
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The three resonance structures for the given molecule
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: According to octet rule, when an atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell (outermost shell), it will be stable. Most of the atom will donate or accept electrons to its outer most orbital to satisfy the octet rule.
The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell.
Sometimes the
All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real.
Resonance is a method used to describe about delocalized electrons inside certain molecules or polyatomic ions since the Lewis structure can’t express it. A molecule or ion containing delocalized electrons can be represented by using several similar structures such structures are called as resonance structures or canonical structures.
The general rules to be followed for drawing resonance structures are given below:
- 1. The position of the atoms does not change only the pi electrons and a lone pair of electrons can change their positions.
- 2. The total number of valence electrons in all the resonance structures remains the same.
- 3. Octet rule must not be violated. No atom can have electrons more than 8 in its valence shell except sulphur.
- 4. Transfer of electrons between the bonds is shown by curved arrows.
Formal charge of an atom can be determined by the given formula.
Answer to Problem 9.54QP
The resonance structure can be drawn as,
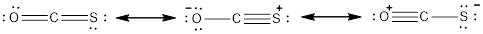
Explanation of Solution
Total electrons in
Accordingly Lewis structure of
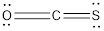
The resonance structures of molecule is as follows,
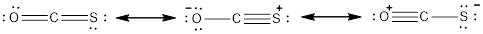
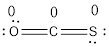
- Oxygen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Sulphur atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
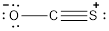
- Oxygen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Sulphur atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
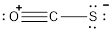
- Oxygen atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Carbon atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
- Sulphur atom
Substituting these values to the equation,
The three resonance structures for the given molecule
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK GENERAL CHEMISTRY: THE ESSENTIAL CO
- What is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forwardWhat is the IP for a amino acid- give an example what are the types of amino acids What are the structures of proteins The N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Try-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val- Tyr- Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward> aw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 1. Eto 1. EtO¯ H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. 3 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacarrow_forward
- There are various factors that affect an equilibrium. Give 3 of these factors and explain using examples andequations how an equilibrium is affected by these factors. Please remember that this is a communication question so that you are communicating your understanding of the factors that affect and equilibrium.arrow_forwardEEZE LETCHUP ID Draw the most likely conjugate base resulting from this acid-base reaction. Include all lone pairs. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Drawing く NaOCH2CH3 :0: :0: 狗arrow_forwardAnswerarrow_forward
- 2. Provide a clear arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reactions. Do not skip proton transfers, do not combine steps, and make sure your arrows are clear enough to be interpreted without ambiguity. a. CH3 Ph OEt هد Ph CH3 Hint: the species on the left is an ynolate, which behaves a lot like an enolate.arrow_forwardb. CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C an unexpected product, containing a single 9- membered ring the expected product, containing two fused rings H3C-I (H3C)2CuLi an enolatearrow_forwardb. H3C CH3 1. 2. H3O+ H3C MgBr H3Carrow_forward
- Predict the major products of this reaction: excess H+ NaOH ? A Note that the first reactant is used in excess, that is, there is much more of the first reactant than the second. If there won't be any products, just check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privarrow_forward1. For each of the reaction "railroads" below, you are either asked to give the structure(s) of the starting material(s) or product(s), or provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the transformation, as indicated by the boxes. a. NaOMe H+ .CO,H HO₂C MeOH (excess) MeOH H3C Br يع CH3 1. LiAlH4 2. H3O+ 3. PBг3 H3C 1. Et-Li 2. H3O+ -CO₂Me -CO₂Me OH CH3 CH3 ল CH3arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe ག1, ད།་, - + H You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. 2 work up Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Parrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





