
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.5.36P
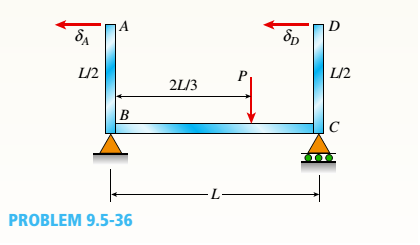
A framework A BCD is acted on by force P at 2L/3 from 8(see figure). Assume that 7f/is constant.
- Find expressions for reactions at supports B and C.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3. Use the method of sections to determine the forces in the members BD, CD, CE in the struc-
ture of Figure 3.
A
B
D
4 kN
6 kN
all dimensions in meters.
Figure 3
A pipeline engineer is considering alternative natural gas pipeline routings. The first route is mostly over land and the second is primarily undersea. Both pipelines will need some valve and fitting replacements in year 25. Cost data for each route is shown in Table P2.21. Notice that the undersea route has a higher initial cost due to higher installation costs and extra corrosion protection for the pipeline. However, the undersea route has cheaper security and maintenance costs which substantially reduces annual costs. The MARR for the project is 15%. Determine which route should be pursued based on a present worth analysis.
The state of stress at a point is σ = -4.00 kpsi, σy
Tyz
=
8.000 kpsi, and T₂ = -14.00 kpsi.
What is the maximum shear stress for this case?
The maximum shear stress is
kpsi.
=
16.00 kpsi, σ = -14.00 kpsi, Try
=
11.00 kpsi,
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a...Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a simply...Ch. 9 - -3 The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam is loaded with a point...Ch. 9 - A I-meter-long, simply supported copper beam (E =...Ch. 9 - A wide-flange beam (W 12 x 35) supports a uniform...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded, steel wide-flange beam with...
Ch. 9 - What is the span length L of a uniformly loaded,...Ch. 9 - -6 Calculate the maximum deflection of a uniformly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam with a uniform load (see figure)...Ch. 9 - A gold-alloy microbeam attached to a silicon wafer...Ch. 9 - Obtain a formula for the ratio c/maxof the...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam model is often used to represent...Ch. 9 - B cams AB and CDE are connected using rigid link...Ch. 9 - -12 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -13 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -14 A cantilever beam AB supporting a triangularly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has a length L = 12 ft and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam with an overhang is subjected to d...Ch. 9 - -17 A cantilever beam AB is acted upon by a...Ch. 9 - -18 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -19 Derive the equations of the deflect ion curve...Ch. 9 - -20 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -21 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -22 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -23 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -1 Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -2 A simple beam AB is subjected to a distrib uted...Ch. 9 - -3 The simple beam AB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - -4 A beam with a uniform load has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -5 The distributed load acting on a cantilever...Ch. 9 - -6 A cantilever beam .4B is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - -7 A beam on simple supports is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -9 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -10 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 1600 ksi) is loaded...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 12 GPa) carries a...Ch. 9 - Copper beam AB has circular cross section with a...Ch. 9 - Beam ABC is loaded by a uniform load q and point...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam of a length L = 2.5 ft has a...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam carries a trapezoidal...Ch. 9 - -5-7 A cantilever beam AB carries three equalaly...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports five equally spaced...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure has an...Ch. 9 - Beam ACE hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - What must be the equation y =f(x) of the axis of...Ch. 9 - -12 Determine the angle of rotation Band...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACE shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to load P at...Ch. 9 - Use the method of superposition to find the angles...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9,5-15 for the anti-symmetric...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCD consisting of a simple span BD and an...Ch. 9 - A horizontal load P acts at end C of the bracket...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC having flexural rigidity EI = 75 kN irT...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation 0Band deflectionCh. 9 - -22 A simple beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - The overhanging beam A BCD supports two...Ch. 9 - A thin metal strip of total weight W and length L...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 9 - A beam A BCD rests on simple supports at B and C...Ch. 9 - The compound beam ABC shown in the figure has a...Ch. 9 - A compound beam ABC DE (see figure) consists of...Ch. 9 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and held...Ch. 9 - -30. Calculate the deflection at point C of a beam...Ch. 9 - Compound beam ABC is loaded by point load P = 1.5...Ch. 9 - The compound beam shown in the figure consists of...Ch. 9 - -33 Find the horizontal deflection hand verti cal...Ch. 9 - The fr a me A BCD shown in the heure is squeezed...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by counterclockwise...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by force P at 2L/3...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCDE has simple supports at B and D and...Ch. 9 - A frame ABC is loaded at point C by a force P...Ch. 9 - The wing of a large commercial jet is represented...Ch. 9 - The wing of a small plane is represented by a...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find required distance d (in terms of L) so that...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has two triangular loads as...Ch. 9 - -1 A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a uniform...Ch. 9 - The load on a cantilever beam AB has a triangular...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation BBand the...Ch. 9 - -5 Calen1ate the deflections S 3a ndCh. 9 - A cantileverbeam^Cßsupportstwo concentrated loads...Ch. 9 - Obtain formulas for the angle of rotation 0Aat...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to a load in the...Ch. 9 - -10 The simple beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to couples M0and 2A0...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - Beam ACB hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - -4 A simple beam ABCD has moment of inertia I near...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC has a rigid segment from A to B and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC has a moment of inertia 1,5 from...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam A B supports a...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam AB supports a...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 97-10, but now use the tapered...