
Concept explainers
Springsteen Company manufactures guitars. The company uses a standard,
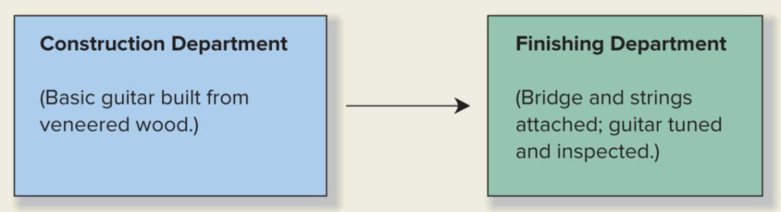
Each finished guitar contains seven pounds of veneered wood. In addition, one pound of wood is typically wasted in the production process. The veneered wood used in the guitars has a standard price of $12 per pound. The other parts needed to complete each guitar, such as the bridge and strings, cost $15 per guitar. The labor standards for Springsteen’s two production departments are as follows:
Construction Department: 6 hours of direct labor at $20 per hour
Finishing Department: 3 hours of direct labor at $15 per hour
The following pertains to the month of July.
- 1. There were no beginning or ending work-in-process inventories in either production department.
- 2. There was no beginning finished-goods inventory.
- 3. Actual production was 500 guitars, and 300 guitars were sold on account for $400 each.
- 4. The company purchased 6,000 pounds of veneered wood at a price of $12.50 per pound.
- 5. Actual usage of veneered wood was 4,500 pounds of the wood purchased during July.
- 6. Enough parts (bridges and strings) to finish 600 guitars were purchased at a cost of $9,000.
- 7. The Construction Department used 2,850 direct-labor hours. The total direct-labor cost in the Construction Department was $54,150.
- 8. The Finishing Department used 1,570 direct-labor hours. The total direct-labor cost in that department was $25,120.
- 9. There were no direct-material variances in the Finishing Department.
Required:
- 1. Prepare a schedule that computes the
standard costs of direct material and direct labor in each production department. - 2. Prepare three exhibits that compute the July direct-material and direct-labor variances in the Construction Department and the July direct-labor variances in the Finishing Department. (Refer to Exhibits 10–2, 10–3, and 10–4 for guidance.)
- 3. Prepare a cost variance report for July similar to that shown in Exhibit 10–5. Springsteen Company investigates all variances greater than $5,000 or 5%.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Access Card for Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment (NEW!!)
- Golding Manufacturing, a division of Farnsworth Sporting, Inc., produces two different models of bows and eight models of knives. The bow-manufacturing process involves the production of two major subassemblies: the limbs and the handle. The limbs pass through four sequential processes before reaching final assembly: lay-up, molding, fabricating, and finishing. In the Lay-Up Department, limbs are created by laminating layers of wood. In Molding, the limbs are heat treated, under pressure, to form a strong resilient limb. In the Fabricating Department, any protruding glue or other processing residue is removed. Finally, in Finishing, the limbs are cleaned with acetone, dried, and sprayed with the final finishes. The handles pass through two processes before reaching final assembly: pattern and finishing. In the Pattern Department, blocks of wood are fed into a machine that is set to shape the handles. Different patterns are possible, depending on the machines setting. After coming out of the machine, the handles are cleaned and smoothed. They then pass to the Finishing Department where they are sprayed with the final finishes. In Final Assembly, the limbs and handles are assembled into different models using purchased parts such as pulley assemblies, weight adjustment bolts, side plates, and string. Golding, since its inception, has been using process costing to assign product costs. A predetermined overhead rate is used based on direct labor dollars (80 percent of direct labor dollars). Recently, Golding has hired a new controller, Karen Jenkins. After reviewing the product costing procedures, Karen requested a meeting with the divisional manager, Aaron Suhr. The following is a transcript of their conversation: KAREN: Aaron, I have some concerns about our cost accounting system. We make two different models of bows and are treating them as if they were the same product. Now I know that the only real difference between the models is the handle. The processing of the handles is the same, but the handles differ significantly in the amount and quality of wood used. Our current costing does not reflect this difference in direct material input. AARON: Your predecessor is responsible. He believed that tracking the difference in direct material cost wasnt worth the effort. He simply didnt believe that it would make much difference in the unit cost of either model. KAREN: Well, he may have been right, but I have my doubts. If there is a significant difference, it could affect our views of which model is more important to the company. The additional bookkeeping isnt very stringent. All we have to worry about is the Pattern Department. The other departments fit what I view as a process-costing pattern. AARON: Why dont you look into it? If there is a significant difference, go ahead and adjust the costing system. After the meeting, Karen decided to collect cost data on the two models: the Deluxe model and the Econo model. She decided to track the costs for one week. At the end of the week, she had collected the following data from the Pattern Department: a. There were a total of 2,500 bows completed: 1,000 Deluxe models and 1,500 Econo models. b. There was no beginning work in process; however, there were 300 units in ending work in process: 200 Deluxe and 100 Econo models. Both models were 80 percent complete with respect to conversion costs and 100 percent complete with respect to direct materials. c. The Pattern Department experienced the following costs: d. On an experimental basis, the requisition forms for direct materials were modified to identify the dollar value of the direct materials used by the Econo and Deluxe models: Required: 1. Compute the unit cost for the handles produced by the Pattern Department, assuming that process costing is totally appropriate. 2. Compute the unit cost of each handle, using the separate cost information provided on materials. 3. Compare the unit costs computed in Requirements 1 and 2. Is Karen justified in her belief that a pure process-costing relationship is not appropriate? Describe the costing system that you would recommend. 4. In the past, the marketing manager has requested more money for advertising the Econo line. Aaron has repeatedly refused to grant any increase in this products advertising budget because its per-unit profit (selling price less manufacturing cost) is so low. Given the results in Requirements 1 through 3, was Aaron justified in his position?arrow_forwardHealthway uses a process-costing system to compute the unit costs of the minerals that it produces. It has three departments: Mixing, Tableting, and Bottling. In Mixing, at the beginning of the process all materials are added and the ingredients for the minerals are measured, sifted, and blended together. The mix is transferred out in gallon containers. The Tableting Department takes the powdered mix and places it in capsules. One gallon of powdered mix converts to 1,600 capsules. After the capsules are filled and polished, they are transferred to Bottling where they are placed in bottles, which are then affixed with a safety seal and a lid and labeled. Each bottle receives 50 capsules. During July, the following results are available for the first two departments (direct materials are added at the beginning in both departments): Overhead in both departments is applied as a percentage of direct labor costs. In the Mixing Department, overhead is 200 percent of direct labor. In the Tableting Department, the overhead rate is 150 percent of direct labor. Required: 1. Prepare a production report for the Mixing Department using the weighted average method. Follow the five steps outlined in the chapter. Round unit cost to three decimal places. 2. Prepare a production report for the Tableting Department. Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Follow the five steps outlined in the chapter. Round unit cost to four decimal places.arrow_forwardCarson Paint Company, which manufactures quality paint to sell at premium prices, uses a single production department. Production begins by blending the various chemicals that are added at the beginning of the process and ends by filling the paint cans. The gallon cans are then transferred to the shipping department for crating and shipment. Direct labor and overhead are added continuously throughout the process. Factory overhead is applied at the rate of $3 per direct labor dollar. The company combines direct labor and overhead in computing product cost. Prior to May, when a change in the manufacturing process was implemented, Work - in - Process Inventories were insignificant. The changed manufacturing process, which has resulted in increased equipment capacity, allows increased production but also results in considerable amounts of Work-in - Process Inventory. Also, the company had 1,000 spoiled gallons in May-one-half of which was normal spoilage and the rest abnormal spoilage. The…arrow_forward
- Arona Corporation manufactures canoes in two departments, Fabrication and Waterproofing. In the Fabrication Department, fiberglass panels are attached to a canoe- shaped aluminum frame. The canoes are then transferred to the Waterproofing department to be coated with sealant. Arona uses a weighted-average process cost system to collect costs in both departments. All materials in the Fabrication Department are added at the beginning of the production process. On July 1, the Fabrication Department had 30 canoes in process that were 20% complete with respect to conversion cost. On July 31, Fabrication had 20 canoes in process that were 40% complete with respect to conversion cost. During July, the Fabrication Department completed 73 canoes and transferred them to the Waterproofing Department. What are the Fabrication Department's equivalent units of production related to materials for July?arrow_forwardArona Corporation manufactures canoes in two departments, Fabrication and Waterproofing. In the Fabrication Department, fiberglass panels are attached to a canoe- shaped aluminum frame. The canoes are then transferred to the Waterproofing department to be coated with sealant. Arona uses a weighted-average process cost system to collect costs in both departments. All materials in the Fabrication Department are added at the beginning of the production process. On July 1, the Fabrication Department had 30 canoes in process that were 20% complete with respect to conversion cost. On July 31, Fabrication had 20 canoes in process that were 40% complete with respect to conversion cost. During July, the Fabrication Department completed 87 canoes and transferred them to the Waterproofing Department. What are the Fabrication Department's equivalent units of production related to conversion costs for July? Multiple Choice 95 117 79 107arrow_forwardArona Corporation manufactures canoes in two departments, Fabrication and Waterproofing. In the Fabrication Department, fiberglass panels are attached to a canoe- shaped aluminum frame. The canoes are then transferred to the Waterproofing department to be coated with sealant. Arona uses a welghted-average process cost system to collect costs in both departments. All materials in the Fabrication Department are added at the beginning of the production process. On July 1, the Fabrication Department had 30 canoes in process that were 20% complete with respect to conversion cost. On July 31, Fabrication had 20 canoes in process that were 40% complete with respect to conversion cost. During July, the Fabrication Department completed 87 canoes and transferred them to the Waterproofing Department. What are the Fabrication Department's equivalent units of production related to materials for July? Multiple Cholce 95 79 117 107arrow_forward
- Kota Toy Corporation manufactures lizard dolls in two departments, Molding and Assembly. In the Molding Department, plastic is injected into a lizard-shaped mold. The dolls that come out of the molds are then transferred to the Assembly Department where hair is applied. Kota uses a weighted-average process cost system to collect costs in both departments. On January 1, the Molding Department had 4,000 dolls in process. These dolls were 100% complete with respect to direct materials and 70% complete with respect to conversion cost. During January, Molding completed 79,000 dolls. On January 31, Molding had 7,000 dolls in work in process. These dolls were 100% complete with respect to direct materials and 25% complete with respect to conversion cost. What account would Kota debit to record the transfer of dolls out of the Molding Department? Multiple Choice Manufacturing Overhead Finished Goods Work in Process - Assembly Work in Process -- Moldingarrow_forwardDiamond Inc. manufactures jewelry. The company has two departments, Assembly and Polishing. For the Polishing Department, material is added when the process is 80% complete. Work happens evenly throughout the process, so Conversion Costs are added evenly to the product. Once assembly is complete, the jewelry pieces are immediately transferred to the Polishing Department. Once the polishing is complete, the final product is transferred to Finished Goods Inventory. Data for the Polishing Department is as follows: Equiv Units Ending Equiv Units Open WIP New Costs Transferred-In 200 60 $250 $15,050 Direct Materials 140 - $500 $1,500 Conversion Costs 182 42 $1,250 $4,000 Actual units Ending Inventory 60 Units Transferred out 140 Provide calculations in good form for the costs per equivalent units and the total cost reconciliation for the department. If Diamond…arrow_forwardGolding Manufacturing, a division of Farnsworth Sporting, Inc., produces two different models of bows and eight models of knives. The bow-manufacturing process involves the production of two major subassemblies: the limbs and the handle. The limbs pass through four sequential processes before reaching final assembly: lay-up, molding, fabricating, and finishing. In the Lay-Up Department, limbs are created by laminating layers of wood. In Molding, the limbs are heat treated, under pressure, to form a strong resilient limb. In the Fabricating Department, any protruding glue or other processing residue is removed. Finally, in Finishing, the limbs are cleaned with acetone, dried, and sprayed with the final finishes. The handles pass through two processes before reaching final assembly: pattern and finishing. In the Pattern Department, blocks of wood are fed into a machine that is set to shape the handles. Different patterns are possible, depending on the machine's setting. After coming out…arrow_forward
- APCO Company manufactures various lines of bicycles. Because of the high volume of each line, the company employs a process costing system using the weighted-average method. Bicycle parts are manufactured in the molding department and then are consolidated into a single bike unit in the molding department and transferred to the assembly department, where they are assembled. After assembly, the bicycle is sent to the packing department. Annual cost and production figures for the assembly department are presented in the schedules below. Defective bicycles are identified at the inspection point when the assembly labor process is 70% complete; all assembly materials have been added at this point. The normal rejection rate for defective bicycles is 5% of the bicycles reaching the inspection point. Any defective bicycles above the 5% quota are considered to be abnormal. All defective bikes are removed from the production process and destroyed. Prior period costs Current period costs Total…arrow_forwardRich company produces a variety of stationery products. One product, sealing wax sticks,passes through two processes: blending and molding. The weighted average method is used toaccount for the cost of production. Two ingredients, paraffin and pigment are added at thebeginning of the process and heated and mixed for several hours. After blending, the resultingproduct is sent to the Molding department, where it is poured into molds and cooled. Thefollowing information relates to the blending process for November:a) Work in process, November 1, had 20,000 pounds, 20% complete with respect toconversion costs. Costs associated with partially completed units withParaffin $ 120,000Pigment $ 100,000Direct Labor $ 30,000Overhead applied $ 10,000b) Work in process, August 31, had 30,000 pounds, 70% complete with respect toconversion costs.c) Units completed and transferred out totaled 500,000 pounds. Costs added during themonth were:Paraffin $ 3,060,000Pigment $ 2,550,000Direct Labor $…arrow_forwardTomlinson Company manufactures car seats in its Houston plant. Each car seat passes through the assembly department and the testing department. This problem focuses on the testing department. Direct materials are added when the testing department process is 90% complete. Conversion costs are added evenly during the testing department's process. As work in assembly is completed, each unit is immediately transferred to testing. As each unit is completed in testing, it is immediately transferred to Finished Goods. Tomlinson Company uses the FIFO method of process costing. Data for the testing department for October 2017 are as follows: Read the requirements2. Requirement 1. What are the percentage of completion for (a) transferred-in costs and direct materials in beginning work-in-process inventory and (b) transferred-in costs and direct materials in ending work-in-process inventory? Transferred-in costs Direct materials (a) Beginning…arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College PubPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning




