
Concept explainers
A uniform beam resting on two pivots has a length L = 6.00 m and mass M = 90.0 kg. The pivot under the left end exerts a normal force n1 on the beam, and the second pivot located a distance ℓ = 4.00 m from the left end exerts a normal force n2. A woman of mass m = 55.0 kg steps onto the left end of the beam and begins walking to the right as in Figure P10.28. The goal is to find the woman’s position when the beam begins to tip. (a) What is the appropriate analysis model for the beam before it begins to tip? (b) Sketch a force diagram for the beam, labeling the gravitational and normal forces acting on the beam and placing the woman a distance x to the right of the first pivot, which is the origin. (c) Where is the woman when the normal force n1 is the greatest? (d) What is n1 when the beam is about to tip? (e) Use Equation 10.27 to find the value of n2 when the beam is about to tip. (f) Using the result of part (d) and Equation 10.28, with torques computed around the second pivot, find the woman’s position x when the beam is about to tip. (g) Check the answer to part (e) by computing torques around the first pivot point.
Figure P10.28
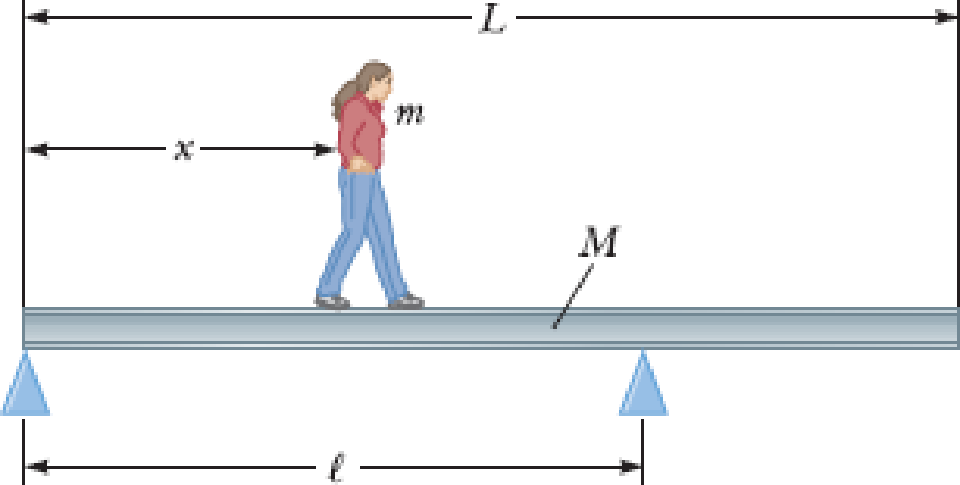
(a)
The model of beam used for analysis before it begins to tip.
Answer to Problem 28P
The object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
Explanation of Solution
Initially the beam is balanced. When an object is at rest the equilibrium maintained by the object is called static equilibrium.
Hence the object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the object is in static equilibrium before it begins to tip.
(b)
Sketch the force diagram for the beam.
Answer to Problem 28P
The force diagram of the beam is given below.
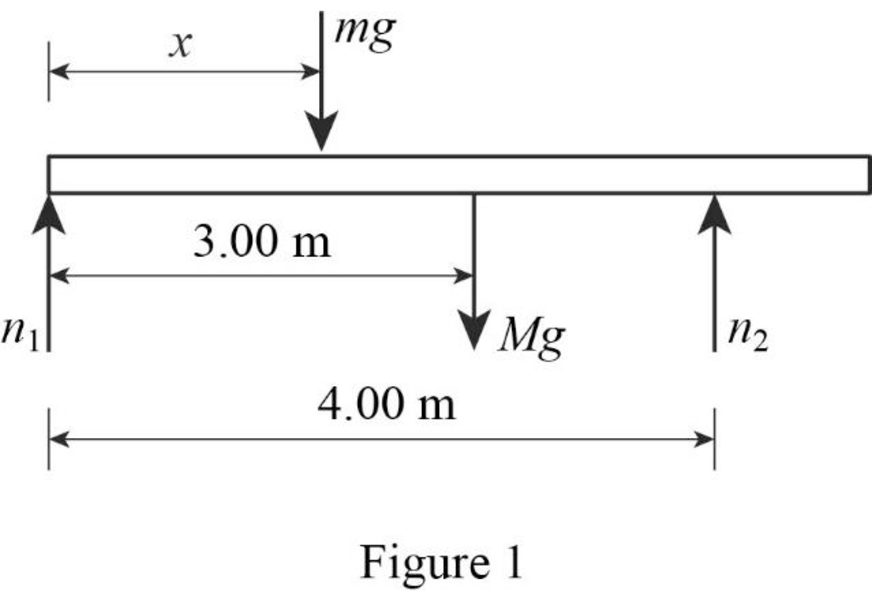
Explanation of Solution
Force diagram represents all the different kinds of forces acting on the given system. Weight of the women,
Conclusion:
The weight of the women is.
Here,
The weight of the beam corresponding to center of mass is.
Substitute,
Substitute,
The force diagram of the beam is given below.
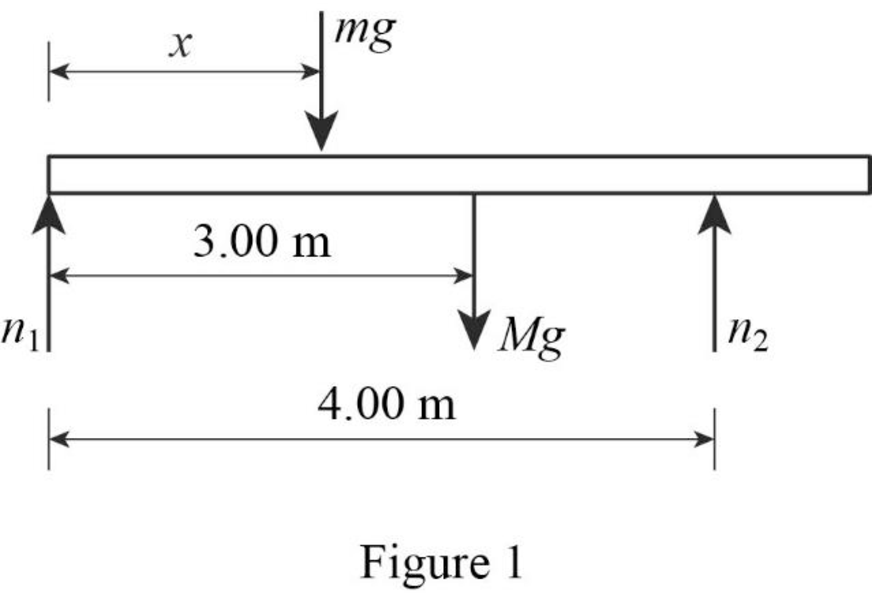
(c)
The position of the women when the normal force is greatest.
Answer to Problem 28P
When the women is at
Explanation of Solution
The normal force
The normal force
Conclusion:
Therefore, the normal force
(d)
The value of
Answer to Problem 28P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
When the women walk from left end to right end she will reach at a point so that the beam start to rotate in clockwise direction about the right pivot. So the beam starts to lift up about the leftmost pivot, thus the normal force exerted by the pivot will be zero.
Thus the normal force
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of
(e)
The value of
Answer to Problem 28P
The value of
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the total force acting on
Since the force exerted on beam, and normal force
Rearrange equation (IV) to obtain an expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, value of
(f)
The position of women when the beam is about to tip.
Answer to Problem 28P
The position of women when the beam is about to tip is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for total torque in the beam.
When the beam is about to the tip, the torque
Substitute,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Therefore, the position of women when the beam is about to tip is
(g)
To check the answer in part (f) computing the torque around the first pivot point.
Answer to Problem 28P
The position of the women is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the net torque about the left pivot.
Conclusion:
The net torque about the left pivot is zero.
Substitute,
The position obtained in part (f) is
Therefore, the position of the women is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Bundle: Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text, 5th Edition, Multi-Term
- Cam mechanisms are used in many machines. For example, cams open and close the valves in your car engine to admit gasoline vapor to each cylinder and to allow the escape of exhaust. The principle is illustrated in the figure below, showing a follower rod (also called a pushrod) of mass m resting on a wedge of mass M. The sliding wedge duplicates the function of a rotating eccentric disk on a camshaft in your car. Assume that there is no friction between the wedge and the base, between the pushrod and the wedge, or between the rod and the guide through which it slides. When the wedge is pushed to the left by the force F, the rod moves upward and does something such as opening a valve. By varying the shape of the wedge, the motion of the follower rod could be made quite complex, but assume that the wedge makes a constant angle of 0 = 15.0°. Suppose you want the wedge and the rod to start from rest and move with constant acceleration, with the rod moving upward 1.00 mm in 8.00 ms. Take m…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
- I tried to solve this question, and I had an "expert" answer it and they got it wrong. I cannot answer this questionarrow_forwardEddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forwardsolve for (_) Narrow_forward
- Two boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forwardAll correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forwardThree long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





