
Cost Classification
Wollogong Group Ltd. of New South Wales, Australia acquired its factory building 10 years ago. For several years, the company has rented out a small annex attached to the rear of the building for $30,000 per year. The renters lease will expire soon, and rather than renewing the lease, the company has decided to use the annex to manufacture a new product.
Direct materials cost for the new product will total $80 per unit. To have a place to store its finished goods, the company will rent a small warehouse for $500 per month. In addition, the company must rent equipment for $4,000 per month to produce the newproduct. Direct laborers will be hired and paid $60 per unit to manufacture the new product. As in prior years, the space in the annex will continue to be
The annual advertising cost for the new product will be $50,000. A supervisor will be hired and paid $3,500 per month to oversee production. Electricity for operating machines will be $120 per unit the cost of shipping the new product to customers will be $9 per unit.
To provide funds to purchase materials, meet payrolls, and so forth. the company will have to liquidate some temporary investments. These investments are presently yielding a return of $3,000 per year.
Required:
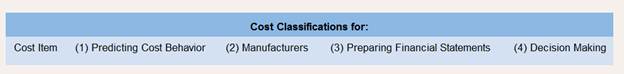
Using the table shown below, describe each of the costs associated with the new product decision in four ways. In terms of cost classifications for predicting cost behavior(column 1), indicate whether the cost is fixed or variable. With respect to cost classifications for manufacturers (column 2), if the item is a
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- General accountingarrow_forwardThe Bubba Company uses the gross profit method to estimate inventory and cost of goods sold for interim reporting purposes. The average gross profit rate is 25% of sales. The following data relate to the month of May: Inventory cost, May 1 $ 30,000 Purchases during the month at cost $ 80,400 Sales $ 1,00,800 $3,600 Sales returns Using the data above, what is the estimated ending inventory on May 31? A. $24,300 B. $25,200 C. $34,800 D. $37,500arrow_forwardWhat is the change in gross profit from 2014 to 2015 ?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub





