
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure is used for predicting the shape of molecules. From the steric number obtained in a Lewis structure, the molecular geometry can be predicted. VSEPR model can predict the shape of molecules considering their Lewis structure. Certain rules has to be followed in for the VSEPR model.
- The molecule will have a shape where there is minimal electrostatic repulsion between the valence‑shell electron pairs.
- The forces of repulsion between two lone pairs of electrons will be higher than the repulsion between lone pair and bond pair of electrons. This in turn will be higher than the bond pair‑bond pair of electrons.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
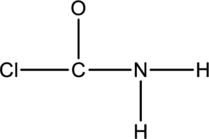
Ten electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining fourteen valence-electrons, six are placed over chlorine atom and six are placed over oxygen atom. Two electrons are placed over nitrogen atom.
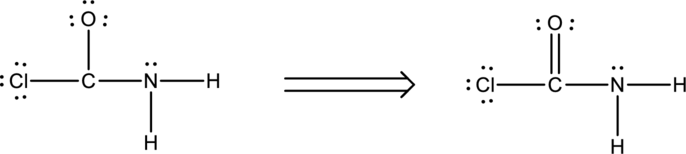
Thus the Lewis structure of
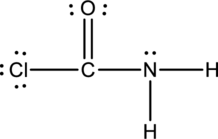
Bond Angles:
There is a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom as central atom in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is three, and only bonding pair of electrons are present, the arrangement is trigonal planar and the bond angle will be
Steric number for nitorgen atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom is one while the number of atoms that are bonded to nitrogen is three. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(b)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
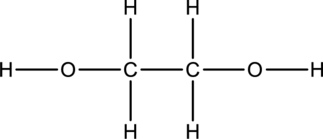
Eighteen electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining eight valence-electrons, four are placed over oxygen atom each. Thus the Lewis structure for
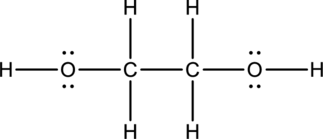
Bond Angles:
There are two carbon atoms as central atoms in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is four. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is four, the arrangement is tetrahedral and the bond angle will be
(c)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Lewis structure for
The total number of valence electrons present in
The skeletal structure can be drawn considering the formula as shown below;
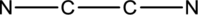
Six electrons are used up in the skeletal structure. Among the remaining twelve valence-electrons, six are placed over nitrogen atom each. Thus the Lewis structure for

Bond Angles:
There are two carbon atoms as central atoms in the Lewis structure. The steric number of the central atom can be used to predict the bond angles of the central atoms.
Steric number for carbon atom:
The number of lone pair of electrons on carbon atom is zero while the number of atoms that are bonded to carbon is two. Therefore, steric number can be calculated as shown below;
As the steric number is two, the arrangement is linear and the bond angle will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry Principles And Practice
- An open tubular column has an inner diameter of 207 micrometers, and the thickness of the stationary phase on the inner wall is 0.50 micrometers. Unretained solute passes through in 63 seconds and a particular solute emerges at 433 seconds. Find the distribution constant for this solute and find the fraction of time spent in the stationary phase.arrow_forwardConsider a chromatography column in which Vs= Vm/5. Find the retention factor if Kd= 3 and Kd= 30.arrow_forwardTo improve chromatographic separation, you must: Increase the number of theoretical plates on the column. Increase the height of theoretical plates on the column. Increase both the number and height of theoretical plates on the column. Increasing the flow rate of the mobile phase would Increase longitudinal diffusion Increase broadening due to mass transfer Increase broadening due to multiple paths You can improve the separation of components in gas chromatography by: Rasing the temperature of the injection port Rasing the temperature of the column isothermally Rasing the temperature of the column using temperature programming In GC, separation between two different solutes occurs because the solutes have different solubilities in the mobile phase the solutes volatilize at different rates in the injector the solutes spend different amounts of time in the stationary phasearrow_forward
- please draw and example of the following: Show the base pair connection(hydrogen bond) in DNA and RNAarrow_forwardNaming and drawing secondary Write the systematic (IUPAC) name for each of the following organic molecules: CH3 Z structure CH3 CH2 CH2 N-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 NH CH3-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Explanation Check ☐ name ☐ 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C Garrow_forwardC This question shows how molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to understand the chemical properties of elemental oxygen O₂ and its anionic derivative superoxide Oz. a) Draw the MO energy diagram for both O2 and O2. Clearly label your diagram with atomic orbital names and molecular orbital symmetry labels and include electrons. Draw the Lewis structure of O2. How does the MO description of O2 differ from the Lewis structure, and how does this difference relate to the high reactivity and magnetic properties of oxygen? ) Use the MO diagram in (a) to explain the difference in bond length and bond energy between superoxide ion (Oz, 135 pm, 360 kJ/mol) and oxygen (O2, 120.8 pm, 494 kJ/mol).arrow_forward
- Please drawarrow_forward-Page: 8 nsition metal ions have high-spin aqua complexes except one: [Co(HO)₁]". What is the d-configuration, oxidation state of the metal in [Co(H:O))"? Name and draw the geometry of [Co(H2O)]? b) Draw energy diagrams showing the splitting of the five d orbitals of Co for the two possible electron configurations of [Co(H2O)]: Knowing that A = 16 750 cm and Пl. = 21 000 cm, calculate the configuration energy (.e., balance or ligand-field stabilization energy and pairing energy) for both low spin and high spin configurations of [Co(H2O)]. Which configuration seems more stable at this point of the analysis? (Note that 349.76 cm = 1 kJ/mol) Exchange energy (IT) was not taken into account in part (d), but it plays a role. Assuming exchange an occur within t29 and within eg (but not between tz, and ea), how many exchanges are possible in the low in configuration vs in the high spin configuration? What can you say about the importance of exchange energy 07arrow_forwardDraw everything please on a piece of paper explaining each steparrow_forward
- Define crystalline, polycrystalline and amorphous materials What crystal system and Bravais lattices are shown in the figure immediately below? What do a, b, C, a, ẞ and y represent and what are their values? You can label the Bravais lattices directly above or under the figure. C aarrow_forward32. The diagrams below show the band structure of an intrinsic semiconductor at absolute zero and room temperature. Room Temperature EF E OK Ep- a) In the space below, sketch a similar pair of diagrams for an n-type semiconductor. D) Give the definition and an example of (i) an intrinsic semiconductor and (ii) an n-type semiconductor.arrow_forward29. a) i Which energy diagram best represents the d-electrons in tetrahedral [Co(NH3)4]²+? b) ii c) iii d) iv 11 ་ ↑↓ ↑t t ↑↓ ↑↓ e) none of these ii In1 According to Slater's rules, what is the effective nuclear charge experienced by a 3d electron in 30. Ge? a) 32.00 b) 21.15 c) 16.05 d) 14.00 e) 10.85arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
