
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781337594318
Author: Barry J. Goodno; James M. Gere
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.9.11P
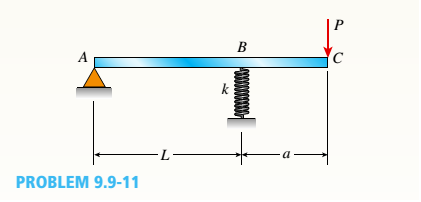
An overhanging beam ABC rests on a simple support at A and a spring support at B (see figure). A concentrated load P acts at the end of the overhang. Span AB has length /_, the overhang has length a, and the spring has stiffness k.
Determine the downward displacement 6Cof the end of the overhang. (Obtain the solution by using the modified form of Castigliano's theorem.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: Mechanics Of Materials, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + Mindtap Engineering, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card
Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a...Ch. 9 - The equation of the deflection curve for a simply...Ch. 9 - -3 The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a simple beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (sec...Ch. 9 - The deflection curve for a cantilever beam AB (see...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam is loaded with a point...Ch. 9 - A I-meter-long, simply supported copper beam (E =...Ch. 9 - A wide-flange beam (W 12 x 35) supports a uniform...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded, steel wide-flange beam with...
Ch. 9 - What is the span length L of a uniformly loaded,...Ch. 9 - -6 Calculate the maximum deflection of a uniformly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam with a uniform load (see figure)...Ch. 9 - A gold-alloy microbeam attached to a silicon wafer...Ch. 9 - Obtain a formula for the ratio c/maxof the...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam model is often used to represent...Ch. 9 - B cams AB and CDE are connected using rigid link...Ch. 9 - -12 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -13 Derive the equation of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -14 A cantilever beam AB supporting a triangularly...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has a length L = 12 ft and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam with an overhang is subjected to d...Ch. 9 - -17 A cantilever beam AB is acted upon by a...Ch. 9 - -18 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -19 Derive the equations of the deflect ion curve...Ch. 9 - -20 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -21 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -22 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -23 The beam shown in the figure has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -1 Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -2 A simple beam AB is subjected to a distrib uted...Ch. 9 - -3 The simple beam AB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - -4 A beam with a uniform load has a sliding...Ch. 9 - -5 The distributed load acting on a cantilever...Ch. 9 - -6 A cantilever beam .4B is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - -7 A beam on simple supports is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Derive the equation of the deflection curve for...Ch. 9 - -9 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - -10 Derive the equations of the deflection curve...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 1600 ksi) is loaded...Ch. 9 - A simply supported beam (E = 12 GPa) carries a...Ch. 9 - Copper beam AB has circular cross section with a...Ch. 9 - Beam ABC is loaded by a uniform load q and point...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam of a length L = 2.5 ft has a...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam carries a trapezoidal...Ch. 9 - -5-7 A cantilever beam AB carries three equalaly...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports five equally spaced...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam AB shown in the figure has an...Ch. 9 - Beam ACE hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - What must be the equation y =f(x) of the axis of...Ch. 9 - -12 Determine the angle of rotation Band...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACE shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to load P at...Ch. 9 - Use the method of superposition to find the angles...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 9,5-15 for the anti-symmetric...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam is subjected to a quadratic...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCD consisting of a simple span BD and an...Ch. 9 - A horizontal load P acts at end C of the bracket...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC having flexural rigidity EI = 75 kN irT...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation 0Band deflectionCh. 9 - -22 A simple beam AB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - The overhanging beam A BCD supports two...Ch. 9 - A thin metal strip of total weight W and length L...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with flexural rigidity EI...Ch. 9 - A beam A BCD rests on simple supports at B and C...Ch. 9 - The compound beam ABC shown in the figure has a...Ch. 9 - A compound beam ABC DE (see figure) consists of...Ch. 9 - A steel beam ABC is simply supported at A and held...Ch. 9 - -30. Calculate the deflection at point C of a beam...Ch. 9 - Compound beam ABC is loaded by point load P = 1.5...Ch. 9 - The compound beam shown in the figure consists of...Ch. 9 - -33 Find the horizontal deflection hand verti cal...Ch. 9 - The fr a me A BCD shown in the heure is squeezed...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by counterclockwise...Ch. 9 - A framework A BCD is acted on by force P at 2L/3...Ch. 9 - A beam ABCDE has simple supports at B and D and...Ch. 9 - A frame ABC is loaded at point C by a force P...Ch. 9 - The wing of a large commercial jet is represented...Ch. 9 - The wing of a small plane is represented by a...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find an expression for required moment MA(in terms...Ch. 9 - Find required distance d (in terms of L) so that...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam has two triangular loads as...Ch. 9 - -1 A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a uniform...Ch. 9 - The load on a cantilever beam AB has a triangular...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB is subjected to a...Ch. 9 - Determine the angle of rotation BBand the...Ch. 9 - -5 Calen1ate the deflections S 3a ndCh. 9 - A cantileverbeam^Cßsupportstwo concentrated loads...Ch. 9 - Obtain formulas for the angle of rotation 0Aat...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB supports two concentrated loads P...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to a load in the...Ch. 9 - -10 The simple beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB is subjected to couples M0and 2A0...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure has...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam ACB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - Beam ACB hangs from two springs, as shown in the...Ch. 9 - -4 A simple beam ABCD has moment of inertia I near...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC has a rigid segment from A to B and a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC has a moment of inertia 1,5 from...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - The tapered cantilever beam AB shown in the figure...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam A B supports a...Ch. 9 - A tapered cantilever beam AB supports a...Ch. 9 - Repeat Problem 97-10, but now use the tapered...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACE is constructed with square cross...Ch. 9 - A uniformly loaded simple beam AB (see figure) of...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L supports a...Ch. 9 - A propped cantilever beam AB of length L and with...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is subjected to loads...Ch. 9 - A beam ABC with simple supports at A and B and an...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supporting a uniform load q over...Ch. 9 - The frame shown in the figure consists of a beam...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L is loaded at the...Ch. 9 - The simple beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC supports a concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam shown in the figure supports a...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ACB supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam ACB supports two concentrated...Ch. 9 - The cantilever beam A CB shown in the hgure is...Ch. 9 - The frame A BC support s a concentrated load P at...Ch. 9 - A simple beam ABC DE supports a uniform load of...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC is subjected to a couple...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC rests on a simple support...Ch. 9 - A symmetric beam A BCD with overhangs at both ends...Ch. 9 - A heavy object of weight W is dropped onto the...Ch. 9 - An object of weight Wis dropped onto the midpoint...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam AB of length L = 6 It is...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 20 kN falls through a height h = 1,0...Ch. 9 - A weight W = 4000 lb falls through a height h =...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC with a rectangular cross...Ch. 9 - A heavy flywheel rotates at an angular speed m...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height /;...Ch. 9 - A cantilever beam JA of length Land height/; (see...Ch. 9 - An overhanging beam ABC of height h has a sliding...Ch. 9 - A simple beam AB of length L and height h (see...Ch. 9 - Beam AB has an elastic support kR at A, pin...