PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781259963667
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10.28P
What
a 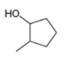 b.
b. 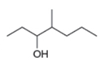 c.
c. 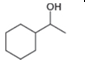
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
QUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression'
*The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been provided
Using the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage
Try Again
Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations.
A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction:
2+
2+
Sn²+ Ba(s)
(aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq)
→>>
Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn
2+
2+
in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba
in the other.
Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.
1.71 V
☐ x10
☑
5
0/5
?
00.
18
Ar
Question: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below:
(x1 -x̄)
370.5
(y1 - ȳ)
5.240
(x2 - x̄)
142.5
(y2 - ȳ)
2.004
(x3 - x̄)
28.5
(y3 - ȳ)
0.390
(x4 - x̄)
-85.5
(y4 - ȳ)
-1.231
(x5 - x̄)
-199.5
(y5 - ȳ)
-2.829
(x6 - x̄)
-256.5
(y6 - ȳ)
-3.575
Chapter 10 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.1PCh. 10 - Problem 10.2 How many degrees of unsaturation are...Ch. 10 -
Problem 10.3 How many degrees of unsaturation...Ch. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each alkene. abcdeCh. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each polyfunctional...Ch. 10 - Problem 10.6 Label each C-C double bond as E or Z....Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.7PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.8PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.9PCh. 10 - Problem 10.10 Rank the following isomers in order...
Ch. 10 - Linolenic acidTable 10.2 and stearidonic acid are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.12PCh. 10 - Problem 10.13 What product is formed when each...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.14PCh. 10 - Problem 10.15 Draw the products formed when each...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.16PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.17PCh. 10 - Addition of HBr to which of the following alkenes...Ch. 10 - Problem 10.19 Draw the products, including...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.20PCh. 10 - Problem 10.21 What two alkenes give rise to each...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.22PCh. 10 - Problem 10.23 Draw the products of each reaction,...Ch. 10 - Problem 10.24 Draw all stereoisomers formed in...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.25PCh. 10 - Problem 10.26 What alkylborane is formed from...Ch. 10 - Draw the products formed when each alkene is...Ch. 10 - What alkene can be used to prepare each alcohol as...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.29PCh. 10 - Draw the products of each reaction using the two...Ch. 10 - Problem 10.31 Devise a synthesis of each compound...Ch. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a.b.Ch. 10 - a Label the carbon-carbon double bond in A as E or...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.34PCh. 10 - 10.35 Calculate the number of degrees of...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.36PCh. 10 - Label the alkene in each drug as E or Z....Ch. 10 - Give the IUPAC name for each compound. a. c. e. b....Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.39PCh. 10 - 10.40 (a) Draw all possible stereoisomers of, and...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.41PCh. 10 - 10.42 Now that you have learned how to name...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.43PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.44PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.45PCh. 10 - Draw the products formed when (CH3)2C=CH2 is...Ch. 10 - What alkene can be used to prepare each alkyl...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.48PCh. 10 - Draw the constitutional isomer formed in each...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.50PCh. 10 - Draw all stereoisomers formed in each reaction. a....Ch. 10 - Draw the products of each reaction, including...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.53PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.54PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.55PCh. 10 - 10.56 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.57PCh. 10 - Draw a stepwise mechanism for the conversion of...Ch. 10 - Draw a stepwise mechanism that shows how all three...Ch. 10 - Less stable alkenes can be isomerized to more...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.61PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.62PCh. 10 - Bromoetherification, the addition of the elements...Ch. 10 - Devise a synthesis of each product from the given...Ch. 10 - 10.65 Draw a synthesis of each compound from...Ch. 10 - 10.66 Explain why A is a stable compound but B is...Ch. 10 - Prob. 10.67PCh. 10 - Prob. 10.68PCh. 10 - 10.69 Lactones, cyclic esters such as compound A,...Ch. 10 - 10.70 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the following...Ch. 10 - 10.71 Like other electrophiles, carbocations add...Ch. 10 - 10.72 Draw a stepwise mechanism for the...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
1. Genetics affects many aspects of our lives. Identify three ways genetics affects your life or the life of a ...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Label each statement about the polynucleotide ATGGCG as true or false. The polynucleotide has six nucleotides. ...
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Describe the role and impact of microbes on the earth.
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
6. How can you use the features found in each chapter?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Single penny tossed 20 times and counting heads and tails: Probability (prediction): _______/20 heads ________/...
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forward
- The following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0mmol/L 262.7mmol/L QUESTION: For both groups (Regular & Salt Reduced tomato sauce) of data provide answers to the following calculations below: 1. Standard Deviation (Sx) 2. T Values (t0.05,4) 3. 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 4. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 5. 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have leucine (2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid), alanine (2-aminopropanoic acid) and phenylalanine (2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid), indicate the tripeptides that can be formed (use the abbreviated symbols Leu., Ala and Phe).arrow_forwardBriefly state why trifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.arrow_forward
- Explain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it. 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added. 4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = .11 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0 262.7 QUESTION: For both groups of data provide answers to the calculations attached in the imagearrow_forward
- 7. Concentration and uncertainty in the estimate of concentration (class data) Class mean for sample (Regular) |[Cl-] (mmol/L) class mean Sn za/2 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forwardGive reason(s) for six from the followings [using equations if possible] a. Addition of sodium carbonate to sulfanilic acid in the Methyl Orange preparation. b. What happened if the diazotization reaction gets warmed up by mistake. c. Addition of sodium nitrite in acidified solution in MO preparation through the diazotization d. Using sodium dithionite dihydrate in the second step for Luminol preparation. e. In nitroaniline preparation, addition of the acid mixture (nitric acid and sulfuric acid) to the product of step I. f. What is the main reason of the acylation step in nitroaniline preparation g. Heating under reflux. h. Fusion of an organic compound with sodium. HAND WRITTEN PLEASEarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Nomenclature: Crash Course Chemistry #44; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U7wavimfNFE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY