
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
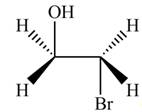
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
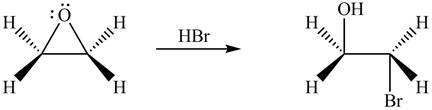
Figure 1
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
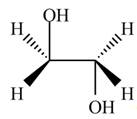
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
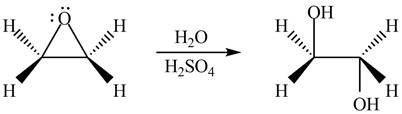
Figure 2
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
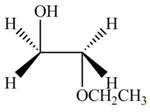
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
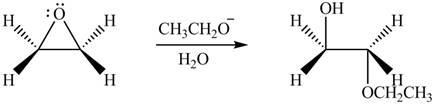
Figure 3
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
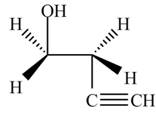
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
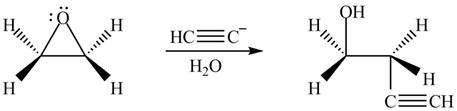
Figure 4
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
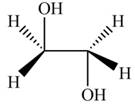
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
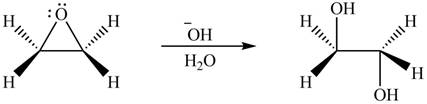
Figure 5
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation: The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.64P
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
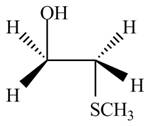
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The opening of an epoxide/ethylene oxide ring is regioselective either it takes place with a strong nucleophile
Thus, the product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is,
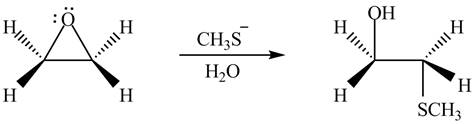
Figure 6
The product formed by the treatment of ethylene oxide with the given reagent is drawn in Figure 6.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- What is the product of the reaction? F3C. CF3 OMe NaOH / H₂Oarrow_forwardWhat would you expect to be the major product obtained from the following reaction? Please explain what is happening here. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reaction occurs. The correct answer to this question is V.arrow_forwardPlease answer the question for the reactions, thank youarrow_forward
- What is the product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalyst to produce the correct product. The correct answer is IV.arrow_forwardPlease complete the reactions, thank youarrow_forwardConsider the synthesis. What is compound Y? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing to show how the compound Y creates the product. The correct answer is D.arrow_forward
- What would be the major product of the following reaction? Please include a detailed explanation of what is happening in this question. Include steps and a drawing to show this reaction proceeds and how the final product is formed. The correct answer is B. I put answer D and I don't really understand what is going on in the question.arrow_forwardWhat is the product of the following reaction? Please explain what is happening in this question. Provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how the reagent is reacting with the catalysts to product the correct product. The correct answer is B.arrow_forwardWhat is the missing intermediate 1 and the final product 2. Please include a detailed explanation explaining the steps of malonic ester synthesis. Please include drawings of the intermediate and how it occurs and how the final product is former.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