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACE is constructed with square cross...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded simple beam AB (see figure) of...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L supports a...Ch. 9 - A propped cantilever beam AB of length L and with...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is subjected to loads...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC with simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supporting a uniform load q over...Ch. 9 - The frame shown in the figure consists of a beam...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is loaded at the...Ch. 9 - The simple beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC supports a concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam ACB supports two concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam A CB shown in the hgure is...Ch. 9 - The frame A BC support s a concentrated load P at...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC DE supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC is subjected to a couple...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC rests on a simple support...Ch. 9 - A symmetric beam A BCD with overhangs at both ends...Ch. 9 - A heavy object of weight W is dropped onto the...Ch. 9 - An object of weight Wis dropped onto the midpoint...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6 It is...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 20 kN falls through a height h = 1,0...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 4000 lb falls through a height h =...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with a rectangular cross...Ch. 9 - A heavy flywheel rotates at an angular speed m...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height /;...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam JA of length Land height/; (see...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC of height h has a sliding...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height h (see...Ch. 9 - Beam AB has an elastic support kR at A, pin...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The initial cost of a proposed heat recovery system is $375,000. The annual operation andmaintenance costs are projected to be $12,000. The salvage value of the system at the end of itsuseful life (projected to be 30 years) is $60,000. The annual savings in fuel costs resulting fromthis system are estimated to be $55,000 per year.a. Assuming annual compounding, determine the rate of return for this heat recovery system.b. If management has set the MARR to be 15% for a heat recovery system like this, what is themaximum initial cost that can be spent on the system (assuming that all other costs and incomesare the same)?arrow_forwardThe initial cost of a machine for a production facility is $225,000. The machine is expected tolast for 10 years with no salvage value. The company’s tax rate is 49% and SLD is used todepreciate the machine. For this type of depreciation, the tax life of the machine is considered 8years and its salvage value is $5,000. The after-tax rate of return is 14.3%. Determine the uniformannual before-tax cash flow.arrow_forwardThree alternatives are being considered for an air cleaning system. All three systems have a lifeof 10 years with no salvage value. System A has an initial cost of $29,000. During the first fiveyears of operation, the annual costs to operate system A are $5,000. During the second five years,the annual cost of system A increases to $16,000. System B has an initial cost of $43,000. Theannual cost to operate system B is $4,000, however, after the first year, this cost increases by$1,600 per year. System C has an initial cost of $58,000 with an annual cost of $2,400. System Crequires two upgrades: one during year 4 which costs $6,000, and the other during year 8 whichcosts $3,000. The MARR for this project is 17%. Determine which air cleaning system should beinstalled based on an economic analysis.arrow_forward
- Show all work as much as you can and box out answersarrow_forwardShow as much work as possible and box out answers pleasearrow_forwardon-the-job conditions. 9 ±0.2- 0.5 M Application questions 1-7 refer to the drawing above. 1. What does the flatness tolerance labeled "G" apply to? Surface F A. B. Surfaces E and F C. Surfaces D, E, H, and I D. The derived median plane of 12 +0.2 0.5 0.5 CF) 20 ±0.2 0.1 7. O 12 ±0.2- H 0.3 ASME Y14.5-2009arrow_forward
- elements, each with a length of 1 m. Determine the temperature on node 1, 2, 3, 4. 3. Solve the strong form analytically (you may choose Maple, MATLAB or Mathematica to help you solve this ODE). Compare the FE approximate temperature distribution through the block against the analytical solution. 1 (1) 200 °C 2 (2) 3 m 3 (3)arrow_forwardCompute the horizontal and vertical components of the reaction at the pin A. B A 30° 0.75 m 1 m 60 N 0.5 m 90 N-marrow_forwardA particle is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped hill of radius R = shown below. The angular motion of the particle is governed by the following ODE: + 0.4 02 - 2 cos 0 + 0.8 sin 0 = 0 where is the angle in rad measured from the top (CCW: +), ė 5m, as = wis the velocity in rad/s, ==a is the angular acceleration in rad/s². Use MATLAB to numerically integrate the second order ODE and predict the motion of the particle. (a) Plot and w vs. time (b) How long does it take for the particle to fall off the ring at the bottom? (c) What is the particle speed at the bottom. Hint v = Rw. in de all questions the particles inside the tube. /2/07/25 Particle R 0 0 R eled witharrow_forward
- If FA = 40 KN and FB = 35 kN, determine the magnitude of the resultant force and specify the location of its point of application (x, y) on the slab. 30 kN 0.75 m 90 kN FB 2.5 m 20 kN 2.5 m 0.75 m FA 0.75 m 3 m 3 m 0.75 marrow_forwardThe elastic bar from Problem 1 spins with angular velocity ω about an axis, as shown in the figure below. The radial acceleration at a generic point x along the bar is a(x) = ω 2 x. Under this radial acceleration, the bar stretches along x with displacement function u(x). The displacement u(x) is governed by the following equations: ( d dx (σ(x)) + ρa(x) = 0 PDE σ(x) = E du dx Hooke’s law (2) where σ(x) is the axial stress in the rod, ρ is the mass density, and E is the (constant) Young’s modulus. The bar is pinned on the rotation axis at x = 0 and it is also pinned at x = L. Determine:1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem.2. The displacement function u(x).3. The stress function σ(x).arrow_forwardThe heated rod from Problem 3 is subject to a volumetric heatingh(x) = h0xLin units of [Wm−3], as shown in the figure below. Under theheat supply the temperature of the rod changes along x with thetemperature function T(x). The temperature T(x) is governed by thefollowing equations:(−ddx (q(x)) + h(x) = 0 PDEq(x) = −kdTdx Fourier’s law of heat conduction(4)where q(x) is the heat flux through the rod and k is the (constant)thermal conductivity. Both ends of the bar are in contact with a heatreservoir at zero temperature. Determine:1. Appropriate BCs for this physical problem.2. The temperature function T(x).3. The heat flux function q(x).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Differences between Temporary Joining and Permanent Joining.; Author: Academic Gain Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PTr8QZhgXyg;License: Standard Youtube License