
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound with appropriate stereochemical designation is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
In naming organic compounds, the
The stereochemical designation and the locators are enclosed in parenthesis at the very beginning of the name. The stereochemistry at the chiral center is determined by assigning the priorities to the groups attached to the chiral center on the basis of
Answer to Problem E.46P
The name of the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
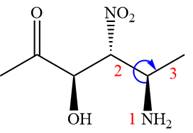
The given compound is:
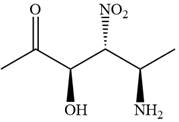
In this compound, the highest priority functional group is
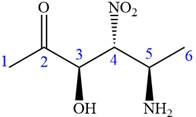
The ketonic carbon is numbered as
The fourth group, attached to chiral center
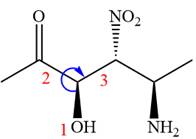
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
The fourth group attached to the chiral center
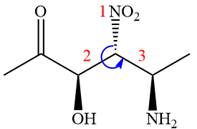
In the order of decreasing sequence rule,
The fourth group, attached to chiral center
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
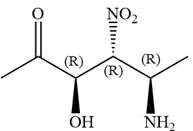
Hence the given compound is named as:
The given compound is named by identifying the main chain containing the functional group and the substituents attached with appropriate stereochemistry.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound with appropriate stereochemical designation is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the “e” from the normal ‘ane’, ‘ene’, or ‘yne’ ending and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Prefixes are used to denote number of identical substituents. Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached get the lowest number. The position of functional group and substituents on parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
The stereochemical designation and the locators are enclosed in parenthesis at the very beginning of the name. The stereochemistry at the chiral center is determined by assigning the priorities to the groups attached to chiral center on the basis of atomic number of directly bonded atom. If the sequence of priority order
Answer to Problem E.46P
The name of the given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
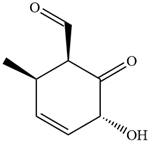
In this compound, the main ring is of six carbon atoms containing
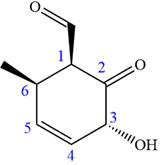
The ketonic carbon is numbered
The fourth group attached to the chiral center
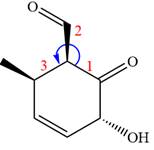
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
The fourth group attached to chiral center
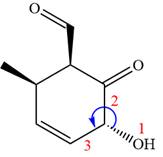
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
The fourth group attached to chiral center
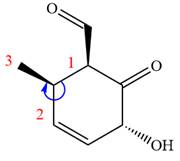
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
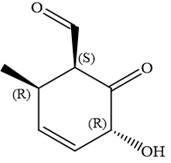
Hence, the given compound is named as:
The given compound is named by identifying the main chain containing functional group and the substituents attached with appropriate stereochemistry.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound with appropriate stereochemical designation is to be assigned.
Concept introduction:
In naming organic compounds, the functional groups other than highest priority functional groups are treated as substituents. The root name is established by identifying the longest carbon chain or a ring containing functional group. Remove the “e” from the normal ‘ane’, ‘ene’, or ‘yne’ ending and add the suffix that corresponds to the highest-priority functional group. Prefixes are used to denote number of identical substituents. Number the carbon chain in a way that the functional group and the substituents attached gets lowest number. The position of functional group and substituents on parent chain or ring is indicated by the respective locant number just before the suffix. The substituents are written in alphabetical order when writing the IUPAC name.
The stereochemical designation and the locators are enclosed in parenthesis at the very beginning of the name. The stereochemistry at the chiral center is determined by assigning the priorities to the groups attached to chiral center on the basis of atomic number of directly bonded atom. If the sequence of priority order
Answer to Problem E.46P
The name of given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
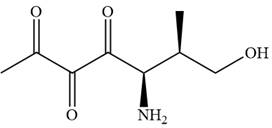
In this compound, the main chain is of seven carbon atoms which indicates the root name as ‘heptane’. The highest priority functional group is ketone. The chain has three carbonyl groups, therefore, the suffix ‘trione’ is added to the root name. The substituents are
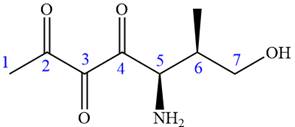
The ketonic carbons are numbered as
The fourth group attached to chiral center
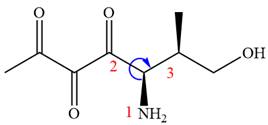
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
The fourth group attached to chiral center
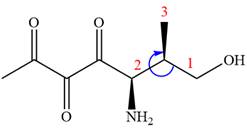
In the order of decreasing sequence rule
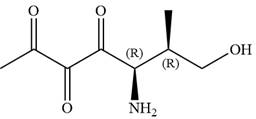
Hence, the given compound is named as:
The given compound is named by identifying the main chain containing functional group and the substituents attached with appropriate stereochemistry.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter E Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- b. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forwardFor the reaction A (g) → 3 B (g), Kp = 0.379 at 298 K. What is the value of ∆G for this reaction at 298 K when the partial pressures of A and B are 5.70 atm and 0.250 atm?arrow_forward14. Calculate the concentrations of Ag+, Ag(S2O3), and Ag(S2O3)23- in a solution prepared by mixing 150.0 mL of 1.00×10-3 M AgNO3 with 200.0 mL of 5.00 M Na2S2O3 Ag+ + S20 Ag(S203)¯ K₁ = 7.4 × 108 Ag(S203)¯ + S20¯ = Ag(S203) K₂ = 3.9 x 104arrow_forward
- ΗΝ, cyclohexanone pH 4-5 Draw Enamine I I CH3CH2Br THF, reflux H3O+ I Drawing Draw Iminium Ionarrow_forward:0: :0: Select to Add Arrows :0: (CH3)2NH :0: ■ Select to Add Arrows :0: :0: (CH3)2NH ■ Select to Add Arrowsarrow_forwardDraw the product of the following H action sequence. Ignore any inorganic byproducts formed. 1. (CH3CH2)2CuLi, THF 2. CH3Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings H Charges ㅁarrow_forward
- Please help me with this the problem is so confusingarrow_forward14 Question (1 point) Disiamylborane adds to a triple bond to give an alkenylborane. Upon oxidation with OH, H2O2, the alkenylborane will form an enol that tautomerizes to an aldehyde. In the first box below, draw the mechanism arrows for the reaction of disiamylborane with the alkyne, and in the last box draw the structure of the aldehyde. 4th attempt Feedback i > 3rd attempt OH, H2O2 i See Periodic Table See Hintarrow_forwardanswer with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward
- Hello I need some help with Smartwork. For drawing structure B, I know the correct answer is CH₃B₂, but when I try to type it in, it keeps giving me CH₄BH₃ instead. Do you know how I should write it properly? Should I use a bond or something else?arrow_forwardTrue or false, chemistryarrow_forwardanswer thse questions with mechanisms and steps. handwritten please!arrow_forward

 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning

