
(a)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named using
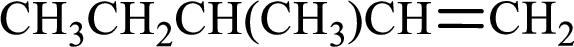
Concept Introduction:
A common nomenclature of naming organic compounds has been developed by IUPAC. By usage of this nomenclature or rules, memorizing of names of organic compounds is not necessary.
IUPAC rules for naming
There are about five rules that has to be followed for naming an alkene and an
- The longest continuous carbon chain in the compound that contains double bond or triple has to be identified. This is known as parent compound.
- Suffix “–ane” (in name of
alkane ) is replaced with “-ene” for alkene or “-yne” for alkyne. - Numbering has to be done so that the lowest number is given to the double or triple bond.
- Naming and numbering has to be given for each atom or group that is attached to the parent chain. Numbering has to be done in a way that substituents get the least numbering.
- If the alkenes have more than one double bond they are called as alkadienes (two double bonds) or alkatrienes (three double bonds). Appropriate suffix has to be used depending on the number of multiple bonds present in the compound.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
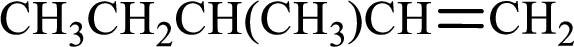
Longest carbon chain with double bond is found to contain five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is pentane. As a double bond is present, the alkene name is pentene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-1 and carbon-2. Therefore, the parent alkene is 1-pentene.
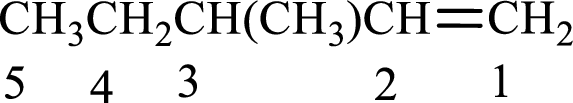
The substituent present in the given structure is a methyl group on carbon-3. Substituents name has to be arranged in the alphabetical order. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 3-methyl-1-pentene.
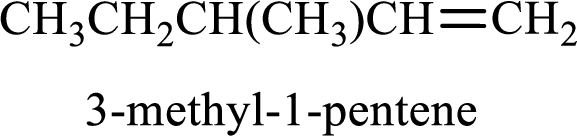
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is pentane. Position of double bond is 1-pentene. Substituents present in the chain are 3-methyl. IUPAC name of the alkene given is 3-methyl-1-pentene.
(b)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named using IUPAC nomenclature.
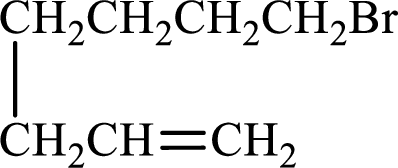
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
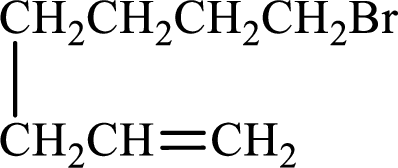
Longest carbon chain with double bond is found to contain seven carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is heptane. As a double bond is present, the alkene name is heptene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-1 and carbon-2. Therefore, the parent alkene is 1-heptene.
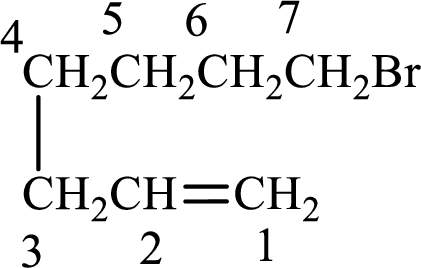
The substituent present in the given structure is a bromine atom on carbon-7. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 7-methyl-1-heptene.
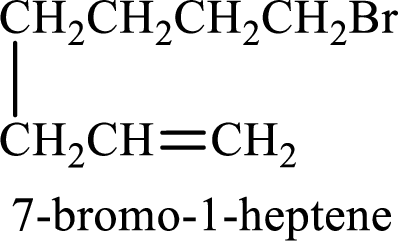
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is heptane. Position of double bond is 1-heptene. Substituents present in the chain are 7-bromo. IUPAC name of the alkene given is 7-bromo-1-heptene.
(c)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named using IUPAC nomenclature.
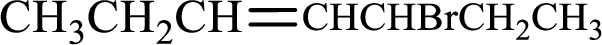
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given compound is,
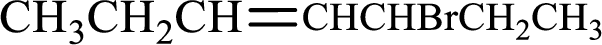
Longest carbon chain with double bond is found to contain seven carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane is heptane. As a double bond is present, the alkene name is heptene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-3 and carbon-4. Therefore, the parent alkene is 3-heptene.
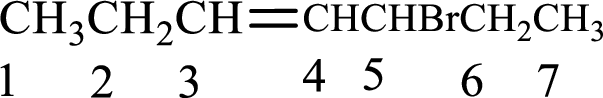
The substituent present in the given structure is a bromine atom on carbon-5. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of alkene as 5-bromo-3-heptene.
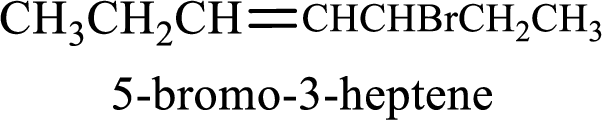
Longest carbon chain containing double bond is heptane. Position of double bond is 3-heptene. Substituents present in the chain are 5-bromo. IUPAC name of the alkene given is 5-bromo-3-heptene.
(d)
Interpretation:
Given compound has to be named using IUPAC nomenclature.
Concept Introduction:
A common nomenclature of naming organic compounds has been developed by IUPAC. By usage of this nomenclature or rules, memorizing of names of organic compounds is not necessary.
IUPAC rules for naming cycloalkenes:
- The number of carbon atoms present in the ring is counted and the name of the alkane that has the same number of carbon atoms is given by adding prefix “cyclo-” to the alkane name. Suffix “-ane” is changed as “-ene”.
- The double bond that is present in the ring is given always the number 1.
- If the ring is substituted, then the names of the group or atoms have to be placed before the name of cycloalkene.
- If the ring contains more than one substituent, then the numbers has to be used in a way that it gives the lowest position for the substituents following position 1 for the double bond.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
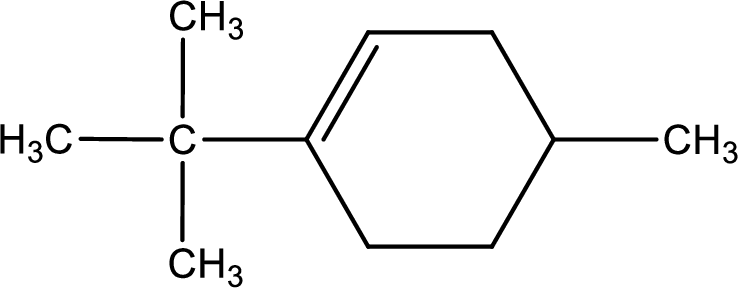
Given compound is,
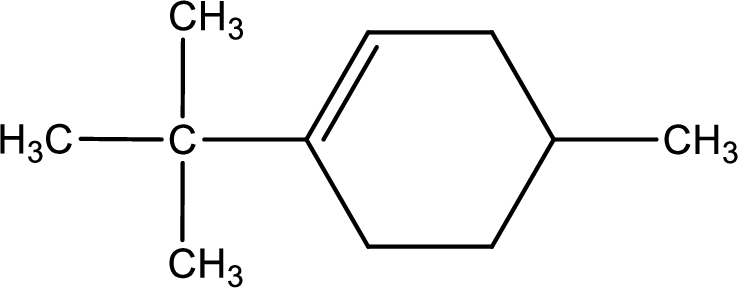
Given compound is found to contain six carbon atoms in a cyclic ring structure. Therefore, the parent cycloalkane is cyclohexane. As there is a double bond present in the ring, the parent compound name is cyclohexene.
Numbering has to be given in a way that the double bond gets the least numbering. In this case, double bond is present between carbon-1 and carbon-2.
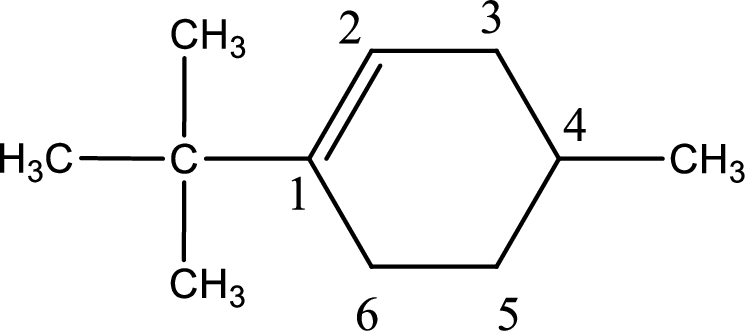
The substituents present in the given structure are a tert-butyl group on carbon-1 and a methyl group on carbon-4. Number has to be added before the substituent names which indicate the carbon atom in which it is present. This gives the name of compound as 1-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexene.
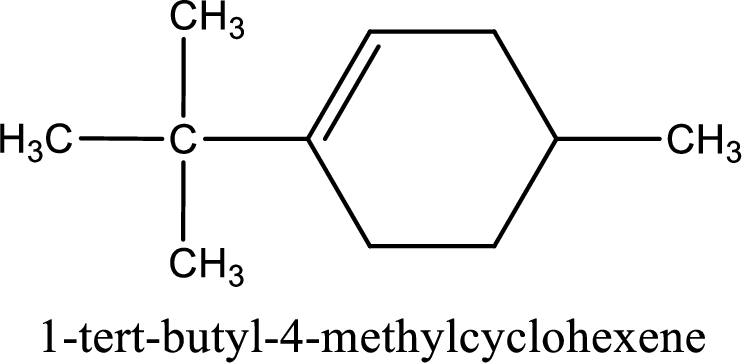
Parent chain is found to be cyclohexene. Position of double bond is carbon-1. Substituent present in the chain is 1-tert-butyl-4-methyl. IUPAC name of the compound given is 1-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





