
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of
In naming organic compounds, the
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
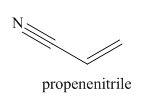
Explanation of Solution
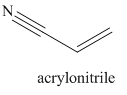
The given trivial name is acrylonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name acrylonitrile correlates the derivative of acrylic acid. Structure for acrylic acid is
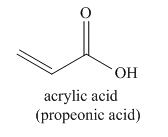
Nitriles are derived from acids where
The main chain in this molecule is of three carbon atoms thus the root name is propan, and the suffix nitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of the nitrile group. The main chain has a C=C bond; thus the IUPAC name for acrilonitrile is propenenitrile.
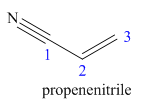
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
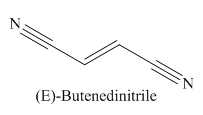
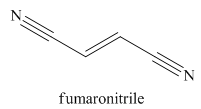
The given trivial name is fumaronitrile.
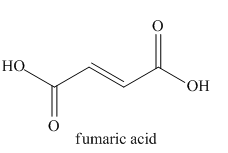
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name fumaronitrile correlates to the derivative of fumaric acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for fumaric acid is
Nitriles are derived from acids where
The main chain in this molecule is of four carbon atoms; thus the root name is butan. The structure has two cynide groups at both terminals; hence the suffix dinitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of the nitrile group.
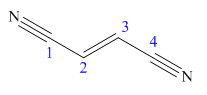
The main chain has a C=C bond; thus the IUPAC name for fumaronitrile is (E) butenedinitrile.
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
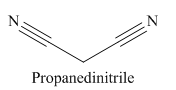
The given trivial name is malonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name malonitrile correlates to the derivative of malonic acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for malonic acid is
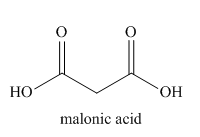
Nitriles are derived from acids where
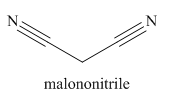
The main chain in this molecule is of three carbon atoms; thus the root name is propane. The structure has two cynide groups; hence the suffix dinitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of nitrile group.
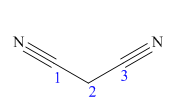
Hence the IUPAC name for malonitrile is propanedinitrile.
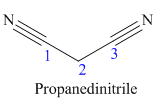
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
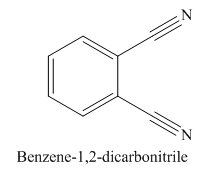
The given trivial name is phthalonitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name phthalonitrile correlates to the derivative of phthalic acid (dicarboxylic acid). Structure for phthalic acid is
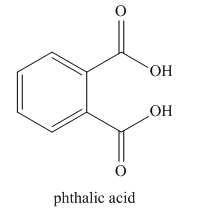
Nitriles are derived from acids where
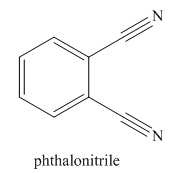
The parent ring in this molecule is benzene ring; thus the root name is benzene. The structure has two cynide groups attached directly to the ring; hence the suffix dicarbonitrile is added to the root name. The ring is numbered such that carbon atoms attached to nitrile groups get least number.
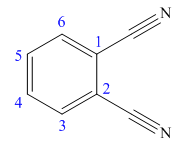
The IUPAC name for phthalonitrile is bemezene-1, 2-dicarbonitrile because two cynide groups are at C1 and C2.
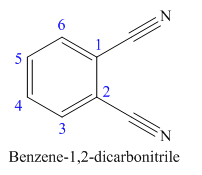
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
(e)
Interpretation:
The structure for the given trivial name is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name is to be written.
Concept introduction:
The trivial names are commonly used names which are not systematic ones. Many trivial names are accepted by IUPAC. Nitriles are derivatives of carboxylic acid. The trivial names of nitriles are deriving from the trivial names of the analogous carboxylic acids.
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than the highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the e from the normal ane, ene, or yne ending, and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Nitriles are the derivatives of carboxylic acid where
Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of the functional group and substituents on the parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. Prefixes are used to denote the number of identical substituents. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
Answer to Problem F.30P
The structure and IUPAC name for the given trivial name is
Explanation of Solution
The given trivial name is valeronitrile.
The given name indicates that the high priority functional group is cynide. The trival name valeronitrile correlates to the derivative of valeric acid. Structure for valeric acid is
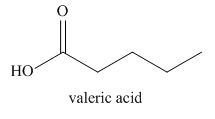
Nitriles are derived from acids where
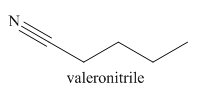
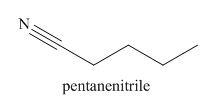
The main chain in this molecule is of five carbon atoms; thus the root name is pentane. The structure has a cynide group; hence the suffix nitrile is added to the root name. The main chain is numbered starting from the carbon atom of nitrile group.
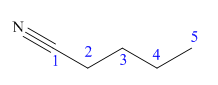
Hence the IUPAC name for valronitrile is pentanenitrile.
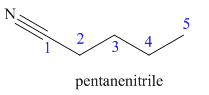
The structure for the given molecule is drawn based on the functional group, and the IUPAC named is written by adding locators to the substituents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter F Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- The following equations represent the formation of compound MX. What is the AH for the electron affinity of X (g)? X₂ (g) → 2X (g) M (s) → M (g) M (g) M (g) + e- AH = 60 kJ/mol AH = 22 kJ/mol X (g) + e-X (g) M* (g) +X (g) → MX (s) AH = 118 kJ/mol AH = ? AH = -190 kJ/mol AH = -100 kJ/mol a) -80 kJ b) -30 kJ c) -20 kJ d) 20 kJ e) 156 kJarrow_forwardA covalent bond is the result of the a) b) c) d) e) overlap of two half-filled s orbitals overlap of a half-filled s orbital and a half-filled p orbital overlap of two half-filled p orbitals along their axes parallel overlap of two half-filled parallel p orbitals all of the abovearrow_forwardCan the target compound at right be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the unsubstituted benzene at left? starting material target If so, draw a synthesis below. If no synthesis using reagents ALEKS recognizes is possible, check the box under the drawing area. Be sure you follow the standard ALEKS rules for submitting syntheses. + More... Note for advanced students: you may assume that you are using a large excess of benzene as your starting material. C T Add/Remove step X ноarrow_forward
- Which one of the following atoms should have the largest electron affinity? a) b) c) d) 으으 e) 1s² 2s² 2p6 3s¹ 1s² 2s² 2p5 1s² 2s² 2p 3s² 3p² 1s² 2s 2p 3s² 3p6 4s2 3ds 1s² 2s² 2p6arrow_forwardAll of the following are allowed energy levels except _. a) 3f b) 1s c) 3d d) 5p e) 6sarrow_forwardA student wants to make the following product in good yield from a single transformation step, starting from benzene. Add any organic reagents the student is missing on the left-hand side of the arrow, and any addition reagents that are necessary above or below the arrow. If this product can't be made in good yield with a single transformation step, check the box below the drawing area. Note for advanced students: you may assume that an excess of benzene is used as part of the reaction conditions. : ☐ + I X This product can't be made in a single transformation step.arrow_forward
- Ppplllleeeaaasssseeee helllppp wiithhh thisss Organic chemistryyyyyy I talked like this because AI is very annoyingarrow_forwardName the family to which each organic compound belongs. The first answer has been filled in for you. compound CH₂ || CH3-C-NH2 0 ။ CH3-C-CH₂ CH=O–CH=CH, CH₂ HO CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 family amine Darrow_forward1b. Br LOHarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
