
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10.6, Problem 10.38P
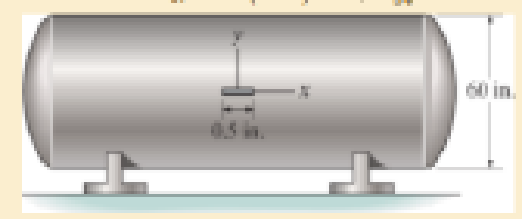
The strain gage is placed on the surface of the steel boiler as shown. If it is 0.5 in. long, determine the pressure in the boiler when the gage elongates 0.2(103□) in. The boiler has a thickness of 0.5 in. and inner diameter of 60 in. Also, determine the maximum x, y in-plane shear strain in the material, Est=29(103) ksi, vst = 0.3.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Quiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size
for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2=6mm, and for w3 is h3 -6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds.
F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx).
163 mm
133 mm
140 mm
w3
wi
E
W
X
FO
FB
F10
F11
F12
Home
Q: Consider the square of Figure below.The left face is maintained at 100°C and the top
face at 500°C, while the other two faces are exposed to an environment at1 00°C, h=10
W/m². C and k=10 W/m.°C. The block is 1 m square. Compute the temperature of the
various nodes as indicated in Figure below and the heat flows at the boundaries.
T= 500°C
Alt
Explain to me in detail how to
calculate the matrix in the Casio
calculator type (fx-991ES plus)
T= 100°C
1
2
4
7
1 m-
3
1 m
5
6
T=
100°C
8
9
Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge?
1)
a₁ = 2+(0.1)"
1-2n
2)
a =
1+2n
1/n
3
16) a =
n
In n
17) an =
n
1/n
1-5n4
3)
an
=
n² +8n³
18) an
=
√4" n
n² -2n+1
n!
20) a =
4)
an
=
106
5)
n-1
a₁ =1+(-1)"
n+1
a-(+) (1-4)
6)
=
7)
a =
2n
(-1)"+1
2n-1
21) an
=
n
-A"
1/(Inn)
3n+1
22) a =
3n-1
1/n
x"
23) a =
, x>0
2n+1
3" x 6"
24) a =
2™" xn!
2n
8)
a =
n+1
πT
1
9)
a„ = sin
+-
2
n
sin n
10) an =
n
25) a = tanh(n)
26) a =
2n-1
27) a = tan(n)
1
-sin
n
n
11) a =
2"
28) an
==
"
1
+
2"
In(n+1)
12) a =
n
(In n) 200
29) a =
n
13) a = 8/n
14) a 1+
=(1+²)"
15) an
7
n
= 10n
30) an-√√n²-n
1"1
31) adx
nix
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 10.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal strains in...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the arm has...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.4PCh. 10.3 - 10-5. The state of strain at the point on the gear...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.8PCh. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain- transformation equations to...
Ch. 10.3 - 10–11. The state of strain on an element has...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain on an...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain which...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain, which...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.17PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.18PCh. 10.3 - 10–19. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–4 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - *10–20. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–5 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 106. The state of strain at a...Ch. 10.5 - The strain at point A on the bracket has...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, (b) the...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.24PCh. 10.5 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.5 - 10–26. The 60° strain rosette is attached to point...Ch. 10.5 - 10–27. The strain rosette is attached at the point...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.28PCh. 10.6 - For the case of plane stress, show that Hookes law...Ch. 10.6 - to develop the strain tranformation equations....Ch. 10.6 - Determine the modulus of elasticity and Polssons...Ch. 10.6 - If it is subjected to an axial load of 15 N such...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - A strain gage having a length of 20 mm Is attached...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the bulk modulus for each of the...Ch. 10.6 - The strain gage is placed on the surface of the...Ch. 10.6 - 10–39. The strain in the x direction at point A on...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the applied load P. What is the shear...Ch. 10.6 - If a load of P = 3 kip is applied to the A-36...Ch. 10.6 - The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.43PCh. 10.6 - *10–44. Strain gauge b is attached to the surface...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.6 - 10?46. The principal strains in a plane, measured...Ch. 10.6 - 10–47. The principal stresses at a point are shown...Ch. 10.6 - *10–48. The 6061-T6 aluminum alloy plate fits...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the normal stresses x and y in the plate...Ch. 10.6 - The steel shaft has a radius of 15 mm. Determine...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.52PCh. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - The yield stress for a zirconium-magnesium alloy...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob. 1061 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.63PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.66PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - The short concrete cylinder having a diameter of...Ch. 10.7 - 10–70. Derive an expression for an equivalent...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.71PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.72PCh. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from brittle...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from cast iron...Ch. 10.7 - 10–75. The components of plane stress at a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.7 - 10–77. If the A-36 steel pipe has outer and inner...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.79PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.80PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.82PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.83PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.7 - 10–85. The state of stress acting at a critical...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.87PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.7 - 10–89. The gas tank has an inner diameter of 1.50...Ch. 10.7 - The gas tank is made from A-36 steel and has an...Ch. 10.7 - The internal loadings at a critical section along...Ch. 10.7 - *10–92. The shaft consists of a solid segment AB...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.93PCh. 10 - In the case of plane stress, where the in-plane...Ch. 10 - The plate is made of material having a modulus of...Ch. 10 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - Determine if yielding has occurred on the basis of...Ch. 10 - The 60 strain rosette is mounted on a beam. The...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - If the strain gages a and b at points give...Ch. 10 - Use the strain-transformation equations and...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - Specify the orientation of the corresponding...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Comprehension Check 7-14
The power absorbed by a resistor can be given by P = I2R, where P is power in units of...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
17–1C A high-speed aircraft is cruising in still air. How does the temperature of air at the nose of the aircra...
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A steel alloy contains 95.7 wt% Fe, 4.0 wt% W, and 0.3 wt% C.arrow_forwardb. A horizontal cantilever of effective length 3a, carries two concentrated loads W at a distance a from the fixed end and W' at a distance a from the free end. Obtain a formula for the maximum deflection due to this loading using Mohr's method. If the cantilever is 250 mm by 150mm steel I beam, 3 m long having a second moment of area I as 8500 cm4, determine W and W'to give a maximum deflection of 6 mm when the maximum stress due to bending is 90 Mpa. Take Young's modulus of material E as 185 Gpa.arrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1/n 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 3 16) a = n 1-2n 2) a = In n 1+2n 17) an = 1/n n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n! n² -2n+1 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forward
- Calculate the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a collector located at (Latitude 17.40S) on June 15 at 1030hrs solar time. The collector is tilted at an angle of 200, with a surface azimuth angle of 150.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, please don't use chatgpt. Strict warningarrow_forwardCompute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward
- Compute the mass fraction of eutectoid cementite in an iron-carbon alloy that contains 1.00 wt% C.arrow_forward! Required information Mechanical engineering, don't use chatgpt. Thanks A 60-kip-in. torque T is applied to each of the cylinders shown. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. 3 in. 4 in. (a) (b) Determine the inner diameter of the 4-in. diameter hollow cylinder shown, for which the maximum stress is the same as in part a. The inner diameter is in.arrow_forwardMechanical engineering, Don't use chatgpt. Strict warning.arrow_forward
- 10:38 PM P 4136 54 A man Homework was due west for and 4km. He then changes directies walks on a bearing south-wes IS How far Point? of 1970 until he of his Starting Port Is he then from his stating What do you think about ... ||| Մ כarrow_forwardA simply supported T-shaped beam of 6m in length has to be designed to carry an inclined central point load W. Find the max- imum value of this load such that the maximum tensile and com- pression stresses on the beam do not exceed 30 and 60 respectively. N mm² N mm², 90 mm 80 mm Y W 60 mm 30° 10 mm 10 mm Xarrow_forwardProblem 9.5 9.5 A 1080-kg car is parked on a sloped street. The figure shows its wheels and the position of its center of mass. The street is icy, and as a result the coefficient of static friction between the car's tires and the street surface is μs = 0.2. Determine the steepest slope (in degrees relative to the horizontal) at which the car could remain in equilibrium if a. the brakes are applied to both its front and rear wheels; b. the brakes are applied to the front (lower) wheels only. Problem 9.5 1380 mm 532 mm 2370 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
An Introduction to Stress and Strain; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQf6Q8t1FQE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY