
Helium is used as the working fluid in a Brayton cycle with regeneration. The pressure ratio of the cycle is 8, the compressor inlet temperature is 300 K, and the turbine inlet temperature is 1800 K. The effectiveness of the regenerator is 75 percent. Determine the thermal efficiency and the required mass flow rate of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of (a) 100 percent and (b) 80 percent.
a)
The thermal efficiency and the required mass flow rate of helium for a net power
output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of 100 percent.
Answer to Problem 166RP
The thermal efficiency of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
The required mass flow rate of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
Explanation of Solution
Draw the
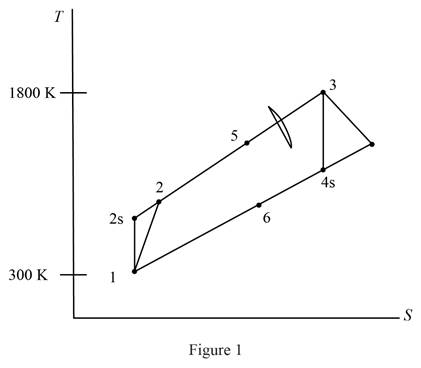
Consider, the pressure is
Consider
Write the expression to calculate the temperature and pressure relation ratio for the isentropic compression process 1-2s.
Here, the specific heat ratio is k.
Write the expression to calculate the temperature and pressure relation ratio for the isentropic expansion process 3-4s.
Write the expression for the effectiveness of the regenerator
Write the expression to calculate the net work output for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the specific heat of helium at constant pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the heat input for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression to calculate the thermal efficiency of the given regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression to calculate the mass flow rate of helium flowing through the given regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the net power output produced by the given regenerative Brayton cycleis
Conclusion:
From Table A-2, “Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases”, obtain the following values for helium gas.
Substitute 300 K for
Substitute 1800 K for
Substitute 0.75 for
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (V).
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
Substitute
Thus, the required mass flow rate of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
b)
The thermal efficiency and the required mass flow rate of helium for a net power
output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of 80 percent.
Answer to Problem 166RP
The required mass flow rate of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
The thermal efficiency of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
Explanation of Solution
Consider
Write the expression to calculate the temperature and pressure relation for the isentropic compression process 1-2.
Write the expression to calculate the isentropic efficiency of the compressor
Write the expression to calculate the temperature and pressure relation for the isentropic expansion process 3-4.
Write the expression for the isentropic efficiency of the turbine
Write the expression for the effectiveness of the regenerator
Write the expression to calculate the net work output for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the specific heat of helium at constant pressure is
Write the expression to calculate the heat input for the regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression to calculate the thermal efficiency of the given regenerative Brayton cycle
Write the expression to calculate the mass flow rate of helium flowing through the given regenerative Brayton cycle
Here, the net power output produced by the given regenerative Brayton cycle is
Conclusion:
Substitute 300 K for
Substitute 300 K for
Substitute 1800 K for
Substitute 1800 K for
Substitute 0.75 for
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the required mass flow rate of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
Substitute
Thus, the thermal efficiency of helium for a net power output of 60 MW, assuming both the compressor and the turbine have an isentropic efficiency of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS(SI UNITS,INTL.ED)EBOOK>I
- 3. - a For an elliptical cross that the tangent to section resultant shear can you s stress is show ellipse with the same 24 i ratio of eccentricity, in passes through to point alb that in question, it + Parrow_forward2. Consider the rod with an elliptical that strain 4 a Cross secton considered in class, Integrate the was displacement displacements, relations to obtain thearrow_forwardPlease answer Oxygen at 300 kPa and 90°C flowing at an average velocity of 3 m/s is expanded in an adiabatic nozzle. What is the maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle when the outlet pressure is 60 kPa? Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The maximum velocity of the oxygen at the outlet of this nozzle is 532.5 Numeric ResponseEdit Unavailable. 532.5 incorrect.m/s.arrow_forward
- A container filled with 70 kg of liquid water at 95°C is placed in a 90-m3 room that is initially at 12°C. Thermal equilibrium is established after a while as a result of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room. Assume the room is at the sea level, well sealed, and heavily insulated. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the amount of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room. The amount of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room is kJ.arrow_forwardA strain gauge rosette that is attached to the surface of a stressed component gives 3 readings (ɛa = A, b = B, &c = C). If the strain gauge rosette is of the D° type (indicating the angle between each of the gauges), construct a Mohr's Strain Circle overleaf. You should assume that gauge A is aligned along the x-axis. Using the Mohr's Strain Circle calculate the: (i) principal strains (ε1, 2)? (ii) principal angles (1, 2)? You should measure these anticlockwise from the y-axis. (iii) maximum shear strain in the plane (ymax)?arrow_forwardQ1. If the yield stress (σy) of a material is 375MPa, determine whether yield is predicted for the stresses acting on both the elements shown below using: (a) Tresca Criterion (b) Von Mises Criterion P Element A R S Element B Note: your values for P (vertical load on Element A) should be negative (i.e. corresponding to a compressive vertical load).arrow_forward
- Q. After a puncture a driver is attempting to remove a wheel nut by applying a force of P KN to one end of a wheel brace as shown in Fig. 1. In cross-section the brace is a hollow steel tube (see section aa) of internal diameter r mm and external diameter q mm. wheel nut n Position S P m r q Section aa Fig, 1 (a) Calculate (i) the twisting moment, (ii) the bending moment, and (iii) the shear force in the brace at position S due to the applied load P. (b) Calculate (i) the shear stress due to twisting, and (ii) the bending stress at position S. Note that the shear force will not produce any shear stress at S. (c) Calculate the maximum shearing stress in the brace at position S using the Maximum Shear Stress Criterion. 2 Mechanics of Materials 2 Tutorials Portfolio: Exercise 5 (d) If the maximum permissible shear stress in the steel is 200 MPa, determine the maximum torque that can be applied by the brace without the risk of failure at S.arrow_forwardCalculate the first 5 Fourier series coefficients (A0-4 and B1-5 ) for the estimated R wave.arrow_forwardRefrigerant-134a is expanded isentropically from 600 kPa and 70°C at the inlet of a steady-flow turbine to 100 kPa at the outlet. The outlet area is 1 m2, and the inlet area is 0.5 m2. Calculate the inlet and outlet velocities when the mass flow rate is 0.65 kg/s. Use the tables for R-134a. The inlet velocity is m/s. The outlet velocity is m/s.arrow_forward
- A container filled with 70 kg of liquid water at 95°C is placed in a 90-m3 room that is initially at 12°C. Thermal equilibrium is established after a while as a result of heat transfer between the water and the air in the room. Assume the room is at the sea level, well sealed, and heavily insulated. NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. Determine the final equilibrium temperature. Use the table containing the ideal gas specific heats of various common gases. The final equilibrium temperature is °C.arrow_forwardSteam at 100 psia and 650°F is expanded adiabatically in a closed system to 10 psia. Determine the work produced, in Btu/lbm, and the final temperature of steam for an isentropic expansion efficiency of 80 percent. Use steam tables. The work produced is Btu/lbm. The final temperature of steam is °F.arrow_forwardComplet the solution : Vavg Ti Te Ts Q hexp Nuexp htheo Re Nutheo Error (m/s) (*C) (*C) (*C) (W) 2.11 18.8 21.3 45.8 2.61 18.5 20.8 46.3arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





