Concept explainers
Scanning Confocal Microscopy
Although modern microscopes are marvels of optical engineering, their basic design is not too different from the 1665 compound microscope of Robert Hooke. Recently, advances in optics, lasers, and computer technology have made practical a new kind of optical microscope, the scanning confocal microscope. This microscope is capable of taking images of breathtaking clarity.
The figure shows the microscope’s basic principle of operation. The left part of the figure shows how the translucent specimen is illuminated by light from a laser. The laser beam is converted to a diverging bundle of rays by suitable optics, reflected off a mirror, then directed through a microscope objective lens to a focus within the sample. The microscope objective focuses the laser beam to a very small (≈ 0.5 μm) spot. Note that light from the laser passes through other regions of the specimen but, because the rays are not focused in those regions, they are not as intensely illuminated as is the point at the focus. This is the first important aspect of the design: Very intensely illuminate one very small volume of the sample while leaving other regions only weakly illuminated.
As shown in the right half of the figure, light is reflected from all illuminated points in the sample and passes back through the objective lens. The mirror that had reflected the laser light downward is actually a partially transparent
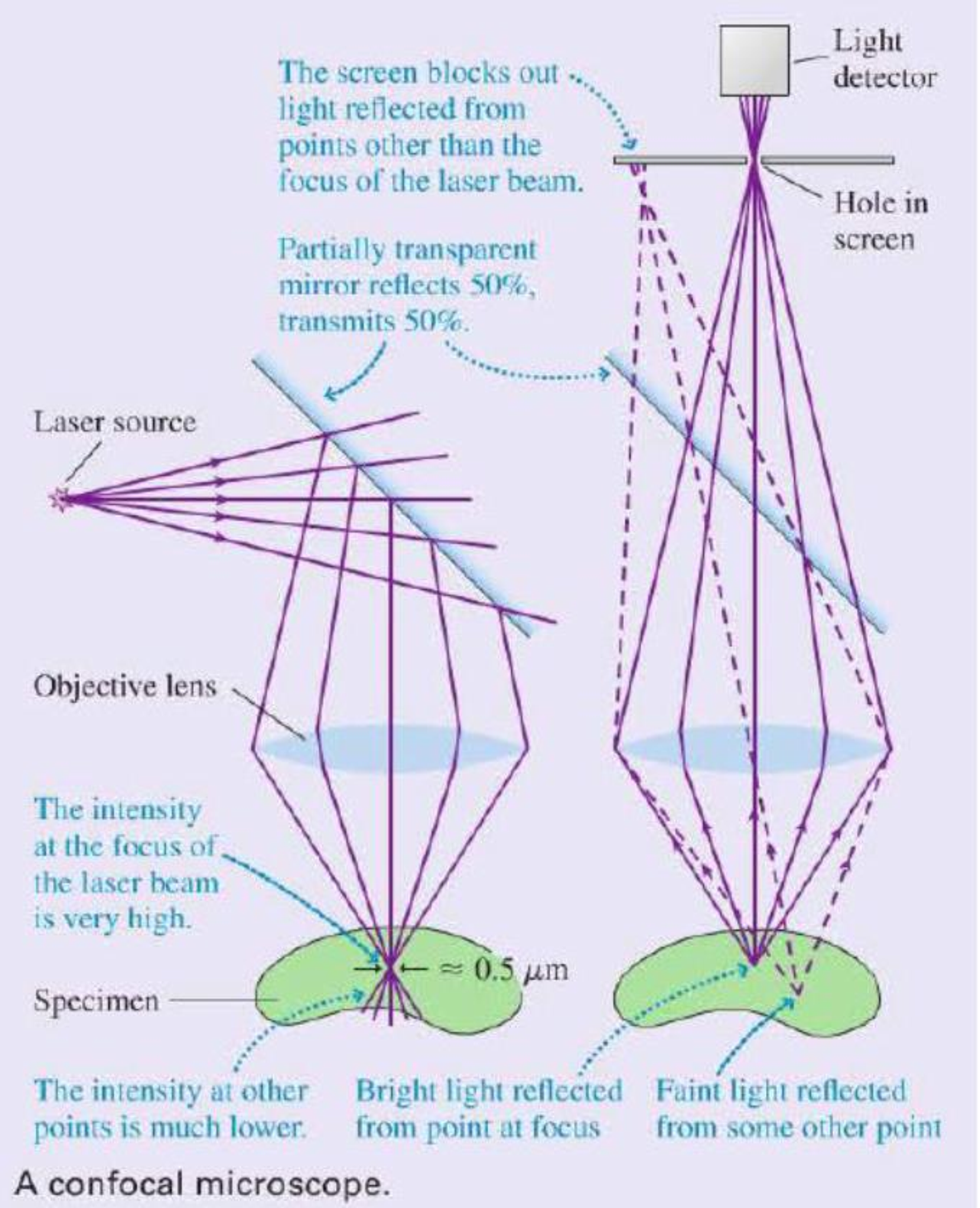
mirror that reflects 50% of the light and transmits 50%. Thus half of the light reflected upward from the sample passes through the mirror and is focused on a screen containing a small hole. Because of the hole, only light rays that emanate from the brightly illuminated volume in the sample can completely pass through the hole and reach the light detector behind it. Rays from other points in the sample either miss the hole completely or are out of locus when they reach the screen, so that only a small fraction of them pass through the hole. This second key design aspect limits the detected light to only those rays that are emitted from the point in the sample at which the laser light was originally focused.
So we see that (a) the point in the sample that is at the focus of the objective is much more intensely illuminated than any other point, so it reflects more rays than any other point, and (b) the hole serves to further limit the detected rays to only those that emanate from the focus. Taken together, these design aspects ensure the detected light comes from a very small, very well-defined volume in the sample.
The microscope as shown would only be useful for examining one small point in the sample. To make an actual image, the objective is scanned across the sample while the intensity is recorded by a computer. This procedure builds up an image of the sample one scan line at a time. The final result is a picture of the sample in the very narrow plane in which the laser beam is focused. Different planes within the sample can be imaged by moving the objective up or down before scanning. It is actually possible to make three dimensional images of a specimen in this way.
The improvement in contrast and resolution over conventional microscopy can be striking. The images show a section of a mouse kidney taken using conventional and confocal microscopy. Because light reflected from all parts of the specimen reaches the camera in a conventional microscope, that image appears blurred and has low contrast. The confocal microscope image represents a single plane or slice of the sample, and many details become apparent that are invisible in the conventional image.
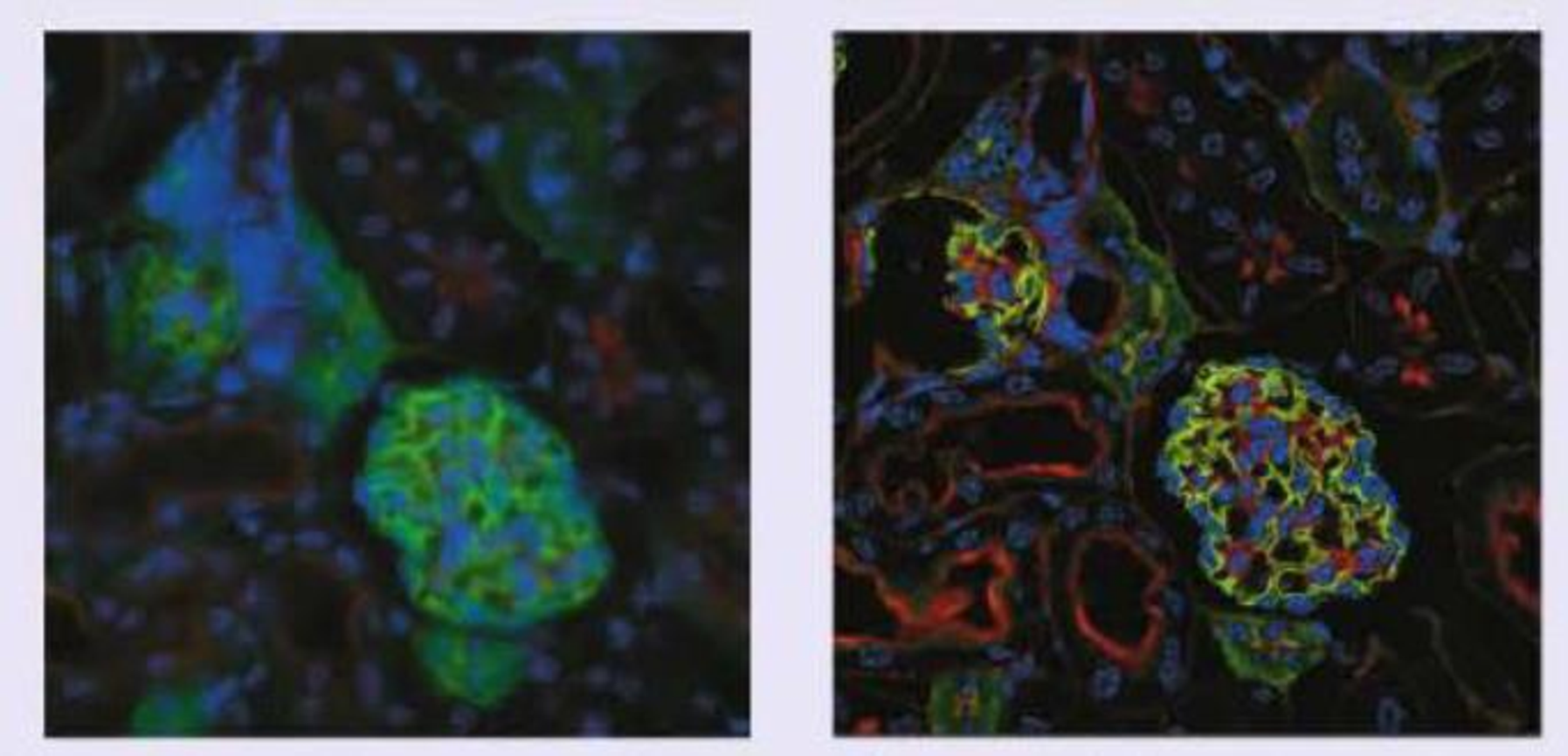
A section of fluorescently stained mouse kidney imaged using standard optical microscopy (left) and scanning confocal microscopy (right).
The following questions are related to the passage “Scanning Con focal Microscopy” on the previous page.
1. A laser beam consists of parallel rays of light. To convert this light to the diverging rays required for a scanning confocal microscope requires
- A. A converging lens.
- B. A diverging lens.
- C. Either a converging or a diverging lens.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Microbiology: An Introduction
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?arrow_forwardSolve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





