
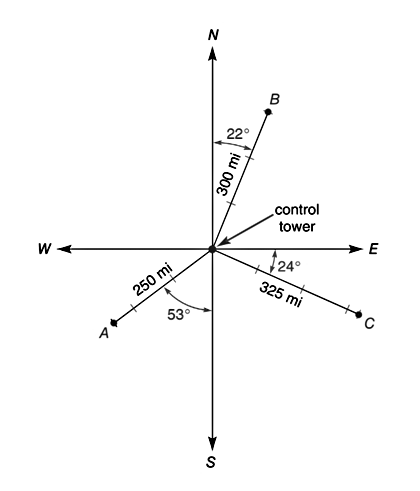
For Exercises 49 to 50, use the following information. Relative to its point departure or some other point of reference, the
Find the bearing of airplane
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
- Match each statement to the set of shapes that best describes them. 1. Similar triangles by SSS 2. Similar triangles by SAS 3. Similar triangles by AA 4. The triangles are not similar > U E 35° 89° S F 89° J 35° 94° G 52° 90° E K 52° Iarrow_forwardMatch each transformation series with the diagram that applies to it. 1. (x, y) (x-10, y + 7) scale factor: 2 2. (x, y)(x-8, y+6) scale factor: 4 3. (x, y)(x+1, y - 5) scale factor: 5 D' 104º 6 2 -10 8 -6 F2 4 5 D 2 E -4 -6 100 E 8 10 Farrow_forwardWhich sets of figures below are similar? Select all that apply. 48 yd 48 yd G 48 yd 26 mm 40 m 23 km 25 m 22 mm 37 mm 25 mi 42 yd 48 yd 48 yd 48 yd U 42 yd 25 mm M T 40 mi 20 mm 25 mm 30 mi 48 m K 37 mm 20 mm 48 m S 30 mi 73 km 29 km 29 kmarrow_forward
- GHUK PTSRQ. What is mz J? H Q I 77° 102° G 77° K J R 135° P T 123° Sarrow_forwardSolve it correctly and in Frencharrow_forwardA rug company weaves rugs that are made by repeating the design in Figure 12.49. Lengths of portions of the design are indicated in the figure. The yarn for the shaded portion of the design costs $5 per square unit, and the yarn for the unshaded portion of the design costs $3 per square unit. How much will the yarn for a 60-unit-by-84-unit rug cost? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- 11:18 91 chisholminstitute.bksblive2.com.au 1.5 ACSF L5 SC Geometry and Measure: Pythagorus' Theorum Pythagorean Problems Calculate the lengths of all of this triangle's sides. x = 64 cm² y A ↑ ४ 225 cm² + ? Image not drawn accurately. 45 45arrow_forwardWhat is WX explain your reasoningarrow_forwardthink about what you know about measurements. fill in each box. use words, numbers, and pictures. Show as many ideas as you can.arrow_forward
- If AB = 10 and AC = 13, what is AD? B A D C Write your answer as a whole number or as a decimal rounded to the nearest hundredth.arrow_forwardHeight = 1 Width=1 How much is the shaded area in the chart above?arrow_forwardLauris Online Back to Subject 不 4 ப 12 2 points T 35° 25° R M 4 N P 6Q 5 What is m/MNT? 120 T 12 What is the length of MR? 120 units 167:02:04 Time Remaining Yama is designing a company logo. The company president requested for the logo to be made of triangles. Yama is proposing the design shown. C 64°F Clear Q Search L 13 Ide dia des You scre Edi 12 L Tarrow_forward
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage LearningAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL





