The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Although seasons come and go, on average the earth’s climate is very steady. To maintain this stability, the earth must radiate thermal energy—electromagnetic waves—back into space at exactly the same average rate that it receives energy from the sun. Because the earth is much cooler than the sun, its thermal radiation is long-wavelength infrared radiation that we cannot see. A straightforward calculation using Stefan's law finds that the average temperature of the earth should be –18°C, or 0°F, for the incoming and outgoing radiation to lie in balance.
This result is clearly not correct; at this temperature, the entire earth would be covered in snow and ice. The measured global average temperature is actually a balmier 15°C, or 59°F. The straightforward calculation fails because it neglects to consider the earth’s atmosphere. At visible wavelengths, as the figure shows, the atmosphere has a wide “window” of transparency, but this is not true at the infrared wavelengths of the earth’s thermal radiation. The atmosphere lets in the visible radiation from the sun, but the outgoing thermal radiation from the earth sees a much smaller “window.” Most of this radiation is absorbed in the atmosphere.
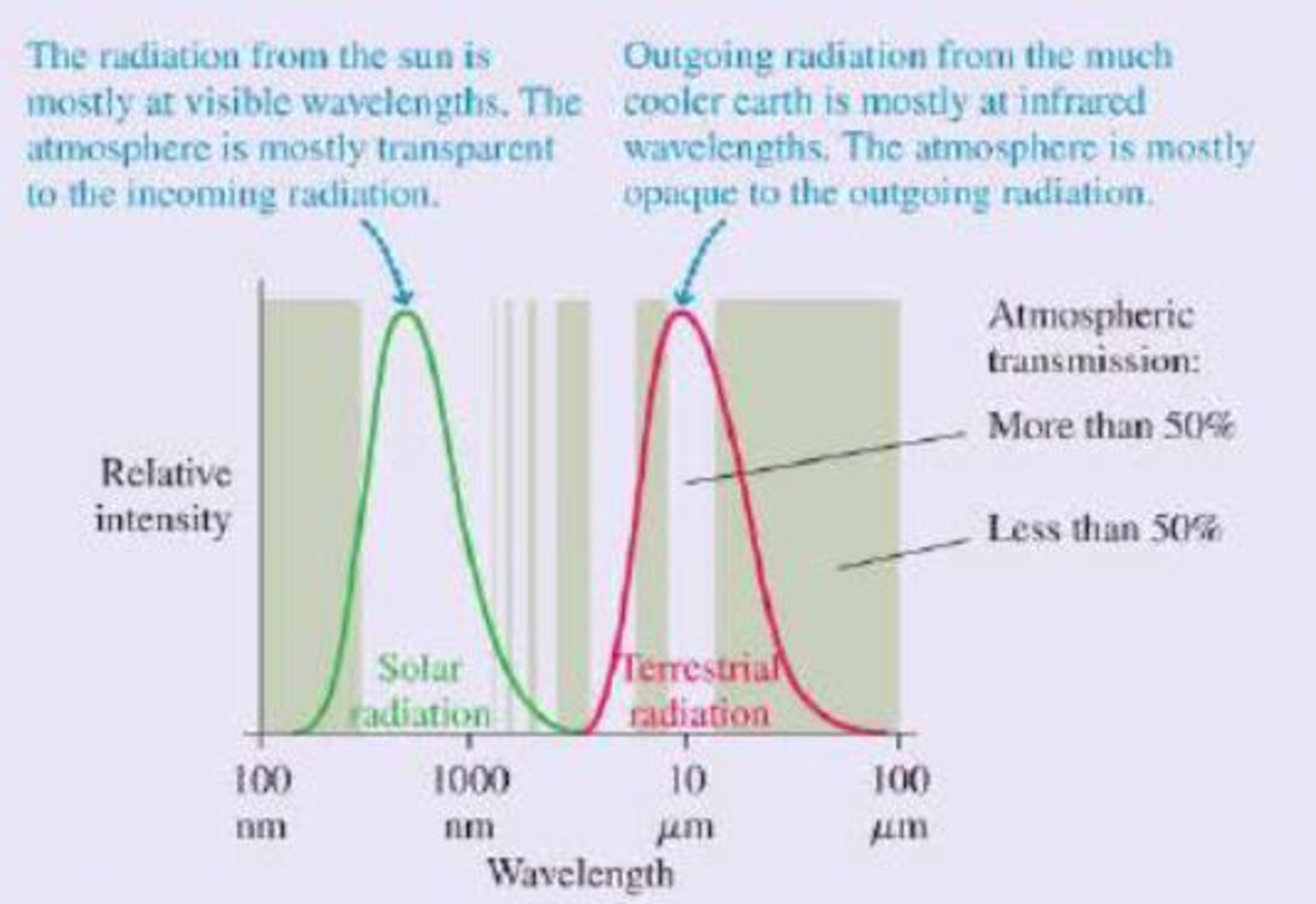
Thermal radiation curves for the sun and the earth. The shaded bands show regions for which the atmosphere is transparent (no shading) or opaque (shaded) to electromagnetic radiation.
Because it’s easier for visible radiant energy to get in than for infrared to get out, the earth is warmer than it would be without the atmosphere. The additional warming of the earth’s surface because of the atmosphere is called the greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect is a natural part of the earth’s physics; it has nothing to do with human activities, although it’s doubtful any advanced life forms would have evolved without it.
The atmospheric gases most responsible for the greenhouse effect are carbon dioxide and water vapor, both strong absorbers of infrared radiation. These greenhouse gases are of concern today because humans, through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, coal, and natural gas), are rapidly increasing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Preserved air samples show that carbon dioxide made up 0.027% of the atmosphere before the industrial revolution. In the last 150 years, human activities have increased the amount of carbon dioxide by nearly 50%, to about 0.040%. By 2050, the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase to 0.054%, double the pre-industrial value, unless the use of fossil fuels is substantially reduced.
Carbon dioxide is a powerful absorber of infrared radiation. And good absorbers are also good emitters. The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere radiates energy back to the surface of the earth, warming it. Increasing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere means more radiation: this increases the average surface temperature of the earth. The net result is global warming.
There is strong evidence that (he earth has warmed nearly 1°C in the last 100 years because of increased greenhouse gases. What happens next? Climate scientists, using sophisticated models of the earth’s atmosphere and oceans, calculate that a doubling of the carbon dioxide concentration will likely increase the earth’s average temperature by an additional 2°C (≈ 3°F) to 6°C (≈9°F) There is some uncertainty in these calculations; the earth is a large and complex system. Perhaps the earth will get cloudier as the temperature increases, moderating the increase. Or perhaps the arctic ice cap will melt, making the earth less reflective and leading to an even more dramatic
But the basic physics that leads to the greenhouse effect, and to global warming, is quite straightforward. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere keeps the earth warm; more carbon dioxide will make it warmer. How much warmer? That’s an important question, one that many scientists around the world are attempting to answer with ongoing research. But large or small, change is coming. Global warming is one of the most serious challenges facing scientists, engineers, and all citizens in the 21st century.
The following questions are related to the passage “The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming” on the previous page.
The intensity of sunlight at the top of the earth’s atmosphere is approximately 1400 W/m2. Mars is about 1.5 times as far from the sun as the earth. What is the approximate intensity of sunlight at the top of Mar’s atmosphere?
- A. 930 W/m2
- B. 620 W/m2
- C. 410 W/m2
- D. 280 W/m2
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
- pls helparrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardPART III - RESISTORS IN PARALLEL Consider (but do not yet build) the circuit shown in the circuit diagram to the left, which we will call Circuit 3. Make sure you are using Bert bulbs. You may want to wire two batteries in series rather than use a single battery. 7. Predict: a) How will the brightness of bulb B3A compare to the brightness to bulb B3B? c) X E B3A b) How will the brightness of bulb BзA compare to the brightness of bulb B₁ from Circuit 1? How will the currents at points X, Y, and Z be related? www d) How will the current at point X in this circuit compare to the current at point X from Circuit 1? Y Z B3B wwwarrow_forward
- PART II - RESISTORS IN SERIES Consider (but do not yet build) the circuit shown in the circuit diagram to the left, which we will call Circuit 2. Make sure you are using Bert bulbs. You may want to wire two batteries in series rather than use a single battery. 4. Predict: a) How will the brightness of bulb B₂ compare to the brighness to bulb B2B? X B2A E Y B2B Ꮓ b) How will the brightness of bulb B2A compare to the brightness of bulb B₁ from Circuit 1? c) How will the currents at points X, Y, and Z be related? d) How will the current at point X in this circuit compare to the current at point X from Circuit 1?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvote Already got wrong chatgpt answerarrow_forwardWhat is the practical benefit (in terms of time savings and efficiency) of defining the potential energy? Be clear about what is required in terms of calculation if we do not use the concept of potential energy.arrow_forward
- What is the critical angle fir the light travelling from the crown glass(n=1.52) into the air(n=1.00)?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardYou are working with a team that is designing a new roller coaster-type amusement park ride for a major theme park. You are present for the testing of the ride, in which an empty 150 kg car is sent along the entire ride. Near the end of the ride, the car is at near rest at the top of a 100 m tall track. It then enters a final section, rolling down an undulating hill to ground level. The total length of track for this final section from the top to the ground is 250 m. For the first 230 m, a constant friction force of 370 N acts from computer-controlled brakes. For the last 20 m, which is horizontal at ground level, the computer increases the friction force to a value required for the speed to be reduced to zero just as the car arrives at the point on the track at which the passengers exit. (a) Determine the required constant friction force (in N) for the last 20 m for the empty test car. Write AK + AU + AE int = W+Q + TMW + TMT + TET + TER for the car-track-Earth system and solve for…arrow_forward
- = 12 kg, and m3 Three objects with masses m₁ = 3.8 kg, m₂ find the speed of m3 after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s 19 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m2. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to m m2 m3 iarrow_forwardThree objects with masses m₁ = 3.8 kg, m₂ = 12 kg, and m 19 kg, respectively, are attached by strings over frictionless pulleys as indicated in the figure below. The horizontal surface exerts a force of friction of 30 N on m2. If the system is released from rest, use energy concepts to find the speed of m¸ after it moves down 4.0 m. m/s m m2 mgarrow_forwardIn order for Jane to return to base camp, she needs to swing across a river of width D that is filled with alligators. She must swing into a wind exerting constant horizontal force F, F = 110 N, L = 40.0 m, 0 = 50.0°, and her mass to be 50.0 kg. Wind →F Tarzan! Jane (a) with what minimum speed (in m/s) must Jane begin her swing to just make it to the other side? (If Jane can make it across with zero initial velocity, enter 0.) m/s on a vine having length L and initially making an angle with the vertical (see below figure). Take D = 48.0 m, (b) Shortly after Jane's arrival, Tarzan and Jane decide to swing back across the river (simultaneously). With what minimum speed (in m/s) must they begin their swing? Assume that Tarzan has a mass of 80.0 kg. m/sarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax





