
Draw the organic product(s) formed when
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
(a)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alcohols undergo dehydration reaction in the presence of strong acids like
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
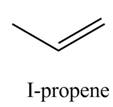
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
Alcohols undergo dehydration reaction in the presence of strong acids like
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
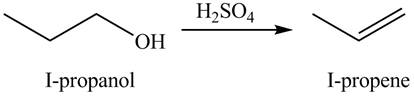
Figure 1
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(b)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: An alkoxide salt is required to prepare ether. The alkoxide salts are prepared from alcohols through the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction. In this reaction,
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
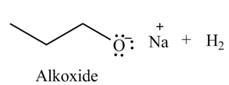
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
An alkoxide salt is required to prepare ether. The alkoxide salts are prepared from alcohols through the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction. In this reaction,
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
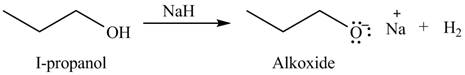
Figure 2
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(c)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: The reactivity of
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
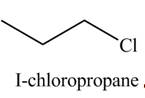
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The reactivity of
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
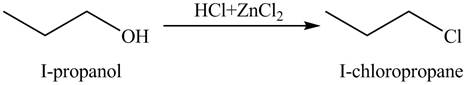
Figure 3
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(d)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: The reaction of alcohols with halogen acids
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
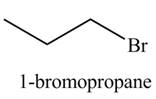
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
The reaction of alcohols with halogen acids
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
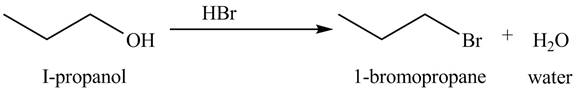
Figure 4
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(e)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkyl chlorides are obtained by the reaction of
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
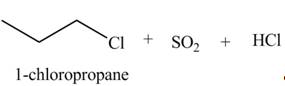
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
Alkyl chlorides are obtained by the reaction of
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
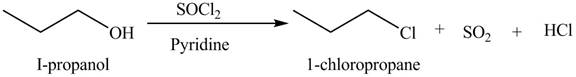
Figure 5
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(f)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alkyl bromides are obtained by the reaction of
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
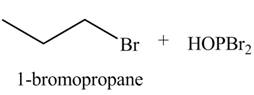
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
Alkyl bromides are obtained by the reaction of
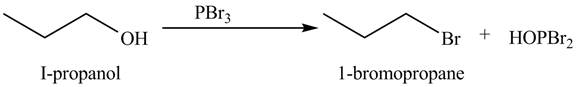
Figure 6
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(g)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
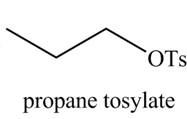
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
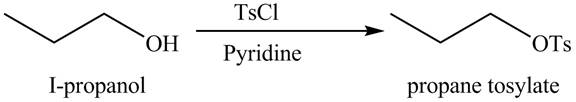
Figure 7
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(h)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: An alkoxide salt is required to prepare ether. The alkoxide salts are prepared from alcohols through the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction. In this reaction,
The formed alkoxide is allowed to react with an alkyl halide to obtain ether. The mechanism of the reaction is
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
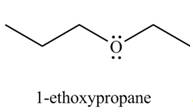
Explanation of Solution
The given reagents are
An alkoxide salt is required to prepare ether. The alkoxide salts are prepared from alcohols through the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base reaction. In this reaction,
The formed alkoxide is allowed to react with an alkyl halide to obtain ether. The mechanism of the reaction is
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
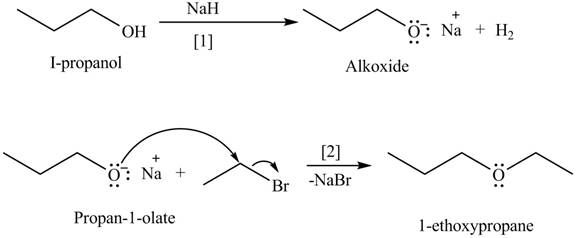
Figure 8
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(i)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
The formed alkyl tosylate reacts with strong nucleophile
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
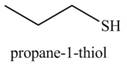
Explanation of Solution
The given reagents are
Alcohols are converted into alkyl tosylates by treatment with
The formed alkyl tosylate react with strong nucleophile
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
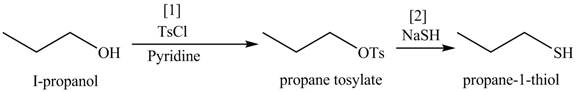
Figure 9
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
(j)
Interpretation: The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Concept introduction: Alcohols undergo dehydration reaction in the presence of
Answer to Problem 9.45P
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
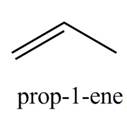
Explanation of Solution
The given reagent is
Alcohols undergo dehydration reaction in the presence of
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
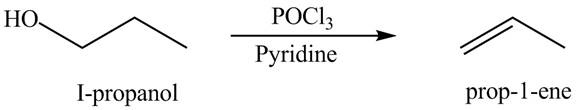
Figure 10
The organic product(s) formed by the treatment of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Concepts of Genetics (12th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Genetics: Analysis and Principles
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- Identify the compound with the longest carbon - nitrogen bond. O CH3CH2CH=NH O CH3CH2NH2 CH3CH2C=N CH3CH=NCH 3 The length of all the carbon-nitrogen bonds are the samearrow_forwardIdentify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forward
- Why isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forwardWhat is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forward
- Complete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardQ Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





