
Concept explainers
a.
To calculate:
The probability of the center
a.
Answer to Problem 8Q
The probability of the center circle is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
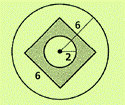
Calculation:
The areas as per the question can be obtained as follows:
Calculate area of circle by using
Area of outer circle
Area of center circle
Calculate area of square by using
Area of square
Thus, the required probability measures are as follows:
The probability of a dart falling in the center circle is given,
Hence the probability of the center circle is
b.
To calculate:
The probability of outside square.
b.
Answer to Problem 8Q
The probability of outside squareis
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
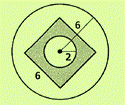
Calculation:
The areas as per the question can be obtained as follows:
Calculate area of circle by using
Area of outer circle
Area of center circle
Calculate area of square by using
Area of square
Thus, the required probability measures are as follows:
The probability of a dart falling in the square is given,
Hence the probability of outside square is
c.
To calculate:
The probability of inside the square but outside thecenter circle.
c.
Answer to Problem 8Q
the probability of inside the square but outside the center circle is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
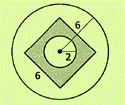
Calculation:
The areas as per the question can be obtained as follows:
Calculate area of circle by using
Area of outer circle
Area of center circle
Calculate area of square by using
Area of square
Thus, the required probability measures are as follows:
The probability of inside the square but outside the center circle is given as,
Hence,the probability of inside the square but outside the center circle is
Chapter 10 Solutions
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 2: Student Edition 2015
- So confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forwardIn simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forward
- In simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forwardWrite each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forward
- In simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step how do you find the zeros of y = 6x2 + 24x - 192arrow_forward
- Step by step Find the zeros of each quadratic relation. a) y = x2 - 16xarrow_forwardIn simplest step by step terms, how do you find the zeros of y = x2 - 16arrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Describe the shape and position of the parabola relative to the graph of y = x 2 y = - 80( x + 9) 2 + 10.8arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





