
Concept explainers
Comprehensive
Miller Toy Company manufactures a plastic swimming pool at its Westwood Plant. The plant problems as shown by its June contribution format income statement below:

Janet Dunn. vio has just been appointed general mnagcr of the Westwood Plant. has been given instnctions to “get things under control. Upon reviewing the plants income statement. Ms. Dunn has concluded that the major problem lies in the variable cost of goods sold. She has been provided with the following
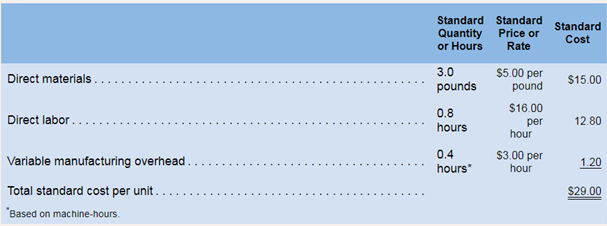
During June the plant produced 15,000 pools and incurred the following costs:
a. Purchased 60,000 pounds of materials at a cost of 54.95 per pound.
b. Used 49,200 pounds of materials in production. (Finished goods and work in process inventories are insignificant and can be ignored.)
c. Worked 11.800 direct labor-hours at a cost of 517.00 per hour.
d. Incurred variable
It is the company’s policy to close all variances to cost of goods solid on a monthly basis.
Required:
1. Compute the following variances for June:
a Materials price and quantity variances.
b. Labor rate and efficiency variances.
c. Variable overhead rate and efficiency variances.
2. Summarize the variances that you computed in (1) above by showing the net overall favorable or unfavorable variance for the month. What impact did this figure have on the company’s income statement? Show computations.
3. Pick out the two most significant variances that you computed in (1) above, Explain to Ms. Dunn possible causes of these variances.
1
Variances
A variance shows the difference between an actual amount and a budgeted or standard amount. Budgeted amount is calculated by a company using certain standards. A variance may either be favorable or unfavorable. It is usually considered as favorable if standard amount is higher than the actual amount.
To calculate: Value of various variances related to materials, labor and overheads.
Answer to Problem 18P
Material price variance is $3,000 Favorable and quantity variance is $3,200 Unfavorable.
Labor rate variance is calculated as $11,800Unfavorable and efficiency variance is $3,200 Favorable.
Overhead rate variance is calculated as $590Unfavorable and efficiency variance is $300 Favorable.
Explanation of Solution
Part a)
Calculation of material price and quantity variance:
Formula to calculate material price variance is
Here, actual quantity is given as 60,000 pounds, actual price is $4.95 per pound and standard price is $5 per pound. So, the variance will be:
Formula to calculate material quantity variance is
Here, actual quantity is given as 49,200, standard quantity is 45,000 (3.0 ponds * 15,000) and standard price is $5. So, the variance will be:
So, material price variance is $3,000 favorable and material quantity variance is $2,100 Unfavorable.
Part b)
Calculation of labor rate and efficiency variances:
Formula to calculate labor rate variance is
Here, actual hours are given as 11,800, actual rate is $17 and standard rate is $16. So, the variance will be:
Formula to calculate labor efficiency variance is
Here, standard rate is $16 per hour, actual hours are 11,800 and standard hours will be 12,000 (15,000 *0.8).So, variance will be:
Labor rate variance is calculated as $11,800unfavorable and efficiency variance is $3,200 Favorable.
Part c)
Calculation of variable overhead rate and efficiency variance:
Formula to calculate variable overhead rate variance is
Here, actual labor hours are 5,900 machine hours, actual rate is $3.10 ($18,290/5,900) and standard rate is $3.00. So, the variance will be:
Formula to calculate variable overhead efficiency variance is:
Here, standard rate is $3.00, actual hours are given as 5,900 and standard hours are 6,000 (15,000*0.4). So, the variance will be:
Variable overhead rate or spending variance is $590 Unfavorable and efficiency variance is $300 favorable.
2
Favorable or unfavorable variance
A variance is considered as a favorable variance if the actual amount is lower than the standard amount and it is considered unfavorable when actual amount is greater than the standard amount. After the calculation of all the variances, favorable or unfavorable amounts of all the variances are added to reach at the net overall effect.
To calculate: Amount of labor rate and efficiency variance.
Answer to Problem 18P
Overall, there is an unfavorable variance of $26,890.
Explanation of Solution
Net overall favorable or unfavorable variance will be calculated as:
| Variances | Amount | Net value |
| Material price variance | $3,000 F | |
| Material efficiency variance | $21,000 U | |
| Labor rate variance | $11,800 U | |
| Labor efficiency variance | $3,200 F | |
| Variable overhead rate or spending variance | $590 U | |
| Variable overhead efficiency variance | $300 F | |
| Net variance | $26,890 U |
There is a net unfavorable variance of $26,890. An unfavorable variance indicates that a company has incurred more, or extra cost as compare to its standard cost and therefore, it reduces the amount of profit earned by the company. This kind of variance alerts the management that profit of the company will be low than the expected profit. It should be detected at the earliest time possible and reasons of unfavorable variance should be fixed.
So, an unfavorable variance increase the cost and decreases the profit shown in the income statement.
3
Material efficiency variance
This variance represents the difference between the actual value of materials used by labor in producing goods and value that was budgeted to be used.
Labor rate variance
This variance represents the difference between actual value incurred on labors and value that was expected to be incurred.
To calculate: Amount of variable overhead rate and efficiency variance.
Answer to Problem 18P
Overhead rate variance is calculated as $280 unfavorable and efficiency variance is $480 Favorable.
Explanation of Solution
I am selecting the following two variances as most significant variances,
1 Material efficiency variance
2 Labor rate variance
I have selected theses two variances as they both have the highest unfavorable amount.
A material efficiency variance can be unfavorable because of several reasons, some of them are stated below:
1 When unskilled or unqualified labor is used.
2 When incorrect standards are used to calculate the standard cost.
2 When material having low quality is purchased.
3. When there is an increase in the wastages because of depreciation.
Labor rate variance can be unfavorable because of many reasons. Some of them are:
1 When incorrect standards are used to calculate the standard amount.
2 When some extra payments are being paid to labors.
3 When amount payable to labors include certain benefits.
4. When there some alterations are made in the product components.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Introduction To Managerial Accounting
- How much was the company's ending inventory?arrow_forwardJordan's Bakery has a monthly target operating income of $8,000. Variable expenses are 45% of sales, and monthly fixed expenses are $5,500. What is Jordan's operating leverage factor at the target level of operating income?arrow_forwardWhat is net income for the year on these financial accounting question?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


