
Concept explainers
A solution containing
Interpretation:
The precipitated mass of calcium fluoride is to be calculated. The reactant which will be in excess is to be stated. The mass of the reactant that will be in excess is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations. In a chemical equation the reactants are represented on the left of the arrow while the products are represented on the right of the arrow. Stoichiometric coefficient is the number preceding each symbol in a reaction which determines the moles of the reactants and products in the reaction. The ratio of moles is termed as mole ratio. In stoichiometry problems, the reactant that controls the amount of the product formed is known as the limiting reactant.
Answer to Problem 10PE
The precipitated mass of calcium fluoride is
Explanation of Solution
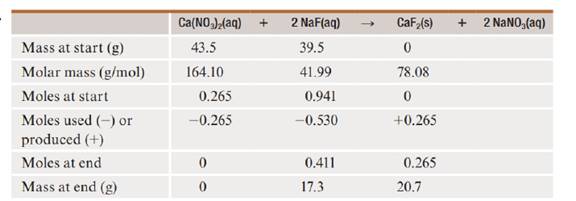
The balanced equation for the reaction is given below.
In the reaction,
Therefore mole to mole ratio is given below.
Therefore, two conversion factors from the mole-to-mole ratio are given below.
The conversion factor to obtain moles of
The molar mass of sodium is
The molar mass of fluorine is
Therefore, the molar mass of
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
Subsitute the mass and molar mass of
The molar mass of calcium is
The molar mass of oxygen is
The molar mass of nitrogen is
Therefore, the molar mass of
The formula to calculate the number of moles of
The mass of
Subsitute the mass and molar mass of
The number of moles of
The number of moles of
Therefore, the number of moles of
The moles of
The formula to calculate the mass of
Substitute molar mass and the mass of
Therefore, the mass of
In the reaction,
Therefore mole to mole ratio is given below.
Therefore, two conversion factors from the mole-to-mole ratio are given below.
The conversion factor to obtain moles of
Therefore, the number of moles of
The molar mass of calcium is
The molar mass of fluorine is
Therefore, the molar mass of
The formula to calculate the mass of
The number of moles of
Subsitute the moles and molar mass of
Therefore the mass of
After the reaction, the mass of
Therefore, the precipitated mass of calcium fluoride is
The precipitated mass of calcium fluoride is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- Basic strength of organic bases.arrow_forwardNucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? What is the name of the intermediate complex? *See imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor” *see attachedarrow_forward
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution: What is the product of the reaction? *see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardThe answer here says that F and K have a singlet and a doublet. The singlet and doublet are referring to the H's 1 carbon away from the carbon attached to the OH. Why don't the H's two carbons away, the ones on the cyclohexane ring, cause more peaks on the signal?arrow_forward
- Draw the Birch Reduction for this aromatic compound and include electron withdrawing groups and electron donating groups. *See attachedarrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardBlocking Group are use to put 2 large sterically repulsive group ortho. Show the correct sequence toconnect the reagent to product with the highest yield possible. * see imagearrow_forward
- Elimination-Addition: What molecule was determined to be an intermediate based on a “trapping experiment”? *please solve and see imagearrow_forwardShow the correct sequence to connect the reagent to product. * see imagearrow_forwardPredict the final product. If 2 products are made, list which should be “major” and “minor”. **see attachedarrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





