1. The formation of nitroanaline (an important intermediate in dyes) is formed from the reaction of orthonitrochlorobenzene (ONCB) and aqueous ammonia with ammonium chloride as a by-product. NO, CI + 2NH, NO, NH, + NH,CL ONCB Nitroanaline Let the reaction be represented symbolically as A + 2B →C + D The reaction occurs in the liquid phase and is first order in both ONCB and ammonia with k = 0.0017 m² /kmol .min at 461K with E = 11273 cal/mol. The initial entering concentrations of A (ONCB) and B (ammonia) are 1.8 kmol/m and 6.6 kmol/m³, respectively. a. Set up a stoichiometric table for this reaction for a flow system b. Write the rate law for the disappearance of ONCB, -TA solely as a function of conversion X c. What is the rate of reaction, -ra when X = 0.9 at i. 461 K ii. 561 K d. What would be the CSTR reactor volume to achieve 90% conversion at 561 K for a molar feed rate of 2 mol/min. Calculate the space time for this reactor. (Use R=1.987 cal/mol. K, where R is the universal gas constant)

Note: Since we only answer up to 3 sub-parts, we’ll answer the first 3. Please resubmit the question and specify the other subparts (up to 3) you’d like to be answered.
The symbolic representation for the formation of nitroaniline (C) and ammonium chloride (D) from ortho-nitro chlorobenzene (ONCB = A) and ammonia (B) is given as:

This reaction takes place in the liquid phase and it is given that the reaction is first order in both A and B.
Stoichiometric coefficients of all the species as:
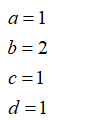
At 461 K, the reaction rate constant is given as:
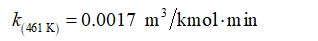
The activation energy of the reaction is given as:
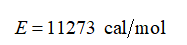
The initial concentration of species entering the reactor is given as:
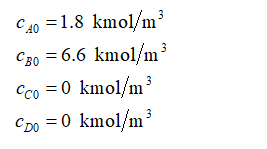
(a)
Since the given reaction occurs in the liquid phase, its density is assumed to be constant and so, v = v0. Express the concentration in terms of the molar rate as:
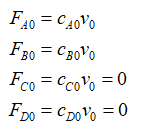
Define the parameter associated with the initial moles of each of the species as:
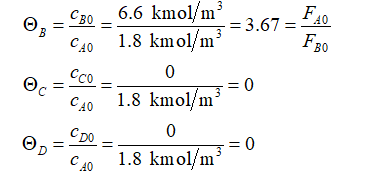
Let X be the conversion of A. The stoichiometric table prepared is shown below as:
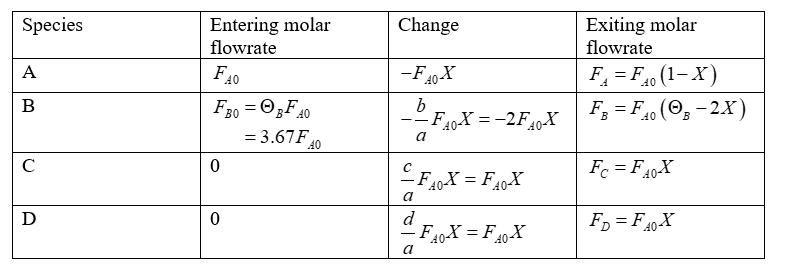
(b)
The rate law for the disappearance of ONCB (A) as a function of conversion X when the reaction is first order in ONCB (A) and ammonia (B) is written as:
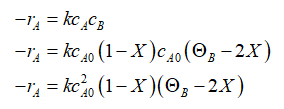
Step by step
Solved in 9 steps with 16 images









