
Bending Beams
If you bend a rod down, it compresses the lower side of the rod and stretches the top, resulting in a restoring force. Figure I.4 shows a
FIGURE 1.4
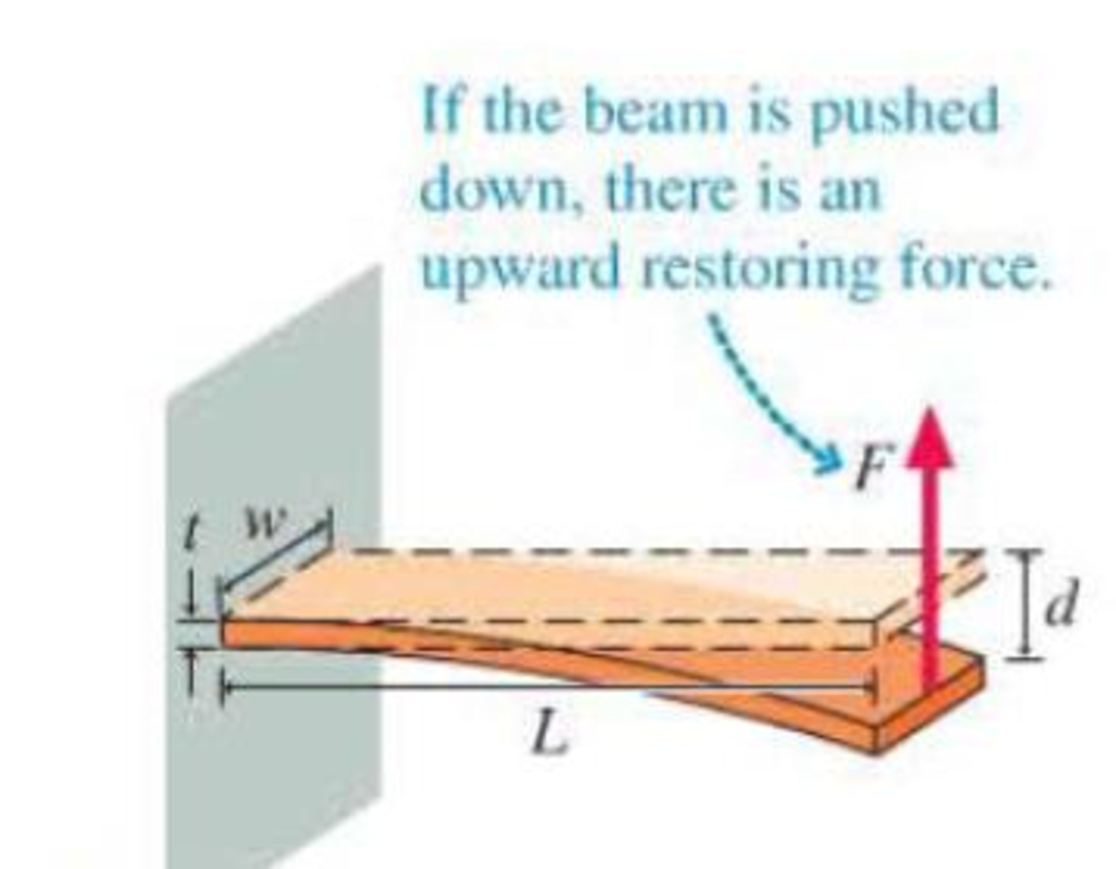
beam of length L, width w, and thickness t fixed at one end and free to move at the other. Deflecting the end of the beam causes a restoring force F at the end of the beam. The magnitude of the restoring force F depends on the dimensions of the beam, the Young’s modulus Y for the material, and the deflection d. For small values of the deflection, the restoring force is
This is similar to the formula for the restoring force of a spring, with the quantity in brackets playing the role of the spring constant k.
When a 70 kg man stands on the end of a springboard (a type of diving board), the board deflects by 4.0 cm.
A 70 kg man jumps up and lands on the end of the board, deflecting it by 12 cm. At this instant, what is the approximate magnitude of the upward force the board exerts on his feet? A. 700 A. 700 N
B. 1400 N
C. 2100N
D. 2800 N
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter P Solutions
Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- R=2.00 12V 2.00 4.00 4.002 What is the current in one of the 4.0 Q resistors? An isolated point charge q is located at point X. Two other points Y and Z are such that YZ2 XY. Y X What is (electric field at Y)/(electric field at Z)?arrow_forwardTwo objects (m₁ = 4.75 kg and m₂ 2.80 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.75-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table mg m (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s (b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.75-kg object hits the table. m/s (c) How much higher does the 2.80-kg object travel after the 4.75-kg object hits the table? marrow_forwardA cell of negligible internal resistance is connected to three identical resistors. The current in the cell is 3.0 A. The resistors are now arranged in series. What is the new current in the cell?arrow_forward
- A negatively charged sphere is falling through a magnetic field. north pole of magnet direction of motion south pole of magnet What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the sphere?arrow_forwardElectrons in a conductor are moving down the page. A proton outside the wire is moving to the right. What is the direction of the magnetic force acting on the proton?arrow_forwardWhat is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter and the resistance of an ideal ammeter? Resistance of an ideal voltmeter Resistance of an ideal ammeter infinite A. zero B. zero zero C. infinite infinite D. infinite zeroarrow_forward
- variable resistor with a resistance range of 0 to 6.0 KQ is connected in series with two resistors of fixed value 6.0 KQ. The cell in the circuit has an emf of 18 V and a negligible internal resistance. 18 V X Y 6.0 ΚΩ 6.0 ΚΩ 0 - 6.0 ΚΩ What is the maximum range of potential difference that can be observed between X and Y?arrow_forwardA positive point charge of magnitude 1.0 μC and a point charge q are separated by a distance d. electron 1.0 με An electron is placed at a distance d from the +1.0 μC charge. The electric force on the electron is zero. What is q?arrow_forwardTwo point charges of +4q and -q are placed a fixed distance apart. Where is the electric field strength equal to zero? B. +49 D. A network of three resistors is connected to a cell of emf 12V and internal resistance R of 2.0 Q as shown.arrow_forward
- Three point charges of equal magnitude are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The signs of the charges are shown. Point P is equidistant from the vertices of the triangle. What is the direction of the resultant electric field at P? B.arrow_forwardA magnetic force per unit length F acts on P due to Q. The distance between the wires is increased to 2d and the current in Q is decreased to 1/2. P Q P 12 2d What is the magnetic force per unit length that acts on P due to Q after the changes?arrow_forwardAn electric field is established between two electrodes separated by distance d, held at a potential difference of V. A charged particle in this field experiences a force F. What is the charge on the particle?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





