
(a)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn and the product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A weak acid can add to an
Answer to Problem 11.11P
The complete mechanism of the given addition reaction is
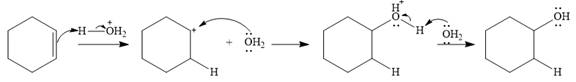
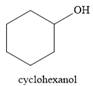
The product of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The given addition reaction is
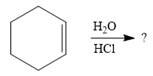
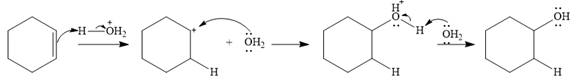
Water is a weak acid and does not add to the alkene in neutral conditions. In the presence of the strong acid HCl, water is protonated to
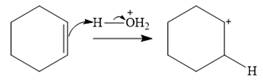
This is the electrophilic addition step. In the next step, a molecule of water acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation to form protonated alcohol.
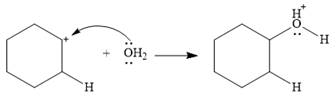
Final deprotonation by another molecule of water gives the final product, cyclohexanol.
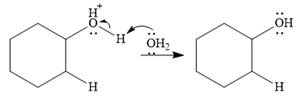
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
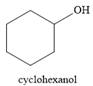
And the product of the reaction is cyclohexanol
Weak Bronsted acids can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid.
(b)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn and the product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A weak acid can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid. Because of the leveling effect, the protonated form of a weak acid is the strongest acid that can exist, so the strong acid protonates the weak acid. This protonated form of the weak acid is a good electrophile because of the positive charge. The double bond in the alkene is an electron-rich region and behaves as a nucleophile. The
Answer to Problem 11.11P
The complete mechanism for the given addition reaction is
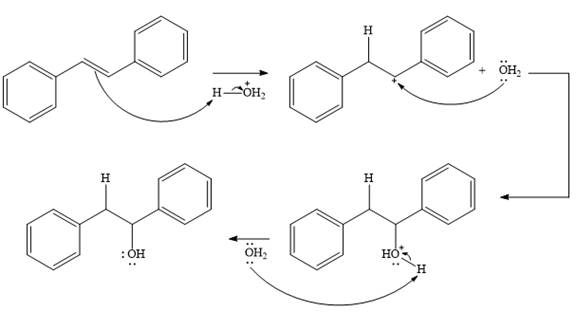
The product of the reaction is
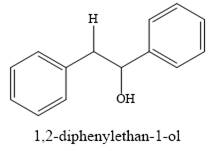
Explanation of Solution
The given addition reaction is
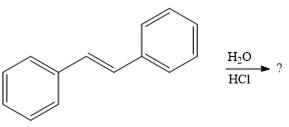
In the presence of HCl, the weak acid
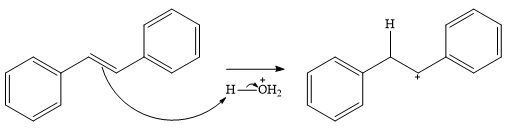
In the next step, a molecule of water acts as a nucleophile and adds to the carbocation to form a protonated alcohol.
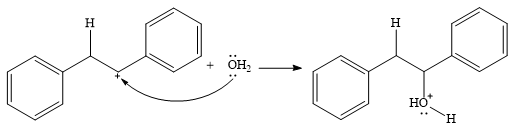
In the final step, another molecule of water deprotonates to give the final product,
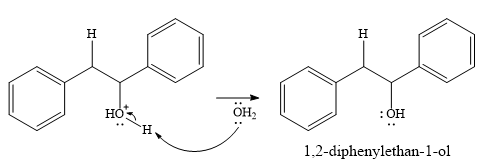
Thus, the complete mechanism for this addition reaction can be drawn as
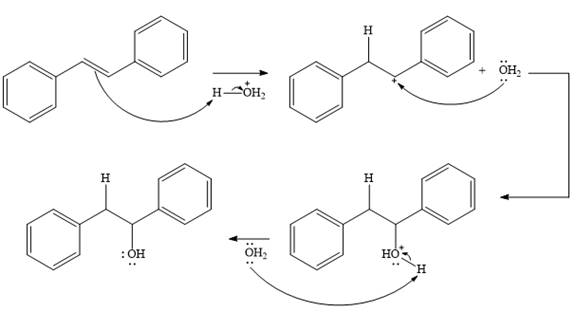
And the product of the reaction is

Weak Bronsted acids can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn and the product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A weak acid can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid. Because of the leveling effect, the protonated form of a weak acid is the strongest acid that can exist, so the strong acid protonates the weak acid. This protonated form of the weak acid is a good electrophile because of the positive charge. The double bond in the alkene is an electron-rich region and behaves as a nucleophile. The
Answer to Problem 11.11P
The complete mechanism for the given addition reaction is
The product of the reaction is
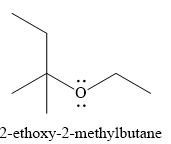
Explanation of Solution
The given reaction is
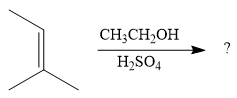
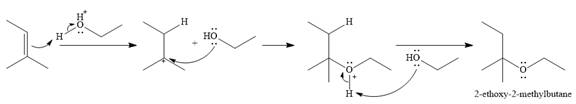
In the presence of a strong acid
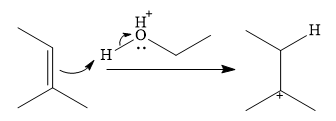
In the next step, a molecule of ethanol will act as a nucleophile and form a bond with the carbocation, using a lone pair on oxygen.
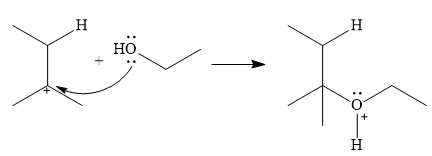
This results in the formation of protonated ether, which is deprotonated by another molecule of ethanol in the final step.
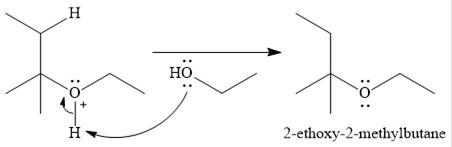
Thus, the complete mechanism for this addition reaction can be drawn as
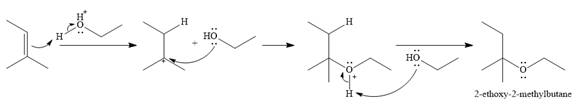
And the product of the reaction is
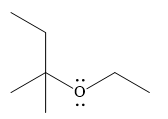
Weak Bronsted acids can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid.
(d)
Interpretation:
The complete, detailed mechanism for the given reaction is to be drawn and the product is to be predicted.
Concept introduction:
A weak acid can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid. Because of the leveling effect, the protonated form of a weak acid is the strongest acid that can exist, so the strong acid protonates the weak acid. This protonated form of the weak acid is a good electrophile because of the positive charge. The double bond in the alkene is an electron-rich region and behaves as a nucleophile. The
Answer to Problem 11.11P
The complete mechanism for the reaction is
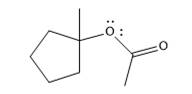
The product of the reaction is
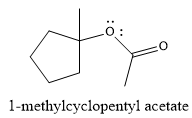
Explanation of Solution
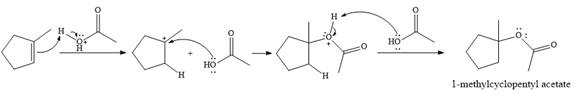
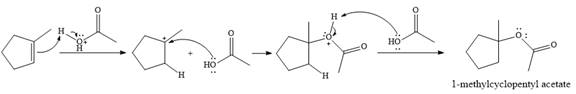
The given reaction is
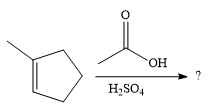
In the presence of
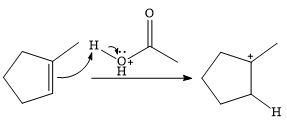
In the next step, a molecule of acetic acid will act as a nucleophile using a lone pair on OH oxygen to form a bond with the carbocation. The result is a protonated form of the ester product.
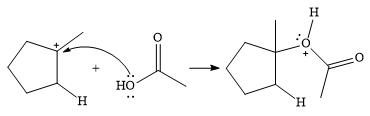
Final deprotonation by another molecule of acetic acid will give the product.
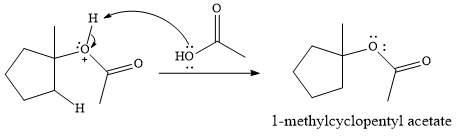
Thus, the complete mechanism for the reaction can be drawn as
The product of the reaction is
Weak Bronsted acids can add to an alkene in the presence of a strong acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Q1: Predict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry when necessary. Write NR if no reaction, try to explain. 1.) LDA, THF 2.) СОН CI OH H2SO4, heat OH m...... OH 1.) PCC, CH2Cl2 2.) CH3CH2MgBr, THF 3.) H3O+ 4.) TsCl, pyr 5.) tBuOK, tBuOH 1.) SOCI 2, CHCI 3 2.) CH3CH2ONA, DMF OH 1.) HBr 2.) Mg, THF 3.) H₂CO, THE 4.) H3O+ OH NaH, THFarrow_forwardWhat is the stepwise mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reactionarrow_forward
- Please provide the IUPAC name for the compound shown herearrow_forwardProblem 6-29 Identify the functional groups in the following molecules, and show the polarity of each: (a) CH3CH2C=N CH, CH, COCH (c) CH3CCH2COCH3 NH2 (e) OCH3 (b) (d) O Problem 6-30 Identify the following reactions as additions, eliminations, substitutions, or rearrangements: (a) CH3CH2Br + NaCN CH3CH2CN ( + NaBr) Acid -OH (+ H2O) catalyst (b) + (c) Heat NO2 Light + 02N-NO2 (+ HNO2) (d)arrow_forwardPredict the organic product of Y that is formed in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic product. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forward
- Please choose the best reagents to complete the following reactionarrow_forwardProblem 6-17 Look at the following energy diagram: Energy Reaction progress (a) Is AG for the reaction positive or negative? Label it on the diagram. (b) How many steps are involved in the reaction? (c) How many transition states are there? Label them on the diagram. Problem 6-19 What is the difference between a transition state and an intermediate? Problem 6-21 Draw an energy diagram for a two-step reaction with Keq > 1. Label the overall AG°, transition states, and intermediate. Is AG° positive or negative? Problem 6-23 Draw an energy diagram for a reaction with Keq = 1. What is the value of AG° in this reaction?arrow_forwardProblem 6-37 Draw the different monochlorinated constitutional isomers you would obtain by the radical chlorination of the following compounds. (b) (c) Problem 6-39 Show the structure of the carbocation that would result when each of the following alkenes reacts with an acid, H+. (a) (b) (c)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





