
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the
In
The rate determination step is formation of carbocation.
The stability order of carbocation is,
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Therefore, tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation. Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends on reactant as well as nucleophile, which are involved in reaction is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
Reactant and nucleophile are present at the rate determination step.
The order of species involving in
Tertiary < Secondary < Primary
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) to yields tosylated product, this reaction is called as tosylation and which is shown below,
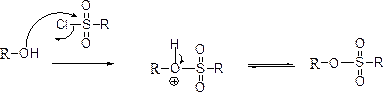
(a)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
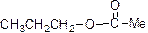
Explanation of Solution
The given Compound (A) is reaction with methane sulfonyl chloride which gives compound (B). This compound (B) reaction with acetate ion and gives the propyl acetate (D). The reaction is given below,
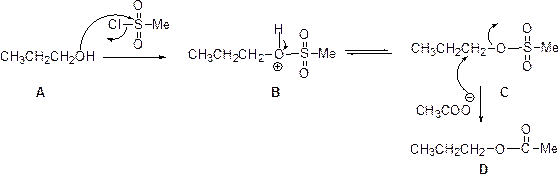
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends only on one reactant, which is involved in reaction is called unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
The rate determination step is formation of carbocation.
The stability order of carbocation is,
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Therefore, tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation. Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends on reactant as well as nucleophile, which are involved in reaction is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
Reactant and nucleophile are present at the rate determination step.
The order of species involving in
Tertiary < Secondary < Primary
This is shown below,
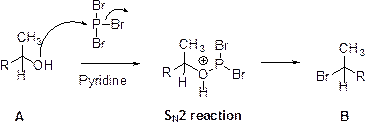
(b)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
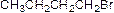
Explanation of Solution
Alcohol (A) is reaction with
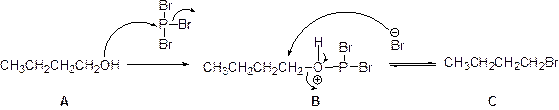
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends only on one reactant, which is involved in reaction is called unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
The rate determination step is formation of carbocation.
The stability order of carbocation is,
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Therefore, tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation. Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends on reactant as well as nucleophile, which are involved in reaction is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
Reactant and nucleophile are present at the rate determination step.
The order of species involving in
Tertiary < Secondary < Primary
Tosylation reaction:
The alcohol is treated with any tosyl chloride (methane sulfonyl chloride) to yields tosylated product, this reaction is called as alkyl tosylation and which is shown below,
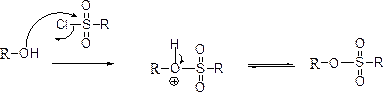
(c)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
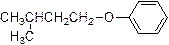
Explanation of Solution
The given Compound (A) is reaction with para toluene sulfonyl chloride which gives compound (B). This compound (B) reaction with phenoxide ion and gives the corresponding ether (D). The reaction is given below,
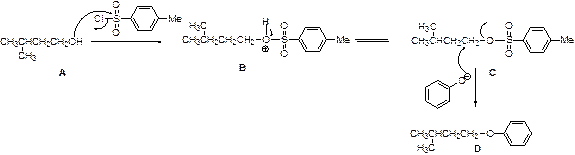
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule, when the alcohol is treated with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
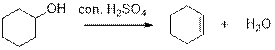
The stability of carbocation is given below,
Tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary and primary.
(d)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
Explanation of Solution
The Compound (A) is undergoes dehydration, because the formation of primary carbocation and it is less stable which forms secondary carbocation and the hydrogen is removed from adjacent β- carbon atom which leads to the formation of alkene (B).
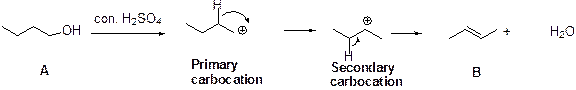
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
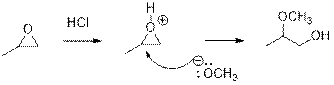
In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial
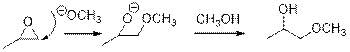
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks Epoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
(e)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
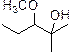
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is shown below,
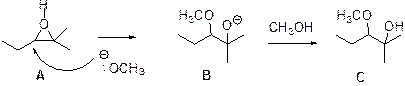
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks the Epoxides (A) in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion (B), then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product (C). Therefore the major product is shown above.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
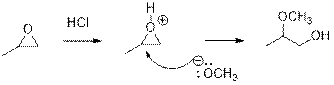
In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial
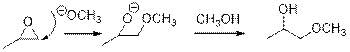
Epoxides are reactive, methoxide ion attacks theEpoxides in a less sterically hindered position which forms the alkoxide ion, and then it gets proton from alcohol which form the product.
(f)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
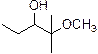
Explanation of Solution
The reaction is shown below,
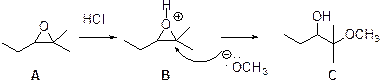
In the presence of acid catalyst, this reaction takes place through partial
(g)
Interpretation:
The product of given reaction should be given.
Concept introduction:
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends only on one reactant, which is involved in reaction is called unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
The rate determination step is formation of carbocation.
The stability order of carbocation is,
Tertiary > Secondary > Primary
Therefore, tertiary alcohols undergo substitution very fast than the secondary alcohols because tertiary carbocation is more stable than the secondary carbocation than the primary carbocation. Primary alcohol is less stable therefore it won’t undergoes
In the nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of reaction depends on reactant as well as nucleophile, which are involved in reaction is called bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
In
Reactant and nucleophile are present at the rate determination step.
The order of species involving in
Tertiary < Secondary < Primary
Chlorination reaction:
The alcohol is treated with thionyl chloride to yields chlorinated product, this reaction is called as chlorination and which is shown below,
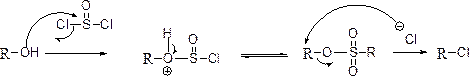
(g)
Answer to Problem 55P
The product is given below,
Explanation of Solution
The given Compound (A) is reaction with thionyl chloride which gives compound (B). This compound (B) reaction with chlorine ion and gives the corresponding chloro compound (C). The reaction is given below,
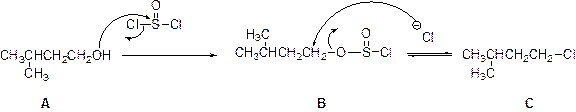
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/S.G+SOLN.MANUAL
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction.arrow_forward2. Provide the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction. Pay particular attention to the regio- and stereochemistry of your product. H3CO + H CN Aarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction.arrow_forward
- 1) The isoamyl acetate report requires eight paragraphs - four for comparison of isoamyl alcohol and isoamyl acetate (one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR) and four for comparison of acetic acid and isoamyl acetate ((one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR. 2) For MS, the differing masses of molecular ions are a popular starting point. Including a unique fragmentation is important, too. 3) For HNMR, CNMR and IR state the peaks that are different and what makes them different (usually the presence or absence of certain groups). See if you can find two differences (in each set of IR, HNMR and CNMR spectra) due to the presence or absence of a functional group. Include peak locations. Alternatively, you can state a shift of a peak due to a change near a given functional group. Including peak locations for shifted peaks, as well as what these peaks are due to. Ideally, your focus should be on not just identifying the differences but explaining them in terms of…arrow_forwardWhat steps might you take to produce the following product from the given starting material? CI Br Он до NH2 NH2arrow_forward1) The isoamyl acetate report requires eight paragraphs - four for comparison of isoamyl alcohol and isoamyl acetate (one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR) and four for comparison of acetic acid and isoamyl acetate ((one paragraph each devoted to MS, HNMR, CNMR and IR. 2) For MS, the differing masses of molecular ions are a popular starting point. Including a unique fragmentation is important, too. 3) For HNMR, CNMR and IR state the peaks that are different and what makes them different (usually the presence or absence of certain groups). See if you can find two differences (in each set of IR, HNMR and CNMR spectra) due to the presence or absence of a functional group. Include peak locations. Alternatively, you can state a shift of a peak due to a change near a given functional group. Including peak locations for shifted peaks, as well as what these peaks are due to. Ideally, your focus should be on not just identifying the differences but explaining them in terms of…arrow_forward
- №3 Fill in the below boxes. HN 1. LAH 2. H3O+ NH2arrow_forwardFor the photochemical halogenation reaction below, draw both propagation steps and include the mechanism arrows for each step. H CH ot CH3 CI-CI MM hv of CH H-CI CH3 2nd attempt See Periodic Table See Hint Draw only radical electrons; do not add lone pair electrons. Note that arrows cannot meet in "space," and must end at either bonds or at atoms. 1 i Add the missing curved arrow notation to this propagation step. 20 H ن S F P H CI Br 品arrow_forwardThe radical below can be stabilized by resonance. 4th attempt Draw the resulting resonance structure. DOCEarrow_forward
- Use curved arrows to generate a second resonance form for the allylic radical formed from 2-methyl-2-pentene. 1 Draw the curved arrows that would generate a second resonance form for this radical. D 2 H S F A Бг Iarrow_forwardDraw the resulting product(s) from the coupling of the given radicals. Inlcude all applicable electrons and non-zero formal charges. H.C öö- CH3 2nd attempt +1 : 招 H₂C CH CH₂ See Periodic Table See H H C S F P Br CH₂ Iarrow_forwardPlease, help me out with the calculation, step by step on how to find what's blank with the given information.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





