Concept explainers
Interpretation: The structure of six
Concept introduction: Alkenes are the compounds in which
Answer to Problem 10.1P
The structure of six alkenes having molecular formula
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula of the compound is
The first possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
![]()
Figure 1
The first possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom.
The second possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
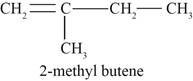
Figure 2
The second possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the second carbon atom.
The third possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
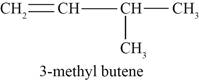
Figure 3
The third possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between first and second carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the third carbon atom.
The fourth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
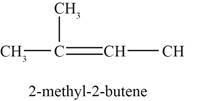
Figure 4
The fourth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. One methyl substituent is attached to the second carbon atom.
The fifth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
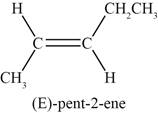
Figure 5
The fifth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. Substituents attached to the second and third carbon atom are on different side.
The sixth possible structure of alkene with molecular formula
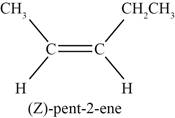
Figure 6
The sixth possible structure of alkene contains five carbon and ten hydrogen atoms. The double bond is present between second and third carbon atom. Substituents attached to the second and third carbon atom are on same side.
A pair of diastereomers exists when two substituents attached to each of the double bonded carbon atoms are different. The fifth and sixth structure indicates that the substituents bonded to the
Therefore, a pair of disatereomers is shown below.
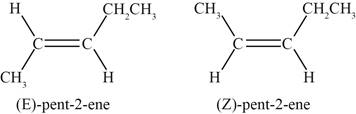
Figure 7
The structure of six alkenes having molecular formula
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- What alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. and two equivalents of CH2=O draw structure ...arrow_forwardH-Br Energy 1) Draw the step-by-step mechanism by which 3-methylbut-1-ene is converted into 2-bromo-2-methylbutane. 2) Sketch a reaction coordinate diagram that shows how the internal energy (Y- axis) of the reacting species change from reactants to intermediate(s) to product. Brarrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 H-CI CH2Cl2 CIarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. དའི་སྐད”“ H3C OH H3C CH CH3 KEq Product acid Product basearrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C NH2 NH2 KEq H3C-CH₂ 1. Product acid Product basearrow_forwardWhat alkene or alkyne yields the following products after oxidative cleavage with ozone? Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure ... andarrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. H3C-C=C-4 NH2 KEq CH H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). C5H10 Br H-Br CH2Cl2 + enant.arrow_forwardDraw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. KEq H₂C-O-H H3C OH Product acid Product basearrow_forward
- Draw the products of the stronger acid protonating the other reactant. OH KEq CH H3C H3C `CH3 Product acid Product basearrow_forward2. Draw the missing structure(s) in each of the following reactions. The missing structure(s) can be a starting material or the major reaction product(s). Ph H-I CH2Cl2arrow_forward3 attempts left Check my work Draw the products formed in the following oxidative cleavage. [1] 03 [2] H₂O draw structure ... lower mass product draw structure ... higher mass productarrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning




