
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.95RP
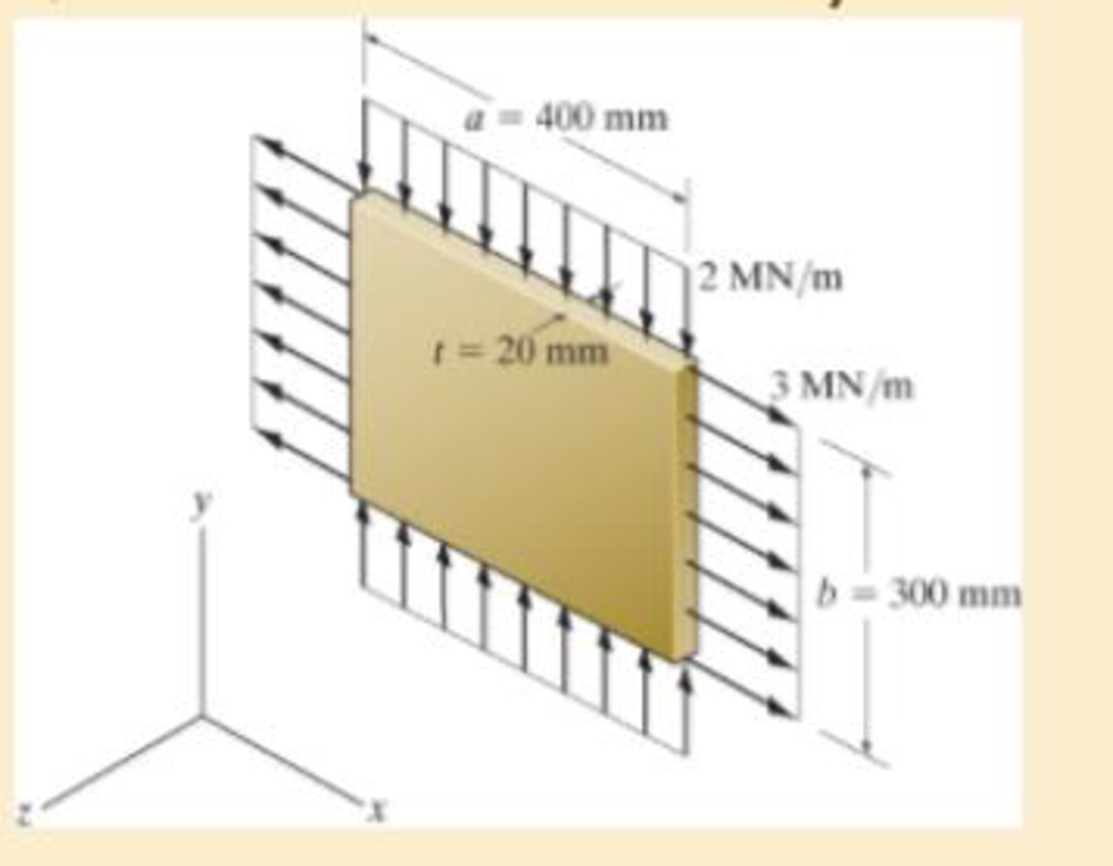
The plate is made of material having a modulus of elasticity E = 200 GPa and Poisson’s ratio v =
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Example-1:
l
D
A uniform rotor of length 0.6 m and diameter 0.4 m is made of steel (density 7810 kg/m³)
is supported by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical
directions. If the distance between the bearings is 0.7 m, determine the natural frequencies
and plot whirl speed map.
Solution:
B
find the laplace transform for the
flowing function
2(1-e)
Ans. F(s)=-
S
12)
k
0
Ans. F(s)=
k
s(1+e)
0 a
2a 3a 4a
13)
2+
Ans. F(s)=
1
s(1+e")
3
14) f(t)=1, 0
Find the solution of the following Differential Equations
Using Laplace Transforms
1) 4y+2y=0.
y(0)=2.
y'(0)=0.
2) y+w²y=0,
(0)=A,
y'(0)=B.
3) +2y-8y 0.
y(0)=1.
y'(0)-8.
4)-2-3y=0,
y(0)=1.
y'(0)=7.
5) y-ky'=0,
y(0)=2,
y'(0)=k.
6) y+ky'-2k²y=0,
y(0)=2,
y'(0) = 2k.
7) '+4y=0,
y(0)=2.8
8) y+y=17 sin(21),
y(0)=-1.
9) y-y-6y=0,
y(0)=6,
y'(0)=13.
10) y=0.
y(0)=4,
y' (0)=0.
11) -4y+4y-0,
y(0)=2.1.
y'(0)=3.9
12) y+2y'+2y=0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=-3.
13) +7y+12y=21e".
y(0)=3.5.
y'(0)=-10.
14) "+9y=10e".
y(0)=0,
y'(0)=0.
15) +3y+2.25y=91' +64.
y(0)=1.
y'(0) = 31.5
16)
-6y+5y-29 cos(2t).
y(0)=3.2,
y'(0)=6.2
17) y+2y+2y=0,
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=1.
18) y+2y+17y=0,
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=12.
19) y"-4y+5y=0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=2.
20) 9y-6y+y=0,
(0)-3,
y'(0)=1.
21) -2y+10y=0,
y(0)=3,
y'(0)=3.
22) 4y-4y+37y=0,
y(0)=3.
y'(0)=1.5
23) 4y-8y+5y=0,
y(0)=0,
y'(0)=1.
24)
++1.25y-0,
y(0)=1,
y'(0)=-0.5
25) y 2 cos(r).
y(0)=2.
y'(0) = 0.
26)
-4y+3y-0,
y(0)=3,
y(0) 7.
27) y+2y+y=e
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=0.
28) y+2y-3y=10sinh(27),
y(0)=0.
y'(0)=4.
29)…
Chapter 10 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 10.3 - Prove that the sum of the normal strains in...Ch. 10.3 - The state of strain at the point on the arm has...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.3PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.4PCh. 10.3 - 10-5. The state of strain at the point on the gear...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations and...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.8PCh. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain- transformation equations to...
Ch. 10.3 - 10–11. The state of strain on an element has...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain on an...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain which...Ch. 10.3 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10.3 - Determine the equivalent state of strain, which...Ch. 10.3 - Prob. 10.17PCh. 10.3 - Prob. 10.18PCh. 10.3 - 10–19. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–4 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - *10–20. Solve part (a) of Prob. 10–5 using Mohr’s...Ch. 10.3 - using Mohrs circle. 106. The state of strain at a...Ch. 10.5 - The strain at point A on the bracket has...Ch. 10.5 - Determine (a) the principal strains at A, (b) the...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.24PCh. 10.5 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10.5 - 10–26. The 60° strain rosette is attached to point...Ch. 10.5 - 10–27. The strain rosette is attached at the point...Ch. 10.5 - Prob. 10.28PCh. 10.6 - For the case of plane stress, show that Hookes law...Ch. 10.6 - to develop the strain tranformation equations....Ch. 10.6 - Determine the modulus of elasticity and Polssons...Ch. 10.6 - If it is subjected to an axial load of 15 N such...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - If it has the original dimensions shown, determine...Ch. 10.6 - A strain gage having a length of 20 mm Is attached...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the bulk modulus for each of the...Ch. 10.6 - The strain gage is placed on the surface of the...Ch. 10.6 - 10–39. The strain in the x direction at point A on...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the applied load P. What is the shear...Ch. 10.6 - If a load of P = 3 kip is applied to the A-36...Ch. 10.6 - The cube of aluminum is subjected to the three...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.43PCh. 10.6 - *10–44. Strain gauge b is attached to the surface...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10.6 - 10?46. The principal strains in a plane, measured...Ch. 10.6 - 10–47. The principal stresses at a point are shown...Ch. 10.6 - *10–48. The 6061-T6 aluminum alloy plate fits...Ch. 10.6 - Determine the normal stresses x and y in the plate...Ch. 10.6 - The steel shaft has a radius of 15 mm. Determine...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.51PCh. 10.6 - Prob. 10.52PCh. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Air is pumped into the steel thin-walled pressure...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - The thin-walled cylindrical pressure vessel of...Ch. 10.6 - Prob. 10.58PCh. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - A material is subjected to plane stress. Express...Ch. 10.7 - The yield stress for a zirconium-magnesium alloy...Ch. 10.7 - Solve Prob. 1061 using the maximum distortion...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.63PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.64PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.65PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.66PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10.7 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10.7 - The short concrete cylinder having a diameter of...Ch. 10.7 - 10–70. Derive an expression for an equivalent...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.71PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.72PCh. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from brittle...Ch. 10.7 - If the 2-in diameter shaft is made from cast iron...Ch. 10.7 - 10–75. The components of plane stress at a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.76PCh. 10.7 - 10–77. If the A-36 steel pipe has outer and inner...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.78PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.79PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.80PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.81PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.82PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.83PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.84PCh. 10.7 - 10–85. The state of stress acting at a critical...Ch. 10.7 - The shaft consists of a solid segment AB and a...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.87PCh. 10.7 - Prob. 10.88PCh. 10.7 - 10–89. The gas tank has an inner diameter of 1.50...Ch. 10.7 - The gas tank is made from A-36 steel and has an...Ch. 10.7 - The internal loadings at a critical section along...Ch. 10.7 - *10–92. The shaft consists of a solid segment AB...Ch. 10.7 - Prob. 10.93PCh. 10 - In the case of plane stress, where the in-plane...Ch. 10 - The plate is made of material having a modulus of...Ch. 10 - If the material is machine steel having a yield...Ch. 10 - Determine if yielding has occurred on the basis of...Ch. 10 - The 60 strain rosette is mounted on a beam. The...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - If the strain gages a and b at points give...Ch. 10 - Use the strain-transformation equations and...Ch. 10 - Use the strain transformation equations to...Ch. 10 - Specify the orientation of the corresponding...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Why is the study of database technology important?
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
This optional Google account security feature sends you a message with a code that you must enter, in addition ...
SURVEY OF OPERATING SYSTEMS
Assume a telephone signal travels through a cable at two-thirds the speed of light. How long does it take the s...
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What types of coolant are used in vehicles?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Auto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- 4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardAuto Controls Hand sketch the root Focus of the following transfer function How many asymptotes are there ?what are the angles of the asymptotes?Does the system remain stable for all values of K NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward
- Please draw the section view of the following problemsarrow_forward7) Please draw the front, top and side view for the following object. Please cross this line outarrow_forwardA 10-kg box is pulled along P,Na rough surface by a force P, as shown in thefigure. The pulling force linearly increaseswith time, while the particle is motionless att = 0s untilit reaches a maximum force of100 Nattimet = 4s. If the ground has staticand kinetic friction coefficients of u, = 0.6 andHU, = 0.4 respectively, determine the velocityof the A 1 0 - kg box is pulled along P , N a rough surface by a force P , as shown in the figure. The pulling force linearly increases with time, while the particle is motionless at t = 0 s untilit reaches a maximum force of 1 0 0 Nattimet = 4 s . If the ground has static and kinetic friction coefficients of u , = 0 . 6 and HU , = 0 . 4 respectively, determine the velocity of the particle att = 4 s .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Relationship Between Elastic Constants and Connecting Equations; Author: Engineers Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=whW5PnM7Pug;License: Standard Youtube License