
Concept explainers
Use the method of superposition to solve the following problems and assume that the flexural rigidity El of each beam is constant.
9.69 through 9.72 For the beam and loading shown, determine (a) the deflection at point C, (b) the slope at end A.
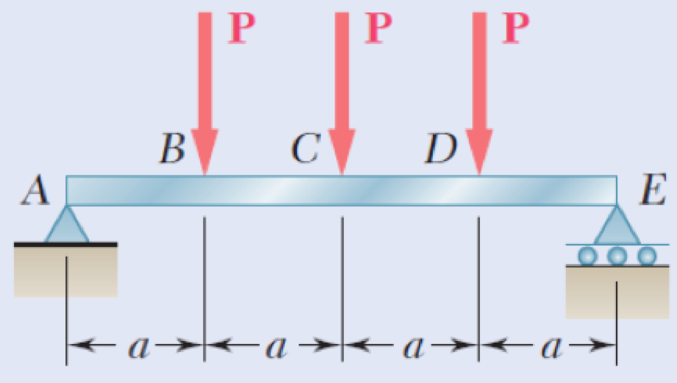
Fig. P9.69
(a)
Find the deflection at point C of the beam using superposition method.
Answer to Problem 69P
The deflection at point C of the beam is
Explanation of Solution
The flexural rigidity of the beam is EI.
Show the free-body diagram of the superimposed beam as in Figure 1.
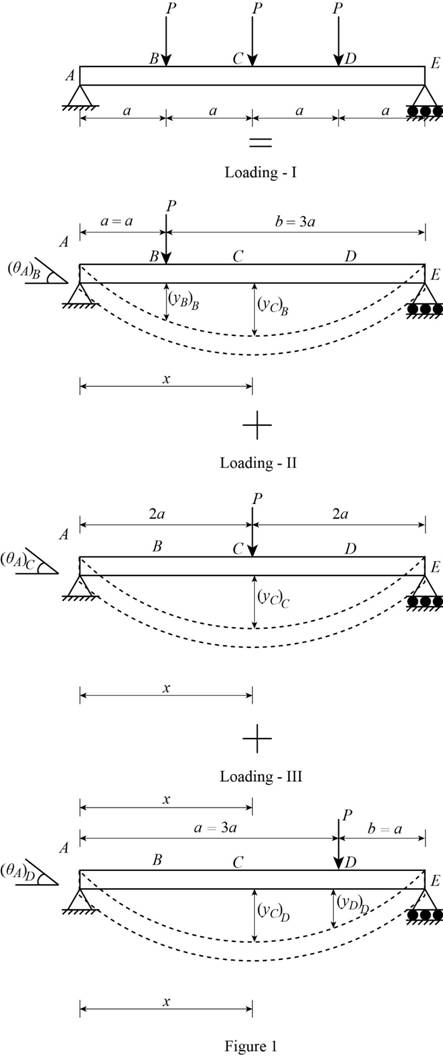
Loading I:
The downward load P is acting at point B of the beam.
Refer to case 5 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting at any point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
When
Find the deflection at point C due to point load P at point B of the beam as follows;
Loading II:
The downward point load P is acting at point C.
Refer to case 4 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting at mid-point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
Find the deflection at point C due to load P at point C as follows;
Loading III:
The downward load P is acting at point D of the beam.
Refer to case 5 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the deflection equation for concentrated load acting at any point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
Find the deflection at point C due to point load P at point D of the beam as follows;
Apply the superimposition concept.
Find the deflection at point C
Substitute
Therefore, the deflection at point C of the beam is
(b)
Find the slope at point A of the beam using superposition method.
Answer to Problem 69P
The slope at point A of the beam is
Explanation of Solution
The flexural rigidity of the beam is EI.
Refer to Figure (1) in Part (a);
Loading I:
The downward load P is acting at point B of the beam.
Refer to case 5 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the slope equation for concentrated load acting at any point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
Find the slope at point A due to point load P at point B of the beam as follows;
Loading II:
The downward point load P is acting at point C.
Refer to case 4 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the slope equation for concentrated load acting at mid-point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
Find the slope at point A due to load P at point C is;
Loading III:
The downward load P is acting at point D of the beam.
Refer to case 5 in Appendix D “Beam Deflections and Slopes” in the textbook.
Write the slope equation for concentrated load acting at any point in the simply supported beam.
Consider
Find the slope at point A due to point load P at point D of the beam is;
Apply the superimposition concept.
Find the slope at point A
Substitute
Therefore, the slope at point A of the beam is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials, 7th Edition
- Q5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forwardA mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forwardmy ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forwardMy ID#016948724. Please help me to find the moment of inertia lx ly are a please show to solve step by stepsarrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

