
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781337517386
Author: WARREN
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 11.2E
Identify cost graphs
The following cost graphs illustrate various types of cost behavior:
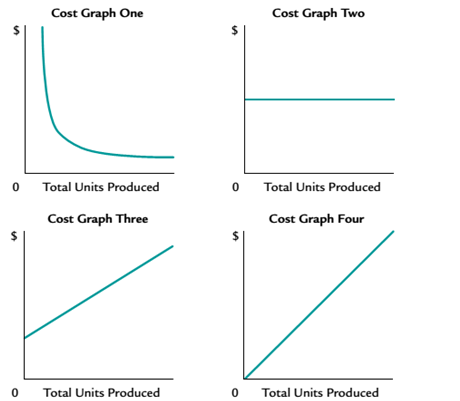
For each of the following costs, identify the cost graph that best illustrates its cost behavior as the number of units produced increases.
a. Direct material cost per unit.
b. Fees for using a patent of $500,000 plus $0.25 for each unit produced.
c. Salary of quality control supervisor.
d. Straight-line
e. Total direct materials cost.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
help me to solve this questions financial accounting
expert of general accounting answer
Need help this question
Chapter 11 Solutions
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Ch. 11 - Which of the following statements describes...Ch. 11 - If sales are $500,000, variable costs are...Ch. 11 - If the unit selling price is $16. the unit...Ch. 11 - Based on the data presented in Question 3, how...Ch. 11 - Prob. 5SEQCh. 11 - Describe how total variable costs and unit...Ch. 11 - How would each of the following costs be...Ch. 11 - Describe the behavior of (a) total fixed costs and...Ch. 11 - How would each of the following costs be...Ch. 11 - In cost analyses, how arc mixed costs treated?
Ch. 11 - Which of the following graphs illustrates how...Ch. 11 - Which of the following graphs illustrates how unit...Ch. 11 - Which of the following graphs best illustrates...Ch. 11 - In applying the high-low method of Cost...Ch. 11 - Prob. 10CDQCh. 11 - Prob. 11CDQCh. 11 - Prob. 12CDQCh. 11 - If insurance rates are increased, what effect will...Ch. 11 - Prob. 14CDQCh. 11 - The reliability of cost-volume-profit (CVP)...Ch. 11 - How does the sales mix affect the calculation of...Ch. 11 - Prob. 17CDQCh. 11 - Classify costs Following is a list of various...Ch. 11 - Identify cost graphs The following cost graphs...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3ECh. 11 - Identify activity bases From the following list of...Ch. 11 - Identify fixed and variable costs Intuit Inc....Ch. 11 - Relevant range and fixed and variable costs Third...Ch. 11 - High-low method Liberty Inc. has decided to use...Ch. 11 - High-low method for service company Miss River...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin ratio a. Matzinger Company...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin and contribution margin ratio...Ch. 11 - Break-even sales and sales to realize operating...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.12ECh. 11 - Prob. 11.13ECh. 11 - Break-even analysis The Garden Club of Palm...Ch. 11 - Break-even analysis Media outlets such as ESPN and...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.16ECh. 11 - Prob. 11.17ECh. 11 - Prob. 11.18ECh. 11 - Prob. 11.19ECh. 11 - Prob. 11.20ECh. 11 - Break-even sales and sales mix for a service...Ch. 11 - Operating leverage SunRise Inc. and SunSet Inc....Ch. 11 - Classify costs Peak Apparel Co. manufactures a...Ch. 11 - Break-even sales under present and proposed...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.2.2PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.2.3PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.2.4PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.2.5PCh. 11 - Break-even sales under present and proposed...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.2.7PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.2.8PCh. 11 - Break-even sales and cost-volume-profit graph For...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3.2PCh. 11 - Break-even sales and cost-volume-profit graph For...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3.4PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.1PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.2PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.3PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.4PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.5.1PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.5.2PCh. 11 - Sales mix and break-even sales Data related to the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.5.4PCh. 11 - Prob. 11.5.5PCh. 11 - Contribution margin, break-even sales,...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin, break-even sales,...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin, break-even sales,...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin, break-even sales,...Ch. 11 - Contribution margin, break-even sales,...Ch. 11 - Margin of safety a. If Go-Go Buggies Company, with...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.2MBACh. 11 - Margin of safety Use the data from E11-12 and...Ch. 11 - Margin of safety Use the data from E11-12 and...Ch. 11 - Sales mix and margin of safety Use the data from...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.4.2MBACh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.3MBACh. 11 - Margin of safety Using the data from P11-2,...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.5.2MBACh. 11 - Margin of safety Using the data from P11-6....Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.6.2MBACh. 11 - Prob. 11.6.3MBACh. 11 - Prob. 11.1CCh. 11 - Break-even sales, contribution margin "Every...Ch. 11 - Break-even analysis Aquarius Games Inc. has...Ch. 11 - Variable costs and activity bases in decision...Ch. 11 - Variable costs and activity bases in decision...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.6C
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Financial accountingarrow_forwardGiven the solution and accounting questionarrow_forwardThe following data were selected from the records of Fluwars Company for the year ended December 31, current year: Balances at January 1, current year: Accounts receivable (various customers) $ 111,500Allowance for doubtful accounts 11,200 The company sold merchandise for cash and on open account with credit terms 1/10, n/30, without a right of return. The following transactions occurred during the current year: Sold merchandise for cash, $252,000.Sold merchandise to Abbey Corp; invoice amount, $36,000.Sold merchandise to Brown Company; invoice amount, $47,600.Abbey paid the invoice in (b) within the discount period.Sold merchandise to Cavendish Inc.; invoice amount, $50,000.Collected $113,100 cash from customers for credit sales made during the year, all within the discount periods.Brown paid its account in full within the discount period.Sold merchandise to Decca Corporation; invoice amount, $42,400.Cavendish paid its account in full after the discount…arrow_forward
- Given solution general accountingarrow_forwardanswer plzarrow_forwardThe following data were selected from the records of Fluwars Company for the year ended December 31, current year: Balances at January 1, current year: Accounts receivable (various customers) $ 111,500 Allowance for doubtful accounts 11,200 The company sold merchandise for cash and on open account with credit terms 1/10, n/30, without a right of return. The following transactions occurred during the current year: Sold merchandise for cash, $252,000. Sold merchandise to Abbey Corp; invoice amount, $36,000. Sold merchandise to Brown Company; invoice amount, $47,600. Abbey paid the invoice in (b) within the discount period. Sold merchandise to Cavendish Inc.; invoice amount, $50,000. Collected $113,100 cash from customers for credit sales made during the year, all within the discount periods. Brown paid its account in full within the discount period. Sold merchandise to Decca Corporation; invoice amount, $42,400. Cavendish paid its account in full after the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Cost Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781305087408
Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. Mitchell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337912020
Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. Tayler
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)
Accounting
ISBN:9781305961883
Author:Carl Warren
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Cost Accounting - Definition, Purpose, Types, How it Works?; Author: WallStreetMojo;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AwrwUf8vYEY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY