
Concept explainers
Zingerone gives ginger its pungent taste.
a. What is the molecular formula of zingerone?
b. How many lone pairs are present?
c. Draw a skeletal structure.
d. How many
e. What orbitals are used to form each indicated bond
(a)
Interpretation: The molecular formula of zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
Answer to Problem 1.38P
The molecular formula of zingerone is
Explanation of Solution
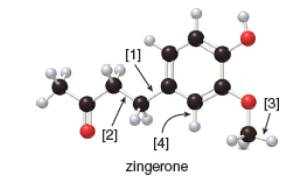
The given ball-and-stick model of zingerone is,
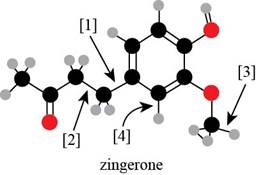
Figure 1
In ball-and-stick model, each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. In this model, each black ball represents
In the above model,
• There are three red balls. Thus, there are three
• There are eleven black balls. Thus, there are eleven
• There are fourteen grey balls. Thus, there are fourteen
Hence, the molecular formula of zingerone is
The molecular formula of zingerone is
(b)
Interpretation: The number of lone pairs in zingerone is to be stated.
Concept introduction: In a compound or molecule, the lone pairs represent number of unshared electrons on atom. An atom may or may not have unshared electrons. For example, carbon and hydrogen atoms have no lone pair but each oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are total
Explanation of Solution
The molecular formula of citric acid is
There are total
(c)
Interpretation: A skeletal structure of zingerone is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
Answer to Problem 1.38P
A skeletal structure of zingerone is,
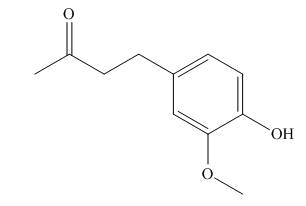
Explanation of Solution
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond. A ball-and-stick model is converted into skeletal structure by replacing black ball with
A skeletal structure of zingerone is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2
In ball-and-stick model each colored ball represents a specific atom and each stick represents a bond.
(d)
Interpretation: The number of
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
There are seven
Explanation of Solution
The Lewis structure of zingerone is,
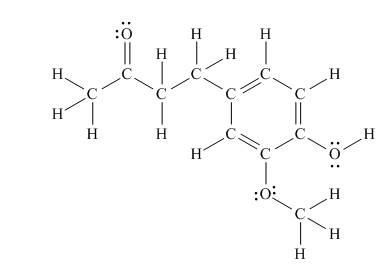
Figure 3
According to the rules of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
The
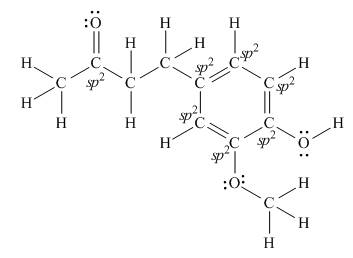
Figure 4
Thus, there are seven
There are seven
(e)
Interpretation: The orbitals that are used to form each indicated bond is to be stated.
Concept introduction: According to the rule of hybridization, an atom that is surrounded with two groups is
Answer to Problem 1.38P
Bond
Explanation of Solution
Bond [1] represents bonding between the carbon atom of benzene
Thus,
Bond
Bond
Thus,
Bond
Thus, bond
The number of surrounded group around any atom predicts the hybridization of that atom, which is further helpful in predicting the orbitals involved in the bond formation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
HUMAN ANATOMY
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward5. A solution of sucrose is fermented in a vessel until the evolution of CO2 ceases. Then, the product solution is analyzed and found to contain, 45% ethanol; 5% acetic acid; and 15% glycerin by weight. If the original charge is 500 kg, evaluate; e. The ratio of sucrose to water in the original charge (wt/wt). f. Moles of CO2 evolved. g. Maximum possible amount of ethanol that could be formed. h. Conversion efficiency. i. Per cent excess of excess reactant. Reactions: Inversion reaction: C12H22O11 + H2O →2C6H12O6 Fermentation reaction: C6H12O6 →→2C2H5OH + 2CO2 Formation of acetic acid and glycerin: C6H12O6 + C2H5OH + H₂O→ CH3COOH + 2C3H8O3arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solution. How many carbons and hydrogens are in the structure?arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning




