The graph on the right represents initial output in the short run. Suppose real interest rates fall. Using the line drawing tool, draw a new line depicting the new aggregate demand. Label this line 'D₂'. Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. C Aggregate demand, D. Output (real income), Y D=Y D₁
The graph on the right represents initial output in the short run. Suppose real interest rates fall. Using the line drawing tool, draw a new line depicting the new aggregate demand. Label this line 'D₂'. Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. C Aggregate demand, D. Output (real income), Y D=Y D₁
Chapter1: Making Economics Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1QTC
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The graph on the right represents initial output in the short run.
Suppose real interest rates fall. Using the line drawing tool, draw a new line
depicting the new aggregate demand. Label this line 'D₂'.
Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object.
C
Aggregate demand, D
Output (real income), Y
D=Y
D₁
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
if real interest rates fall, output in the short run will (Rise or Fall)
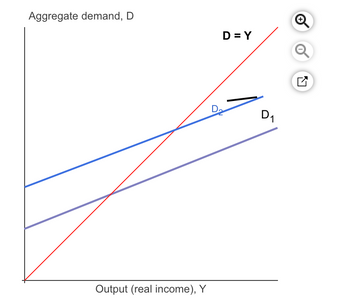
Transcribed Image Text:**Graph Explanation for Educational Website**
This graph illustrates the relationship between aggregate demand (D) and output (real income, Y). The graph has two main lines and a diagonal reference line:
1. **Axes:**
- The vertical axis represents aggregate demand, denoted as D.
- The horizontal axis represents output (real income), denoted as Y.
2. **Lines:**
- The red line labeled **D = Y** represents the condition where aggregate demand equals output. This line serves as a reference for equilibrium in the economy where demand matches supply.
- The blue line labeled **D₁** represents an initial level of aggregate demand.
- The second blue line, shifted upwards and labeled **D₂**, indicates an increase in aggregate demand. The black arrow between D₁ and D₂ shows the direction of this shift.
The upward shift from D₁ to D₂ suggests that at each level of real income, the aggregate demand has increased, which could be due to various economic factors such as increased consumer confidence, government spending, or investment.
This graphical representation helps in understanding how changes in aggregate demand can affect economic equilibrium.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134078779
Author:
Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:
PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:
9780134870069
Author:
William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-…
Economics
ISBN:
9781259290619
Author:
Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education