
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 9QP
- a. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be intermediates in the pathway for production of protein E. To determine where the block in protein-E production occurred in each individual, the various intermediates were given to each individual’s cel Is in culture. After a few weeks of growth with the intermediate, the cells were assayed for the production of protein E. The results for each individual’s cells are given in the following table. A plus sign means that protein E was produced after the cells were given the intermediate listed at the top of the column. A minus sign means that the cells still could not produce protein E even after being exposed to the intermediate at the top of the column.
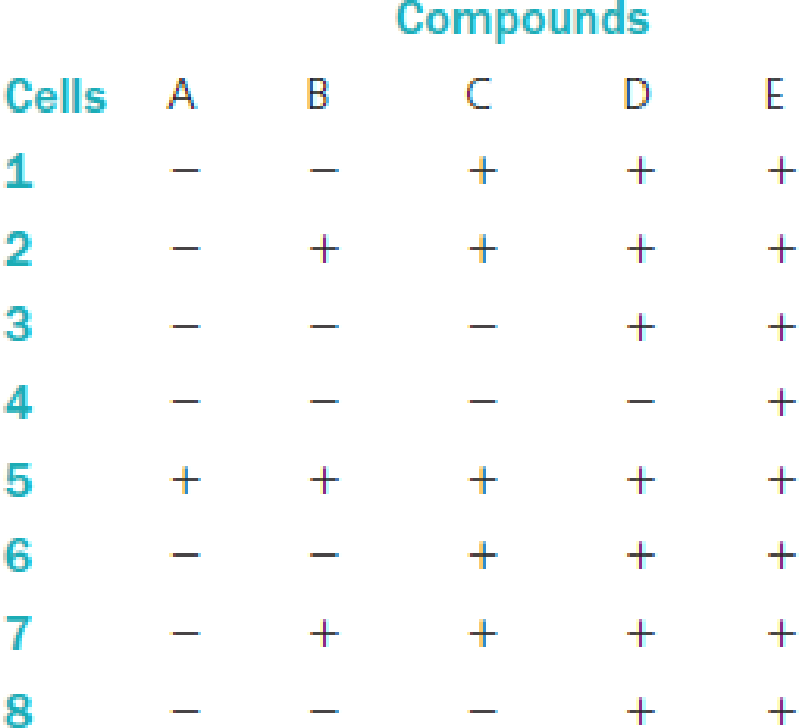
Draw the pathway leading to the production of protein E.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Which of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why.
A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects
B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate
C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs
D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problems
This question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!
They got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 1GRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 2GRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 1EGCh. 10.7 - Prob. 2EGCh. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - Many individuals with metabolic diseases are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2QPCh. 10 - Enzymes have all the following characteristics...
Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Prob. 6QPCh. 10 - Prob. 7QPCh. 10 - Prob. 8QPCh. 10 - a. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - b. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - a. If an individual who is homozygous for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 12QPCh. 10 - Suppose that in the formation of phenylalanine...Ch. 10 - If phenylalanine was not an essential amino acid,...Ch. 10 - Phenylketonuria and alkaptonuria are both...Ch. 10 - The normal enzyme required for converting sugars...Ch. 10 - Knowing that individuals who are homozygous for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 18QPCh. 10 - A person was found to have very low levels of...Ch. 10 - If an extra nucleotide is inserted in the first...Ch. 10 - Transcriptional regulators are proteins that bind...Ch. 10 - Prob. 22QPCh. 10 - Prob. 23QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forward
- Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning



cell culture and growth media for Microbiology; Author: Scientist Cindy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EjnQ3peWRek;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY