
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from the respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The
Answer to Problem 11.39P
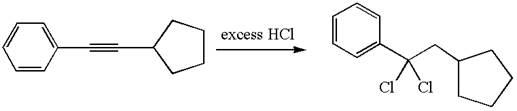
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with a major product is:
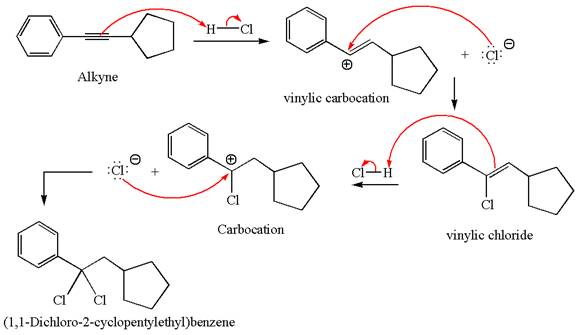
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
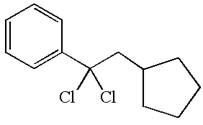
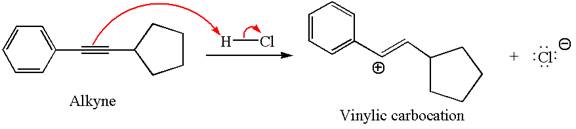
The given compound is germinal dichloride, and thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
In the second step, the chloride ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic chloride product.
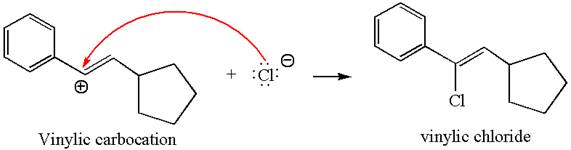
The vinylic chloride again undergoes the addition of
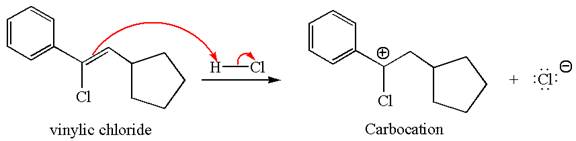
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic chloride ion to form a germinal dichloride product.
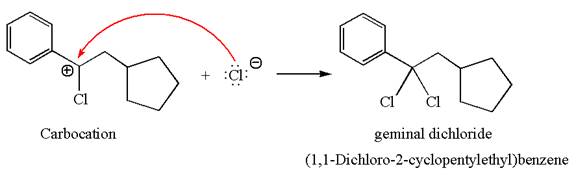
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(b)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In excess of reagent, the reaction occurs twice forming a geminal dihalide compound as a major product.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with the major product is:
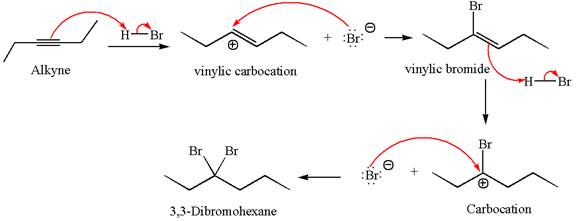
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound
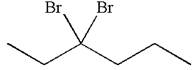
The given compound is germinal dibromide, thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
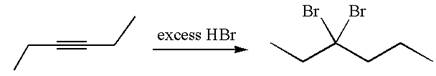
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
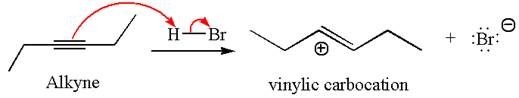
In the second step, the bromide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic bromide product.
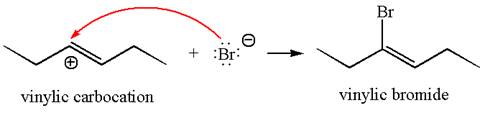
The vinylic bromide again undergoes the addition of
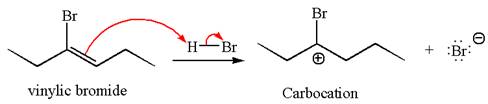
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic bromide ion to form germinal dibromide product.
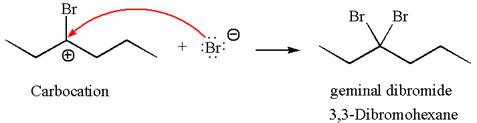
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(c)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In a single addition reaction, the reaction occurs only once forming a vibylic halide compound as a major product. The deuterium is an isotope of a hydrogen atom and reacts the same as hydrogen.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with a major product is:
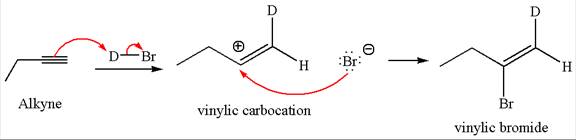
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
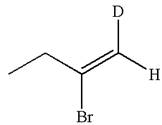
The given compound is vinylic bromide having deuterium at adjacent carbon, thus can be produced by single electrophilic addition of
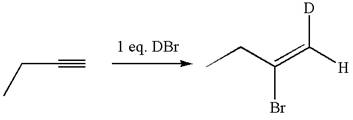
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
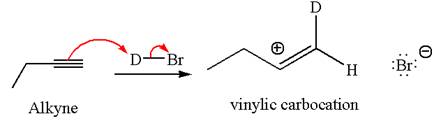
In the second step the bromide ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic bromide product.
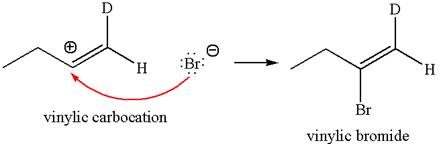
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
(d)
Interpretation:
The detailed mechanism for the production of given compounds from respective alkyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The alkynes are electron rich system like alkenes and can undergo an electrophilic addition reaction with strong Bronsted acids just like the alkenes do. The reaction proceeds with proton transfer reaction to form a stable carbocation followed by the action of water as a nucleophile. In excess of reagent, the reaction occurs twice forming a geminal dihalide compound as a major product.
Answer to Problem 11.39P
The detailed mechanism for the given reaction with the major product is:
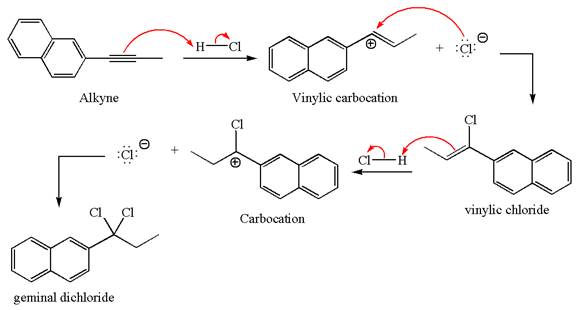
Explanation of Solution
The structure for the given compound is:
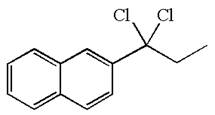
The given compound is germinal dichloride, thus can be produced by electrophilic addition of an excess of
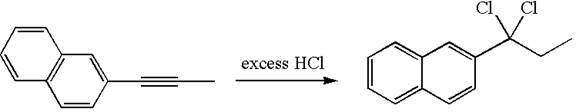
In the given reaction the alkyne is the electron rich site and the hydrogen from the
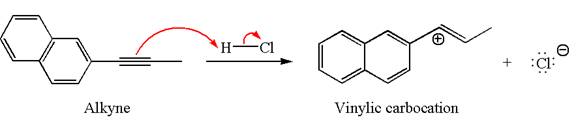
In the second step, the chloride ion acts as a nucleophile and attacks at vinylic carbocation forming vinylic chloride products.
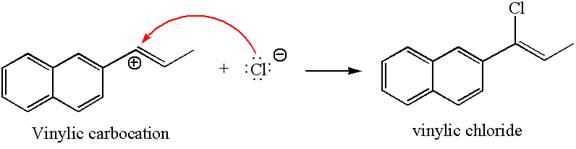
The vinylic chloride again undergoes the addition of
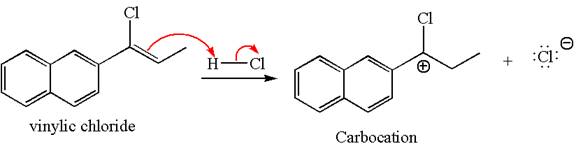
This carbocation further reacts with nucleophilic chloride ion to form a germinal dichloride product.
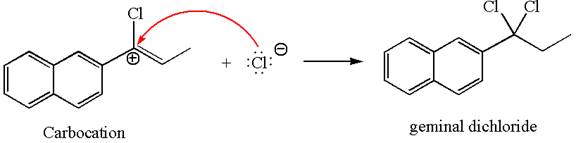
The detailed mechanism is drawn for the given reaction with showing the formation of stable carbocations and major product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- n Feb 3 A T + 4. (2 pts) Draw the structure of the major component of the Limonene isolated. Explain how you confirmed the structure. 5. (2 pts) Draw the fragment corresponding to the base peak in the Mass spectrum of Limonene. 6. (1 pts) Predict the 1H NMR spectral data of R-Limonene. Proton NMR: 5.3 pon multiplet (H Ringarrow_forwardPart VI. Ca H 10 O is the molecular formula of compound Tom and gives the in the table below. Give a possible structure for compound Tom. 13C Signals summarized C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 13C shift (ppm) 23.5 27.0 33.0 35.8 127 162 205 DEPT-90 + DEPT-135 + +arrow_forward2. Using the following data to calculate the value of AvapH o of water at 298K. AvapH o of water at 373K is 40.7 kJ/mol; molar heat capacity of liquid water at constant pressure is 75.2J mol-1 K-1 and molar heat capacity of water vapor at constant pressure is 33.6 J mol-1 K-1.arrow_forward
- Part VII. Below are the 'HNMR 13 3 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 20-NMR (Similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H13 O. Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum ли 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9 0.8 f1 (ppm)arrow_forward3. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-pentene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: 4. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-methyl-3-heptene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: following structurearrow_forwardPart IV. Propose a plausible Structure w/ the following descriptions: a) A 5-carbon hydrocarbon w/ a single peak in its proton decoupled the DEPT-135 Spectrum shows a negative peak C-NMR spectrum where b) what cyclohexane dione isomer gives the largest no. Of 13C NMR signals? c) C5H120 (5-carbon alcohol) w/ most deshielded carbon absent in any of its DEPT Spectivaarrow_forward
- 13C NMR is good for: a) determining the molecular weight of the compound b) identifying certain functional groups. c) determining the carbon skeleton, for example methyl vs ethyl vs propyl groups d) determining how many different kinds of carbon are in the moleculearrow_forward6 D 2. (1 pt) Limonene can be isolated by performing steam distillation of orange peel. Could you have performed this experiment using hexane instead of water? Explain. 3. (2 pts) Using GCMS results, analyze and discuss the purity of the Limonene obtained from the steam distillation of orange peel.arrow_forwardPart III. Arrange the following carbons (in blue) in order of increasing chemical shift. HO B NH 2 A CIarrow_forward

 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