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A fixed-end beam AB of a length L is subjected to a uniform load of intensity q acting over the middle region of the beam (sec figure). Obtain a formula for the fixed-end moments MAand MBin terms of the load q, the length L, and the length h of the loaded part of the beam. Plot a graph of the fixed-end moment MAversus the length b of the loaded part of the beam. For convenience, plot the graph in the following nondimensional form: MAqL2/l2versusbL with the ratio b/L varying between its extreme values of 0 and 1. (c) For the special case in which ù = h = L/3, draw the shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the beam, labeling all critical ordinates.arrow_forwardA foot bridge on a hiking trail is constructed using two timber logs each having a diameter d = 0.5 m (see figure a). The bridge is simply supported and has a length L = 4 m. The top of each log is trimmed to form the walking surface (see Fig, b)LA simplified model of the bridge is shown in Fig. g. Each log must carry its own weight w = 1.2 kN/m and the weight (P = 850 N) of a person at mid-span, (see Fig. b). Determine the maximum tensile and compressive stresses in the beam (Fig, b) due to bending. If load h is unchanged, find the maximum permissible value of load ... if the allowable normal stress in tension and compression is 2.5 M Pa.arrow_forwardBeam ABCD represents a reinforced-concrete foundation beam that supports a uniform load of intensity q1= 3500 lb/ft (see figure). Assume that the soil pressure on the underside of the beam is uniformly distributed with intensity q2 Find the shear force VBand bending moment MBat point B. Find the shear force Vmand bending moment M at the midpoint of the beam.arrow_forward
- Cantilever beam AB carries an upward uniform load of intensity q1from x = 0 to L/2 (see Fig. a) and a downward uniform load of intensity q from x = L/2 to L. Find q1in terms of q if the resulting moment at A is zero. Draw V and M diagrams for the case of both q and qtas applied loadings. Repeat part (a) for the case of an upward triangularly distributed load with peak intensity q0(see Fig. b). For part (b), find q0, instead of q1arrow_forwardA beam ABCD with a vertical arm CE is supported as a simple beam al A and D (see figure part a). A cable passes over a small pulley that is attached to the arm at E. One end of the cable is attached to the beam at point B. (a) What is the force P in the cable if the bending moment in the beam just lo the left of point C is equal numerically to 640 lb-ft? Note: Disregard the widths of the beam and vertical arm and use centerline dimensions when making calculations. (b) Repeat part (a) if a roller support is added at C and a shear release is inserted just left of C (see figure part b).arrow_forwardA compound beam (see figure) has an shear release just to the left of C and a moment release just to the right of C. A plot of the moment diagram is provided below the beam for applied load P at B and triangular distributed loads v(x) on segments Z/C and CD. First, solve for reactions using statics; then plot axial force (A) and shear force (K) diagrams. Confirm that the moment diagram is that shown below. Label all critical N, V, and M values and also the distance to points where N, V, and/or M are zero.arrow_forward
- Find expressions for shear force V and moment M at mid-span of beam AB in terms of peak load intensity q0and beam length variables a and L Let a = 5L/b.arrow_forwardSolve the preceding problem for a cantilever beam with data as b = 4 in., h = 9 in., L = 10 ft, P = 325 lb, and x = 45°.arrow_forwardFrame ABCD carries two concentrated loads (2P at T and P at ZX see figure) and also a linearly varying distributed load on AB, Find expressions for shear force Fand moment A/at x = L/3 of beam AB in terms of peak load intensity q0, force P, and beam length variable L. Let q0= P/L.arrow_forward
- A beam A BCD rests on simple supports at B and C (see figure). The beam has a slight initial curvature so that end A is 18 mm above the elevation of the supports and end D is 12 mm above. What moments Mtand M^, acting at points A and Dtrespectively, will move points A and D downward to the level of the supports? (The flexural rigidity EI of the beam is 2.5 X 106 N m2 and L = 2.5m).arrow_forwardA fixed-end beam is loaded by a uniform load q = 15 kN/m and a point load P = 30 kN at mid-span. The beam has a length of 4 m and modulus of elasticity of 205 GPa. Find reactions at A and B. Calculate the height of the beam if the displacement at mid-span is known to be 3 mm. Assume that the beam has rectangular cross section with h/b = 2.arrow_forward(a) A simple beam AB with length L and height h supports a uniform load of intensity q (see the figure part a). Obtain a formula for the curvature shortening A of this beam. Also, obtain a formula for the maximum bending stress b in the beam due to the load q. Now assume that the ends of the beam are pinned so that curvature shortening is prevented and a horizontal force H develops at the supports (see the figure part b). Obtain a formula for the corresponding axial tensile stress t . Using the formulas obtained in parts (a) and (b), calculate the curvature shortening , the maximum bending stress b, and the tensile stress t for the following steel beam: length L = 3m, height h = 300 mm, modulus of elasticity E = 200 GPa, and moment of inertia I = 36 x 106 mm4. Also, the load on the beam has intensity q = 25 kN/m. Compare the tensile stress tproduced by the axial forces with the maximum bending stress bproduced by the uniform load.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials Lecture: Beam Design; Author: UWMC Engineering;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-wVs5pvQPm4;License: Standard Youtube License