
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
iso is a trivial name for the alkyl group, and its structure is
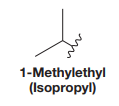
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so that to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure is to be drawn, and the correct IUPAC name for the given trivial name is to be provided.
Concept introduction:
Alcohols consist of an alkyl group attached to a hydroxyl group,
In a tertiary alcohol, the
IUPAC name for the given structure is determined by first identifying the longest continuous carbon chain or the largest ring containing the functional group. The chain is then numbered so as to assign the lowest possible locator numbers to the carbon atoms that contain the functional group. The suffix is replaced by ol while writing the name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter E Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles And Mechanisms
- Provide an IUPAC name for each of the compounds shown. (Specify (E)/(Z) stereochemistry, if relevant, for straight chain alkenes only. Pay attention to commas, dashes, etc.) H₁₂C C(CH3)3 C=C H3C CH3 CH3CH2CH CI CH3 Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 2 more group attempts remaining Previous Nextarrow_forwardArrange the following compounds / ions in increasing nucleophilicity (least to most nucleophilic) CH3NH2 CH3C=C: CH3COO 1 2 3 5 Multiple Choice 1 point 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 2, 3, 1 The other answers are not correct 0000arrow_forwardcurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. using the provided starting and product structures, draw the cured electron-pushing arrows for thw following reaction or mechanistic steps. be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond making stepsarrow_forward
- Using the graphs could you help me explain the answers. I assumed that both graphs are proportional to the inverse of time, I think. Could you please help me.arrow_forwardSynthesis of Dibenzalacetone [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the enone below. Question 1 1 pt Question 2 1 pt Question 3 1 pt H Question 4 1 pt Question 5 1 pt Question 6 1 pt Question 7 1pt Question 8 1 pt Progress: 7/8 items Que Feb 24 at You do not have to consider stereochemistry. . Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. ⚫ Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ? 4arrow_forwardShown below is the mechanism presented for the formation of biasplatin in reference 1 from the Background and Experiment document. The amounts used of each reactant are shown. Either draw or describe a better alternative to this mechanism. (Note that the first step represents two steps combined and the proton loss is not even shown; fixing these is not the desired improvement.) (Hints: The first step is correct, the second step is not; and the amount of the anhydride is in large excess to serve a purpose.)arrow_forward
- Hi I need help on the question provided in the image.arrow_forwardDraw a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction:arrow_forwardDraw the mechanism for the following reaction: CH3 CH3 Et-OH Et Edit the reaction by drawing all steps in the appropriate boxes and connecting them with reaction arrows. Add charges where needed. Electron-flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. H± EXP. L CONT. י Α [1] осн CH3 а CH3 :Ö Et H 0 N о S 0 Br Et-ÖH | P LL Farrow_forward
- 20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.025 M HCl is titrated with 0.035 M KOH. What volume of KOH is needed?arrow_forward20.00 mL of 0.150 M NaOH is titrated with 37.75 mL of HCl. What is the molarity of the HCl?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



