
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305251052
Author: Michael Cummings
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 4QP
Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following hypothetical pathway in which substance A is converted to substance C by enzymes 1 and 2. Substance B is the intermediate produced in this pathway:
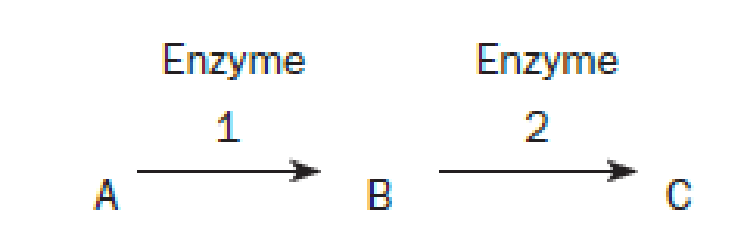
a. If an individual is homozygous for a null mutation in the gene that codes for enzyme 1, what will the result be?
b. If an individual is homozygous for a null mutation in enzyme 2, what will the result be?
c. What if an individual is heterozygous for a dominant mutation in which enzyme 1 is overactive?
d. What if an individual is heterozygous for a mutation that abolishes the activity of enzyme 2 (a null mutation)?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Question #3:
In the KeyGene paper, the authors state that it would be useful if pollen from an apomict would
transmit apomixis-inducing genes to the female in the cross (assuming the pollen is viable). Assuming
there was just one gene conferring gametophytic obligate apomixis, and that the two parents are
inbreds, what would be the consequences of such a cross if:
a) The apomixis was a dominant trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non-
apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic
and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female
first (left side) in the parental cross.
b) The apomixis was a recessive trait? Indicate the genotypes and phenotypes (apomict or non-
apomict) of the parents, F1 and F2 generations. Remember to include the expected genotypic
and phenotypic ratios (or percentages) in the F1 and F2 generations, and to position the female
first (left side) in the…
Question #5:
Assume that two genes are identified that confer gametophytic facultative apomixis in soybean. The
genes show independent assortment. Recessive alleles at both loci are required for the facultative
apomixis. Facultative apomixis is triggered when the temperature at pollination is above 20 degrees C.
At temperatures below 20 degrees C, all reproduction is sexual, independent of genotype.
A facultative apomict male, capable of producing viable pollen, was crossed with a sexually
reproducing female. Assuming the parents are completely inbred, what are the predicted phenotypic
ratios (apomict: non-apomict) for the F1, F2, and DH (F1-derived) generations at each of the following
temperatures*:
a) 15°C?
b) 25°C?
*for full credit, show crosses and genotypes where appropriate. Remember to position the
female first (left side) in the cross.
Type your answer here:
a. What percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent.
b. What will happen to elimination of the drug in the previous question if the system is saturated? explain and show any math involved
Chapter 10 Solutions
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 10.4 - Prob. 1GRCh. 10.4 - Prob. 2GRCh. 10.7 - Prob. 1EGCh. 10.7 - Prob. 2EGCh. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - A couple was referred for genetic counseling...Ch. 10 - Many individuals with metabolic diseases are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 2QPCh. 10 - Enzymes have all the following characteristics...
Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Questions 4 through 6 refer to the following...Ch. 10 - Prob. 6QPCh. 10 - Prob. 7QPCh. 10 - Prob. 8QPCh. 10 - a. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - b. Compounds A, B, C, and D are known to be...Ch. 10 - a. If an individual who is homozygous for the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 12QPCh. 10 - Suppose that in the formation of phenylalanine...Ch. 10 - If phenylalanine was not an essential amino acid,...Ch. 10 - Phenylketonuria and alkaptonuria are both...Ch. 10 - The normal enzyme required for converting sugars...Ch. 10 - Knowing that individuals who are homozygous for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 18QPCh. 10 - A person was found to have very low levels of...Ch. 10 - If an extra nucleotide is inserted in the first...Ch. 10 - Transcriptional regulators are proteins that bind...Ch. 10 - Prob. 22QPCh. 10 - Prob. 23QP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- If you wanted to reduce the difference between peak and trough levels that occur with repeated administration of a drug, how would you adjust the dose and dose interval without changing the plateau concentration (plateau is the average of peak and trough levels)? Select your answers for both dose and interval. Hint: It may be helpful to think about this problem using an example such as food. How would you eat if you wanted to maintain very steady hunger/satiety levels without changing your total caloric intake? Options: A. Dose; Increase dose B. Dose; Decrease dose C. Dose; Do not change dose D. Interval; Increase the interval between doses (give the drug less frequently) E. Interval; Decrease the interval between doses (give the drug more frequently) F. Interval; Do not change the intervalarrow_forwardWhat percentage of a drug is eliminated after 4 half-lives? Please round to the nearest percent. Show the matharrow_forwardBriefly explain the 6 domain of interprofessional collaboration: Role clarification, Team functioning, Interprofessional communication, Patient/client/family/community-centered care, Interprofessional conflict resolution, Collaborative leadership. Provide a specific negative events that nursing student would observe in a clinical setting for each domain.arrow_forward
- what is an intermittent water course and what kind of fish habitat it would providearrow_forwardwhy are native freshwater mussels are an important part of great lakes ecosystemarrow_forwardwhat morphological features differentiate the lamprey species and other species in the great lakesarrow_forward
- There are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forwardfour fish or mussel species that are native to the great lakesarrow_forwardThere are a wide range of therapeutic applications available as options for patients. Medical professionals should be aware of these applications so they can make informed recommendations to patients. To gain a better understanding of some therapeutic applications and how they are related to RNA and mRNA, research long non-coding RNA. Respond to the following in a minimum of 175 words: What is lncRNA and what does it do? How does IncRNA differ from mRNA? What are some therapeutic applications associated with lncRNA? Think about possible future uses of this application. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this application and its continued use?arrow_forward
- four physial characteristics of a fish or a mussel that would help you identify it to a speciesarrow_forwarddescribe what you would do in this situation, you are working ona. river and it will take 20 minutes by boat to get back to the field truck, you are 1 hour from finishing the field work on the last day of field trip. you hear thunder int he dsitnace, what did you do?arrow_forwardunu grow because auxin is still produced in the tip to Another of Boysen and Jensen's experiments included the use of mica, explain why one of the shoots was able to show phototropism and the other was not. Mica Wafer Ligh c. They then t but this time permeable n shoot. Why phototropis Light Mica Wafer Coleoptile tips Tips removed: agar Explain why the shoo direction after the ag the cut shoot, even tarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Mitochondrial mutations; Author: Useful Genetics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GvgXe-3RJeU;License: CC-BY