
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The heating curve for ethanol from -150°C to 100°C should be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
When the system receives heat, energy is transferred into the system. In result, to the energy received by the system, the change in it occurs. For an example: By increase in temperature of the system.
A graph which represents the phase changes of the substance occurs with decrease or increase in temperature is known as heating curve.
General representation of graph is given by:
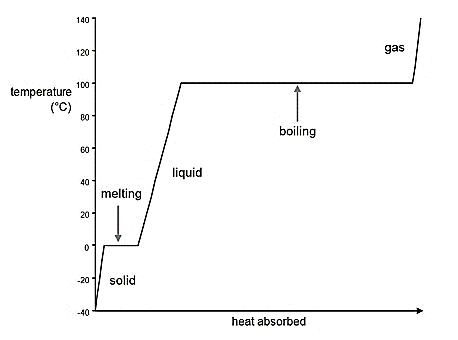
(b)
Interpretation:
The required energy in kilojoules should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
The mathematical expression for energy required is given by:
Where, q = amount of energy required
m= mass of substance
(c)
Interpretation:
The volume of ethanol in liters should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
An arithmetical multiplier which is used for converting a quantity expressed in one unit into another equivalent set of units is said to be conversion factor.
The conversion factor for gallon into liters is given by:
Since, 1 gallon = 3.785 L
Thus,
(d)
Interpretation:
The balanced chemical equation for complete combustion of ethanol should be written.
Concept Introduction:
A
(e)
Interpretation:
The mass of carbon dioxide in kilograms which is produced by the complete combustion of ethanol in 15.0-gal gas tank should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Density is defined as the ratio of mass to the volume of a substance.
The mathematical expression of density is given by:
(f)
Interpretation:
The intermolecular forces (strong) present between the liquid molecules of ethanol should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
An intermolecular (forces present between the molecule) or intramolecular (forces present within the molecule) interaction which takes place between molecules with hydrogen bond donors and molecules with hydrogen bond acceptors is known as hydrogen bonding. When the hydrogen is linked to an electronegative atom is known as hydrogen bond donors whereas when a lone pair of electrons is present on electronegative atom in a molecule is known as hydrogen bond acceptors. It is stronger than van der Waals forces but less strong than ionic and covalent bonds.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 10 Solutions
EBK BASIC CHEMISTRY
- Please answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- Consider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forwardWhat would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forward
- What is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forwardWhat would be the reagents and conditions above and below the arrow that will complete the proposed acetoacetic ester synthesis? If it cannot be done efficiently, then I will choose that answer. There could be 2 or 4 reagents involved. Please provide a detailed explanation and drawings showing how it would proceed with the correct reagents.arrow_forwardFor benzene, the ∆H° of vaporization is 30.72 kJ/mol and the ∆S° of vaporization is 86.97 J/mol・K. At 1.00 atm and 228.0 K, what is the ∆G° of vaporization for benzene, in kJ/mol?arrow_forward
- The reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reaction. it is spontaneous only at High T, it is spontaneous at low T it is nonspontaneous at all T it is spontanrous at all T. it is non spontaneous only at low T.arrow_forwardThe reaction Q(g) + R(g) → Z(l) is shown to be exothermic. Which of the following is true concerning the reactionarrow_forwardWhich of the following has the largest standard molar entropy, S° (298.15 K) He H2 NaCl KBr Hgarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





