
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.6, Problem 10.49P
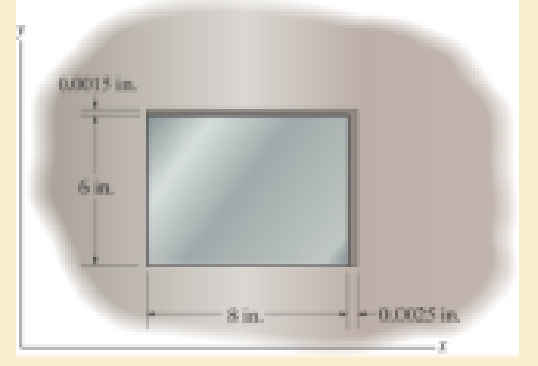
Determine the normal stresses σx and σy in the plate if the temperature is increased by ΔT = 100 °F. Hint: To solve, add the thermal strain αΔT to the equations for Hooke’s law.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The heated rod from Problem 3 is subject to a volumetric heating
h(x) = h0
x
L in units of [Wm−3], as shown in the figure below. Under the
heat supply the temperature of the rod changes along x with the
temperature function T (x). The temperature T (x) is governed by the
d
following equations:
−
dx (q(x)) + h(x) = 0 PDE
q(x) =−k dT
dx Fourier’s law of heat conduction (4)
where q(x) is the heat flux through the rod and k is the (constant)
thermal conductivity. Both ends of the bar are in contact with a heat
reservoir at zero temperature.
Determine:
1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem.
2. The temperature function T (x).
3. The heat flux function q(x).
Side Note: Please see that both ends of bar are in contact with a heat reservoir at zero temperature so the boundary condition at the right cannot be du/dx=0 because its not thermally insulated. Thank you
The elastic bar from Problem 1 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω2x. Under this radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement d u(x) is governed by the following equations: dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (2) where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ is the mass density, and E is the (constant) Young’s modulus. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0 and it is also pinned at x = L. Determine: 1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem. 2. The displacement function u(x). 3. The stress function σ(x). SIDE QUESTION: I saw a tutor solve it before but I didn't understand why the tutor did not divide E under the second term (c1x) before finding u(x). The tutor only divided E under first term. please explain and thank you
calculate the total power required to go 80 mph in a VW Type 2 Samba Bus weighing 2310 lbs. with a Cd of 0.35 and a frontal area of 30ft^2. Consider the coefficient of rolling resistance to be 0.018. What is the increase in power required to go the same speed if the weight is increased by 2205 pounds (the rated carrying capacity of the vehicle). If the rated power for the vehicle is 49 bhp, will the van be able to reach 80 mph at full carrying capacity?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 10.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal strains in...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the arm has...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.4PCh. 10.3 - 10-5. The state of strain at the point on the gear...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.8PCh. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain- transformation equations to...
Ch. 10.3 - 10–11. The state of strain on an element has...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain on an...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain which...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain, which...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.17PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.18PCh. 10.3 - 10–19. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–4 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - *10–20. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–5 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 106. The state of strain at a...Ch. 10.5 - The strain at point A on the bracket has...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, (b) the...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.24PCh. 10.5 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.5 - 10–26. The 60° strain rosette is attached to point...Ch. 10.5 - 10–27. The strain rosette is attached at the point...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.28PCh. 10.6 - For the case of plane stress, show that Hookes law...Ch. 10.6 - to develop the strain tranformation equations....Ch. 10.6 - Determine the modulus of elasticity and Polssons...Ch. 10.6 - If it is subjected to an axial load of 15 N such...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - A strain gage having a length of 20 mm Is attached...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the bulk modulus for each of the...Ch. 10.6 - The strain gage is placed on the surface of the...Ch. 10.6 - 10–39. The strain in the x direction at point A on...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the applied load P. What is the shear...Ch. 10.6 - If a load of P = 3 kip is applied to the A-36...Ch. 10.6 - The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.43PCh. 10.6 - *10–44. Strain gauge b is attached to the surface...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.6 - 10?46. The principal strains in a plane, measured...Ch. 10.6 - 10–47. The principal stresses at a point are shown...Ch. 10.6 - *10–48. The 6061-T6 aluminum alloy plate fits...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the normal stresses x and y in the plate...Ch. 10.6 - The steel shaft has a radius of 15 mm. Determine...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.52PCh. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - The yield stress for a zirconium-magnesium alloy...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob. 1061 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.63PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.66PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - The short concrete cylinder having a diameter of...Ch. 10.7 - 10–70. Derive an expression for an equivalent...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.71PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.72PCh. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from brittle...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from cast iron...Ch. 10.7 - 10–75. The components of plane stress at a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.7 - 10–77. If the A-36 steel pipe has outer and inner...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.79PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.80PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.82PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.83PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.7 - 10–85. The state of stress acting at a critical...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.87PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.7 - 10–89. The gas tank has an inner diameter of 1.50...Ch. 10.7 - The gas tank is made from A-36 steel and has an...Ch. 10.7 - The internal loadings at a critical section along...Ch. 10.7 - *10–92. The shaft consists of a solid segment AB...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.93PCh. 10 - In the case of plane stress, where the in-plane...Ch. 10 - The plate is made of material having a modulus of...Ch. 10 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - Determine if yielding has occurred on the basis of...Ch. 10 - The 60 strain rosette is mounted on a beam. The...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - If the strain gages a and b at points give...Ch. 10 - Use the strain-transformation equations and...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - Specify the orientation of the corresponding...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
What are the design issues for character string types?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Computers process data under the control of sets of instructions called
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A distillation column with a total of 13 actual stages (including a partial condenser) is used to perform a separation which requires 7 ideal stages. Calculate the overall column efficiency, and report your answer in %arrow_forward6. Consider a 10N step input to the mechanical system shown below, take M = 15kg, K = 135N/m, and b = 0.4 Ns/m. (a) Assume zero initial condition, calculate the (i) System pole (ii) System characterization, and (iii) The time domain response (b) Calculate the steady-state value of the system b [ www K 个 х M -F(+)arrow_forward2. Solve the following linear time invariant differential equations using Laplace transforms subject to different initial conditions (a) y-y=t for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 1 (b) ÿ+4y+ 4y = u(t) for y(0) = 0 and y(0) = 1 (c) y-y-2y=0 for y(0) = 1 and y(0) = 0arrow_forward
- 3. For the mechanical systems shown below, the springs are undeflected when x₁ = x2 = x3 = 0 and the input is given as fa(t). Draw the free-body diagrams and write the modeling equations governing each of the systems. K₁ 000 K₂ 000 M₁ M2 -fa(t) B₂ B₁ (a) fa(t) M2 K₂ 000 B K₁ x1 000 M₁ (b)arrow_forwardThis question i m uploading second time . before you provide me incorrect answer. read the question carefully and solve accordily.arrow_forward1. Create a table comparing five different analogous variables for translational, rotational, electrical and fluid systems. Include the standard symbols for each variable in their respective systems.arrow_forward
- 2) Suppose that two unequal masses m₁ and m₂ are moving with initial velocities v₁ and v₂, respectively. The masses hit each other and have a coefficient of restitution e. After the impact, mass 1 and 2 head to their respective gaps at angles a and ẞ, respectively. Derive expressions for each of the angles in terms of the initial velocities and the coefficient of restitution. m1 m2 8 m1 m2 βarrow_forward4. Find the equivalent spring constant and equivalent viscous-friction coefficient for the systems shown below. @ B₁ B₂ H B3 (b)arrow_forward5. The cart shown below is inclined 30 degrees with respect to the horizontal. At t=0s, the cart is released from rest (i.e. with no initial velocity). If the air resistance is proportional to the velocity squared. Analytically determine the initial acceleration and final or steady-state velocity of the cart. Take M= 900 kg and b 44.145 Ns²/m². Mg -bx 2 отarrow_forward
- 9₁ A Insulated boundary Insulated boundary dx Let's begin with the strong form for a steady-state one-dimensional heat conduction problem, without convection. d dT + Q = dx dx According to Fourier's law of heat conduction, the heat flux q(x), is dT q(x)=-k dx. x Q is the internal heat source, which heat is generated per unit time per unit volume. q(x) and q(x + dx) are the heat flux conducted into the control volume at x and x + dx, respectively. k is thermal conductivity along the x direction, A is the cross-section area perpendicular to heat flux q(x). T is the temperature, and is the temperature gradient. dT dx 1. Derive the weak form using w(x) as the weight function. 2. Consider the following scenario: a 1D block is 3 m long (L = 3 m), with constant cross-section area A = 1 m². The left free surface of the block (x = 0) is maintained at a constant temperature of 200 °C, and the right surface (x = L = 3m) is insulated. Recall that Neumann boundary conditions are naturally satisfied…arrow_forward1 - Clearly identify the system and its mass and energy exchanges between each system and its surroundings by drawing a box to represent the system boundary, and showing the exchanges by input and output arrows. You may want to search and check the systems on the Internet in case you are not familiar with their operations. A pot with boiling water on a gas stove A domestic electric water heater A motor cycle driven on the roadfrom thermodynamics You just need to draw and put arrows on the first part a b and carrow_forward7. A distributed load w(x) = 4x1/3 acts on the beam AB shown in Figure 7, where x is measured in meters and w is in kN/m. The length of the beam is L = 4 m. Find the moment of the resultant force about the point B. w(x) per unit length L Figure 7 Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Lec21, Part 5, Strain transformation; Author: Mechanics of Materials (Libre);https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sgJvz5j_ubM;License: Standard Youtube License