
Concept explainers
Selection of a Denominator:
Morton Company's budgeted variable manufacturing overhead is S4.50 per direct labor-hour and its budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is S270.000 per year.
The company manufactures a single product whose standard direct labor-hours per unit is 2 hours. The standard direct labor wage rate is $15 per hour. The standards also allow 4 feet of raw material per unit at a standard cost of $8.75 per foot.
Although normal activity is 30.000 direct labor-hours each year, the company expects to operate at a 40.000-hour level of activity this year.
Required:
1. Assume that the company chooses 30.000 direct labor-hours as the denominator level of activity. Compute the predetermined overhead rate, breaking it down into variable and fixed cost elements.
2. Assume that the company chooses 40.000 direct labor-hours as the denominator level of activity. Compute the predetermined overhead rate, breaking it down into variable and fixed cost elements.
3. Complete two standard cost cards as outlined below.

4. Assume that the company actually produces 18.000 units and works 38.000 direct labor-hours during the year. Actual

Do the following:
a. Compute the standard direct labor-hours allowed for this year's production.
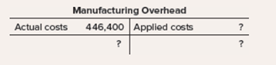
b. Complete the Manufacturing Overhead T-account below. Assume that the company uses 30.000 direct labor-hours (normal activity) as the denominator activity in computing predetermined overhead rates, as you have done in (1) above.
c. Determine the cause of the underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year by computing the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances and the fixed overhead budget and volume variances.
5. Looking at the variances you have computed, what appears to be the major disadvantage of using normal activity ratherthan expected actual activity as a denominator in computing the predetermined overhead rate? What advantages can you see to offset this disadvantage?
1
Predetermined overhead rate
It is a rate that is used by a company to allocate its manufacturing overhead cost to all the products. A predetermined overhead rate consists of a fixed portion and a variable portion.
To calculate: Predetermined overhead rate for 30,000 direct labor hours, fixed and variable portion of predetermined overhead rate.
Answer to Problem 12P
Predetermined overhead rate is calculated as $13.5 per hour. Variable portion in the rate is $4.5 per hour and fixed portion is $9 per hour.
Explanation of Solution
A predetermined overhead rate can be calculated by the sum of variable manufacturing overhead rate and fixed manufacturing overhead rate. So, it can be written as:
Here, variable overhead rate is given as $4.5for each hour and fixed manufacturing overhead rate will be calculated as:
So, the predetermined overhead rate will be:
Therefore, predetermined overhead rate is $13.5 per hour. Fixed portion of the predetermined overhead rate is $9 and variable portion is $4.5.
2
Predetermined overhead rate
It is a rate that is used by a company to allocate its total manufacturing overhead cost to all the products. A predetermined overhead rate consists of a fixed portion and a variable portion.
To calculate: Predetermined overhead rate for 40,000 direct labor hours, fixed and variable portion of predetermined overhead rate.
Answer to Problem 12P
Predetermined overhead rate is calculated as $11.25 per hour. Variable portion in the rate is $4.5 per hour and fixed portion is $6.75 per hour.
Explanation of Solution
A predetermined overhead rate is the sum of variable manufacturing overhead rate and fixed manufacturing overhead rate. So, it can be written as:
Here, variable overhead rate is given as $4.5 for each hour and fixed manufacturing overhead rate will be calculated as:
So, the predetermined overhead rate will be:
Therefore, predetermined overhead rate is $11.25 per hour. Fixed portion of the predetermined overhead rate is $6.75 and variable portion is $4.5.
3
Standard cost card
A standard cost card helps in the calculationof the total standard cost of one unit by showing necessary information about standard rate, price, quantity and hours.
To prepare: Standard cost cards for 30,000 and 40,000 direct labor hours.
Answer to Problem 12P
Total standard cost of one unit for 30,000 hours is $92 and for 40,000 hours is $87.5.
Explanation of Solution
For 30,000 labor hours, standard cost card will be prepared as follows:
| Particulars | Standard quantity or hours | Standard price or rate | Standard cost |
| Direct material | 3 feet | $8.75 per foot | $35 |
| Direct labor | 2 hours | $15 per hour | $30 |
| Variable manufacturing overhead | 2 hours | $4.5 per hour | $9 |
| Fixed manufacturing overhead | 2 hours | $9 per hour | $18 |
| Total standard cost | $92 |
Therefore, total standard cost of one unit while using 30,000 hours is $54.
For 40,000 labor hours, standard cost card will be prepared as follows:
| Particulars | Standard quantity or hours | Standard price or rate | Standard cost |
| Direct material | 3 feet | $8.75 per foot | $35 |
| Direct labor | 2 hours | $15 per hour | $30 |
| Variable manufacturing overhead | 2 hours | $4.5 per hour | $9 |
| Fixed manufacturing overhead | 2 hours | $6.75 per hour | $13.5 |
| Total standard cost | $87.5 |
Therefore, total standard cost of one unit while using 40,000 hours is $87.5.
4
Standard hours
Standard hours represent number of hours that should be used by labors in the production process. These hours are compared with actual hours used and variance is computed.
Manufacturing overheads account
This account shows actual amount of variable manufacturing overhead, actual fixed manufacturing overheads, applied variable and fixed manufacturing overheads and helps in the calculation of over or under applied overheads.
To calculate: Number of standard labor hours allowed, over applied overheads in manufacturing overheads account, variances related to variable overheads and fixed overheads.
Answer to Problem 12P
Allowed Standard direct labor hours are 36,000 and overapplied overheads in manufacturing overheads account are $39,600.
Variable overhead rate variance is $3,800 (U), variable overhead efficiency variance is 9,000 (U), fixed overhead budget variance is $1,600 (U) and fixed overhead volume variance is $54,000 (U).
Explanation of Solution
Part 4a
Allowed standard labor hours are calculated by the following formula:
Here, actual number of units produced are 18,000 and standard hours allowed for one unit are 2. So, total standard hours will be calculated as:
Part 4b
Manufacturing overhead account will be prepared as follows:
Manufacturing overhead account
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Actual Variable manufacturing overheads incurred | 174,800 | Variable overhead applied ($4.5*18,000*2) | 162,000 |
| Fixed manufacturing overheads incurred | 271,600 | Fixed overhead applied ($9*18,000*2) | 324,000 |
| Overheadsoverapplied (balance) | 39,600 | ||
| 486,000 | 486,000 |
Overapplied overheads are $39,600.
Part 4c
Formula to calculate variable overhead rate variance is,
Here, standard rate is $4.5 (given), actual hours are 38,000 and actual rate is $4.6 (174,800/38,000). So, the variance will be:
Formula to calculate variable overhead efficiency variance is,
Here, standard rate is $4.5, actual hours are 38,000 and standard hours are 36,000 (2 hours * 18,000 units). So, the variance will be,
Formula to calculate fixed overhead budget variance is,
Here, budgeted overheads are $270,000 and actual fixed overheads are $271,600. So, the variance will be:
Formula to calculate fixed overhead volume variance is,
Here, budgeted fixed overheads are $270,000 and fixed overheads applied to WIP are $324,000 (18,000 units *2 hours* $9). So, the variance will be:
Variable overhead rate variance is $3,800 unfavorable, variable overhead efficiency variance is $9,000 unfavorable, fixed overhead budget variance is $1,600 unfavorable and fixed overhead efficiency variance is $54,000 unfavorable.
5
Predetermined overhead rate
It is a rate that a company calculates using the estimated cost and estimated hours. It helps in the process of allocation of cost.
To explain: Disadvantages of using normal activity as denominator activity in the calculation of predetermined overhead rate rather than estimated activities and one advantage that can cover those advantages.
Explanation of Solution
Predetermined overhead rate is computed using the estimated or expected data and not the actual data. This rate is known as predetermined rate because it uses budgeted activities rather than the normal or actual activities.
In this question, company has used 30,000 hours and 40,000 hours as the denominator activities rather than the estimated data and all the variances related to variable overheads and fixed overheads (computed in sub parts 4) are unfavorable.
So, disadvantages of using normal activities rather than estimated activities may include, 1. Accurate standard rate, price or rates for the calculation of several variances cannot be calculated, 2. Using normal activities in mist cases make all the variances related to manufacturing overhead negative or unfavorable, 3 As wrong standard rates or hours are used in the calculation of variances, correct amount of variances may not be calculated.
Only estimated data should be used for the calculation of predetermined overhead rate. An advantage that can cover the above disadvantages is that it saves the company from the calculation of standard rate or standard hours.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- need help this questionsarrow_forwardquestion 1. Toodles Inc. had sales of $1,840,000. Cost of goods sold, administrative and selling expenses, and depreciation expenses were $1,180,000, $185,000 and $365,000 respectively. In addition, the company had an interest expense of $280,000 and a tax rate of 35 percent. (Ignore any tax loss carry-back or carry-forward provisions.)Arrange the financial information for Toodles Inc. in an income statement and compute its OCF?Question 2 Anti-Pandemic Pharma Co. Ltd. reports the following information in its income statement: Sales = $5,250,000;Costs = $2, 173,000;Other expenses = $187,400; Depreciation expense = $79,000; Interest expense= $53,555; Taxes = $76,000; Dividends = $69,000. $136,700 worth of new shares were also issued during the year and long-term debt worth $65,300 was redeemed.a) Compute the cash flow from assetsb) Compute the net change in working capitalQuestion 3Footfall Manufacturing Ltd. reports the following financial information at the end of the current year:…arrow_forwardhi expert please help mearrow_forward
- compared to the individual risks of constituting assets. Question 5 (6 marks) The common shares of Almond Beach Inc, have a beta of 0.75, offer a return of 9%, and have an historical standard deviation of return of 17%. Alternatively, the common shares of Palm Beach Inc. have a beta of 1.25, offer a return of 10%, and have an historical standard deviation of return of 13%. Both firms have a marginal tax rate of 37%. The risk-free rate of return is 3% and the expected rate of return on the market portfolio is 9½%. 1. Which company would a well-diversified investor prefer to invest in? Explain why and show all calculations. 2. Which company Would an investor who can invest in the shares of only one firm prefer to invest in? Explain why. RELEASED BY THE CI, MGMT2023, MARCH 2, 2025 5 Use the following template to organize and present your results: Theoretical CAPM Actual offered prediction for expected return (%) return (%) Standard deviation of return (%) Beta Almond Beach Inc. Palm Beach…arrow_forwardprovide correct answerarrow_forwardPlease solve. The screen print is kind of split. Please look carefully.arrow_forward
- Coronado Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The home model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds of multi- purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI. Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,000+10,200)]. Estimated annual manufacturing overhead is $1,566,090. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.26 or ($1,566,090 ÷ 96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related…arrow_forwardCoronado Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The home model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds of multi- purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI. Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,000+ 10,200)]. Estimated annual manufacturing overhead is $1,566,090. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.26 or ($1,566,090 ÷ 96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related…arrow_forwardThe completed Payroll Register for the February and March biweekly pay periods is provided, assuming benefits went into effect as anticipated. Required: Using the payroll registers, complete the General Journal entries as follows: February 10 Journalize the employee pay. February 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 14 Issue the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 24 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employee will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 28 Issue the employee pay. February 28 Issue payment for the payroll liabilities. March 10 Journalize the employee pay. March 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the March 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base.…arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning  Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





