
Concept explainers
Draw a Lewis structure for each ion.
a.
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are electron dot representations for molecules. These structures show the bonding between the atoms or molecules and the lone pairs of electrons. The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms in a molecule is represented by its Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 1.7P
The Lewis structure for
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular formula,
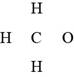
Figure 1
The total valence electrons in
The bonds and lone pairs are added to form
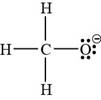
Figure 2
The Lewis structure for
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are electron dot representations for molecules. These structures show the bonding between the atoms or molecules and the lone pairs of electrons. The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms in a molecule is represented by its Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 1.7P
The Lewis structure of
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular formula,
![]()
Figure 3
The total valence electrons in
The bonds and lone pairs are added to form
![]()
Figure 4
The Lewis structure for
![]()
Figure 5
The Lewis structure of
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are electron dot representations for molecules. These structures show the bonding between the atoms or molecules and the lone pairs of electrons. The arrangement of valence electrons among the atoms in a molecule is represented by its Lewis structure.
Answer to Problem 1.7P
The Lewis structure of
Explanation of Solution
In the given molecular formula,
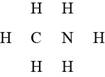
Figure 6
The total valence electrons in
The bonds and lone pairs are added to form
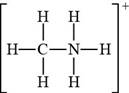
Figure 7
The Lewis structure of
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure for
Concept Introduction: Lewis structures are electron dot representations for molecules. These structures show the bonding between the atoms or molecules and the lone pairs of electrons. These structures can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecules.
Answer to Problem 1.7P
The Lewis structure of
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular formula,
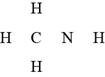
Figure 8
The total valence electrons in
The bonds and lone pairs are added to form
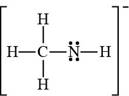
Figure 9
The Lewis structure of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology (12th Edition)
- 5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solution. How many carbons and hydrogens are in the structure?arrow_forward13. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B 2°C. +2°C. cleavage Bond A •CH3 + 26.← Cleavage 2°C. + Bond C +3°C• CH3 2C Cleavage E 2°C. 26. weakest bond Intact molecule Strongest 3°C 20. Gund Largest argest a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. C Weakest bond A Produces Most Bond Strongest Bond Strongest Gund produces least stable radicals Weakest Stable radical b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. 13°C. formed in bound C cleavage ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. • CH3 methyl radical Formed in Gund A Cleavage c.…arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning




