver weighing 500 N... Problem 11.12E: A uniform aluminum beam 9.00 m long, weighing 300 N, rests symmetrically on two supports 5.00 m... Problem 11.13E: Find the tension T in each cable and the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on the strut... Problem 11.14E: The horizontal beam in Fig. E11.14 weighs 190 N. and its center of gravity is at its center. Find... Problem 11.15E: The boom shown in Fig. E11.15 weighs 2600 N and is attached to a friction less pivot at its lower... Problem 11.16E: Suppose that you can lift no more than 650 N (around 150 lb) unaided, (a) How much can you lift... Problem 11.17E: A 9.00-m-long uniform beam is hinged to a vertical wall and held horizontally by a 5.00-m-long cable... Problem 11.18E: A 15,000-N crane pivots around a friction-free axle at its base and is supported by a cable making a... Problem 11.19E: A 3.00-m-long. 190-N, uniform rod at the zoo is held in a horizontal position by two ropes at its... Problem 11.20E: A nonuniform beam 4.50 m long and weighing 1.40 kN makes an angle of 25.0 below the horizontal. It... Problem 11.21E: A Couple. Two forces equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, acting on an object at two... Problem 11.22E: BIO A Good Workout. You are doing exercises on a Nautilus machine in a gym to strengthen your... Problem 11.23E: BIO Neck Muscles. A student bends her head at 40.0 from the vertical while intently reading her... Problem 11.24E: BIO Biceps Muscle. A relaxed biceps muscle requires a force of 25.0 N for an elongation of 3.0 cm;... Problem 11.25E: A circular steel wire 2.00 m long must stretch no more than 0.25 cm when a tensile force of 700 N is... Problem 11.26E: Two circular rods, one steel and the other copper, are joined end to end. Each rod is 0.750 m long... Problem 11.27E: A metal rod that is 4.00 m long and 0.50 cm2 in cross-sectional area is found to stretch 0.20 cm... Problem 11.28E: Stress on a Mountaineers Rope. A nylon rope used by mountaineers elongates 1.10 m under the weight... Problem 11.29E: In constructing a large mobile, an artist hangs an aluminum sphere of mass 6.0 kg from a vertical... Problem 11.30E: A vertical, solid steel post 25 cm in diameter and 2.50 m long is required to support a load of 8000... Problem 11.31E: BIO Compression of Human Bone. The bulk modulus for bone is 15 GPa. (a) If a diver-in-training is... Problem 11.32E: A solid gold bar is pulled up from the hold of the sunken RMS Titanic. (a) What happens to its... Problem 11.33E: A specimen of oil having an initial volume of 600 cm3 is subjected to a pressure increase of 3.6 ... Problem 11.34E: In the Challenger Deep of the Marianas Trench, the depth of seawater is 10.9 km and the pressure is... Problem 11.35E: A copper cube measures 6.00 cm on each side. The bottom face is held in place by very strong glue to... Problem 11.36E: A square steel plate is 10.0 cm on a side and 0.500 cm thick. (a) Find the shear strain that results... Problem 11.37E: In lab tests on a 9.25-cm cube of a certain material, a force of 1375 N directed at 8.50 to the cube... Problem 11.38E: A brass wire is to withstand a tensile force of 350N without breaking. What minimum diameter must... Problem 11.39E: In a materials testing laboratory, a metal wire made from a new alloy is found to break when a... Problem 11.40E: A 4.0-m-long steel wire has a cross-sectional area of 0.050 cm2. Its proportional limit has a value... Problem 11.41E: CP A steel cable with cross-sectional area 3.00 cm2 has an elastic limit of 2.40 108 Pa. Find the... Problem 11.42P: A door 1.00 m wide and 2.00 m high weighs 330 N and is supported by two hinges, one 0.50 m from the... Problem 11.43P: A box of negligible mass rests at the lett end of a 2.00-m, 25.0-kg plank (Fig. P11.43) The width of... Problem 11.44P: Sir Lancelot rides slowly out of the castle at Camelot and onto the 12.0-m-long drawbridge that... Problem 11.45P: Mountain Climbing. Mountaineers often use a rope to lower themselves down the face of a cliff (this... Problem 11.46P: A uniform, 8.0-m, 1150-kg beam is hinged to a wall and supported by a thin cable attached 2.0 m from... Problem 11.47P: A uniform, 255.N rod that is 2.00 m long carries a 225.N weight at its right end and an unknown... Problem 11.48P: A claw hammer is used to pull a nail out of a board (Fig. P11.48). The nail is at an angle of 60 to... Problem 11.49P: You open a restaurant and hope to entice customers by hanging out a sign (Fig. P11.49). The uniform... Problem 11.50P: End A of the bar AB in Fig. P11.50 rests on a friction-less horizontal surface, and end B is hinged.... Problem 11.51P: BIO Supporting a Broken Leg. A therapist tells a 74-kg patient with a broken leg that he must have... Problem 11.52P: A Truck on a Drawbridge. A loaded cement mixer drives onto an old drawbridge, where it stalls with... Problem 11.53P: BIO Leg Raises. In a simplified version of the musculature action in leg raises, the abdominal... Problem 11.54P: BIO Pumping Iron. A 72.0-kg weightlifter doing arm raises holds a 7.50-kg weight. Her arm pivots... Problem 11.55P Problem 11.56P: You are asked to design the decorative mobile shown in Fig. P11.56. The strings and rods have... Problem 11.57P: A uniform, 7.5-m-long beam weighing 6490 N is hinged to a wall and supported by a thin cable... Problem 11.58P: CP A uniform drawbridge must be held at a 37 angle above the horizontal to allow ships to pass... Problem 11.59P: BIO Tendon-Stretching Exercises. As part of an exercise program, a 75-kg person does toe raises in... Problem 11.60P: (a) In Fig. P11.60 a 6.00-m-loog, uniform beam is hanging from a point 1.00 m to the right of its... Problem 11.61P: A uniform, horizontal flagpole 5.00 m long with a weight of 200 N is hinged to a vertical wall at... Problem 11.62P: A holiday decoration consists of two shiny glass spheres with masses 0.0240 Kg and 0.0360 Kg... Problem 11.63P: BIO Downward-Facing Dog. The yoga exercise Downward-Facing Dog requires stretching your hands... Problem 11.64P: A uniform metal bar that is 8.00 m long and has mass 30.0 kg is attached at one end to the side of a... Problem 11.65P: A worker wants to turn over a uniform. 1250-N, rectangular crate by pulling at 53.0 on one of its... Problem 11.66P: One end of a uniform meter stick is placed against a vertical wall (Fig. P11.66). The other end is... Problem 11.67P: Two friends are carrying a 200-kg crate up a flight of stairs. The crate is 1.25 m long and 0.500 m... Problem 11.68P: BIO Forearm. In the human arm, the forearm and hand pivot about the elbow joint. Consider a... Problem 11.69P: BIO CALC Refer to the discussion of holding a dumbbell in Example 11.4 (Section 11.3). The maximum... Problem 11.70P: In a city park a nonuniform wooden beam 4.00 m long is suspended horizontally by a light steel cable... Problem 11.71P: You are a summer intern for an architectural firm. An 8.00-m-long uniform steel rod is to be... Problem 11.72P: You are trying to raise a bicycle wheel of mass m and radius R up over a curb of height h. To do... Problem 11.73P: The Farmyard Gate. A gate 4.00 m wide and 2.00 m high weighs 700 N. Its center of gravity is at its... Problem 11.74P: If you put a uniform block at the edge of a table, the center of the block must be over the table... Problem 11.75P: Two uniform, 75.0-g marbles 2.00 cm in diameter are stacked as shown in Fig. P11.75 in a container... Problem 11.76P: Two identical, uniform beams weighing 260 N each are connected at one end by a frictionless hinge. A... Problem 11.77P: An engineer is designing a conveyor system for loading hay bales into a wagon (Fig. P11.77). Each... Problem 11.78P: A weight W is supported by attaching it to a vertical uniform metal pole by a thin cord passing over... Problem 11.79P: A garage door is mounted on an overhead rail (Fig. P11.79). The wheels at A and B have rusted so... Problem 11.80P: Pyramid Guilders. Ancient pyramid builders are balancing a uniform rectangular slab of stone tipped... Problem 11.81P: CP A 12.0-kg mass, fastened to the end of an aluminum wire with an unstretched length of 0.70 m, is... Problem 11.82P: Hookes Law for a Wire. A wire of length l0 and cross-sectional area A supports a hanging weight W.... Problem 11.83P: A 1.05-m-long rod of negligible weight is supported at its ends by wires A and B of equal length... Problem 11.84P: CP An amusement park ride consists of airplane-shaped cars attached to steel rods (Fig. P11.84).... Problem 11.85P: CP BIO Stress on the Shin Bone. The compressive strength of our bones is important in everyday life.... Problem 11.86P: DATA You are to use a long, thin wire to build a pendulum in a science museum. The wire has an... Problem 11.87P Problem 11.88P: DATA You are a construction engineer working on the interior design of a retail store in a mall. A... Problem 10.89CP: Two ladders, 4.00 m and 3.00 m long, are hinged at point A and tied together by a horizontal rope... Problem 10.90CP: Knocking Over a Post. One end of a post weighing 400 N and with height h rests on a rough horizontal... Problem 10.91CP: An angler hangs a 4.50-kg fish from a vertical steel wire 1.50 m long and 5.00 103cm2 in... Problem 10.92PP: BIO TORQUES AND TUG-OF-WAR. In a study of the biomechanics of the tug-of-war, a 2.0-m-tall, 80.0-kg... Problem 10.93PP: If he leans slightly farther back (increasing the angle between his body and the vertical) but... Problem 10.94PP: BIO TORQUES AND TUG-OF-WAR. In a study of the biomechanics of the tug-of-war, a 2.0-m-tall, 80.0-kg... Problem 10.95PP: BIO TORQUES AND TUG-OF-WAR. In a study of the biomechanics of the tug-of-war, a 2.0-m-tall, 80.0-kg... format_list_bulleted


 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




