
Concept explainers
A projectile of mass m moves to the right with a speed vi (Fig. P10.81a). The projectile strikes and sticks to the end of a stationary rod of mass M, length d, pivoted about a frictionless axle perpendicular to the page through O (Fig. P10.81b). We wish to find the fractional change of kinetic energy in the system due to the collision. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model to describe the projectile and the rod? (b) What is the
Figure P10.81
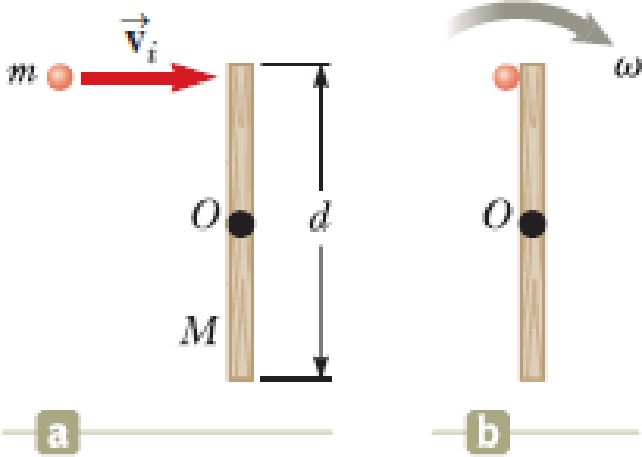
(a)
The appropriate model to analyze the system.
Answer to Problem 81P
The appropriate model to analyze the system is by considering it as an
Explanation of Solution
The striking and sticking of the given projectile on the stationary rod can be considered as a collision. The collision occurring between two object is an isolated system for which the total momentum is conserved. The momentum of both objects before and after collision will be same. This is because the system is free from any external force which changes the momentum.
Since the rod and projectile is not experiencing any external force and torque the total momentum of the system will be conserved, and the system can be considered as isolated. Thus, the best suited analysis model is by treating the system as isolated.
Conclusion
Therefore, the appropriate model to analyze the system is by considering it as an
(b)
The angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
Explanation of Solution
The total angular momentum is the sum of the angular momentum of projectile and the rod. Since the rod is initially at rest its angular momentum before collision will be zero.
Write the expression for the total angular momentum.
Here,
Write the expression for the angular momentum of the projectile at
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular momentum of the system before collision about an axis passing through
(c)
The moment of inertia of the rod after collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The moment of inertia of the rod after collision is
Explanation of Solution
The total moment of inertia is the sum of the moment of inertia of rod and the projectile.
Write the expression for the total moment of inertia.
Here,
Let
Here,
Write the expression for the moment of inertia of the projectile about an axis passing through
Conclusion:
Substitute, equation (IV) and (V) in (III).
Therefore, the moment of inertia of the rod after collision is
(d)
The angular momentum of the system after collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular momentum of the system after collision is
Explanation of Solution
After the collision there is only a single angular momentum since the projectile stick to the rod after striking.
Write the expression for the final angular momentum.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular momentum of the system after collision is
(e)
The angular speed after the collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The angular speed after the collision is
Explanation of Solution
According to principle of conservation of angular momentum the momentum after and before collision will be same.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the angular speed after the collision is
(f)
The kinetic energy of the system before collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The kinetic energy of the system before collision is
Explanation of Solution
Since the rod is at rest the kinetic energy is only for the projectile. The projectile has mass
Hence the kinetic energy of the projectile is.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system before collision is
(g)
The kinetic energy of the system after collision
Answer to Problem 81P
The kinetic energy of the system after collision is
Explanation of Solution
The kinetic energy after the collision is the rotational kinetic energy of the system.
Write the expression for the rotational kinetic energy.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the kinetic energy of the system after collision is
(h)
The fractional change in kinetic energy due o collision.
Answer to Problem 81P
The fractional change in kinetic energy due to collision is
Explanation of Solution
The change in energy is obtained by taking the difference of energy before, and after collision.
Write the expression for change in kinetic energy.
Substitute,
Write the expression for the fractional change in kinetic energy.
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the fractional change in kinetic energy due to collision is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Please solve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve all the questions correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve this problem correctly please and be sure to provide explanation on each step so I can understand what's been done thank you. (preferrably type out everything)arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward2. 1. Tube Rating Charts Name: Directions: For the given information state if the technique is safe or unsafe and why. 60 Hertz Stator Operation Effective Focal Spot Size- 0.6 mm Peak Kilovolts MA 2 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 2501 60 50 40 30 .01 .02 .04.06 .1 .2 .4.6 1 8 10 Maximum Exposure Time In Seconds Is an exposure of 80 kVp, 0.1 second and 200 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above? Is an exposure of 100 kVp, 0.9 second and 150 mA within the limits of the single phase, 0.6 mm focal spot tube rating chart above?arrow_forward
- Q: You have a CO2 laser resonator (λ = 10.6 μm). It has two curved mirrors with R₁=10m, R2= 8m, and mirror separation /= 5m. Find: R2-10 m tl Z-O 12 R1-8 m 1. Confocal parameter. b= 21w2/2 =√1 (R1-1)(R2-1)(R1+R2-21)/R1+R2-21) 2. Beam waist at t₁ & t2- 3. Waist radius (wo). 4. 5. The radius of the laser beam outside the resonator and about 0.5m from R₂- Divergence angle. 6. Radius of curvature for phase front on the mirrors R₁ & R2-arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardSARET CRKS AUTOWAY 12. A stone is dropped from the top of a cliff. It is seen to hit the ground below after 3.55 s. How high is the cliff? 13. A ball is dropped from rest at the top of a building that is 320 m tall. Assuming no air resistance, what is the speed of the ball just before it strikes the ground? 14. Estimate (a) how long it took King Kong to fall straight down from the top of the Empire State Building (280m high), and (b) his velocity just before "landing". Useful equations For Constant Velocity: V => D X = V₁t + Xo For Constant Acceleration: Vr = V + at X = Xo+Vot + v=V+2a(X-Xo) \prom = V +V V velocity t = time D Distance X = Final Position Xo Initial Position V = Final Velocity Vo Initial Velocity a = acceleration For free fall Yf = Final Position Yo Initial Position g = 9.80 m $2 For free fall: V = V + gt Y=Yo+Vo t + +gt V,² = V₁²+2g (Y-Yo) V+Vo Vprom= 2 6arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University





