
The following experimental data were obtained for the reaction of \'I14* and NOf in acidic solution.
NH/(aq) + NO2-(aq) — N;(g) + 2 H,O(f)
| INH/I (mol L1) | [NO21 (mol L-1, | Rate = A[NJ/At (mol L-1 s’) |
| 0.0092 | 0.098 | 3.33 X IO"7 |
| 0.0092 | 0.049 | 1.66 X 10‘7 |
| 0.0488 | 0.196 | 3.51 X 10"6 |
| 0.0249 | 0.196 | 1.80 X 10-6 |
Determine the rate law for this reaction and calculate the rate constant.
Interpretation: Given the experimental data obtained for a reaction, determine the rate law for the reaction and the value of rate constant
Concept Introduction: Orders of reaction are constantly determined by doing experiments. Consequently without experimental information, we can't conclude anything about the order of a reaction just by having a look at the equation for the reaction. By doing experiments involving a reaction between A and B, the rate of the reaction is identified to be related to the concentrations of A and B as follows:
This is the Rate Equation.
Where,
Rate is in the units of mol dm-3s-1
k is the rate constant
A, B- concentrations in mol dm-3
a - Order of reaction with respect to A
b- Order of reaction with respect to B
Answer to Problem 11.33PAE
Solution: The rate law of the reaction is
Explanation of Solution
Given information: Reaction of
Experimental Data
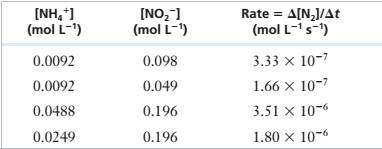
Step 1: For the reaction:
The rate law can be determined using the rate equation as follows:
Where,
a= Order of the reaction with respect to
b= Order of the reaction with respect to
Step 2: From the first and second rows of the given experimental data,
Step 3: Divide (1) by (2), we get
Step 4: From the third and fourth rows of the given experimental data,
Step 5: Divide (3) by (4), we get
Step 6: Rate Equation = >
To determine k, pick equation (1)
It does not make a difference what the number of reactants there are. The concentration of every reactant will be present in the rate equation, raised to some power. These powers resemble the individual orders with respect to each reactant. The sum of these powers results in the overall order of the reaction. The rate constant will be a constant value for a given reaction only if the concentration of the reactants is changed without changing any other factors.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry for Engineering Students, 3rd, Loose-Leaf + OWLv2 with Quick Prep and Student Solutions Manual 24-Months Printed Access Card
- Nonearrow_forwardUnshared, or lone, electron pairs play an important role in determining the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Thus, it is important to know which atoms carry unshared pairs. Use the structural formulas below to determine the number of unshared pairs at each designated atom. Be sure your answers are consistent with the formal charges on the formulas. CH. H₂ fo H2 H The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c is HC HC HC CH The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c isarrow_forwardDraw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 H H-O-H +/ H3C-C+ H3C-C-0: CH3 CH3 Harrow_forward
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

