
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products formed when
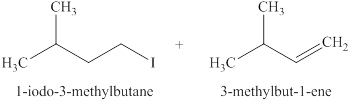
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions those occurs when
The products that are obtained via
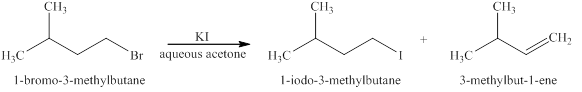
Figure 1
The
An
The products formed when
(b)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
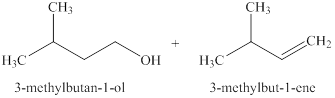
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions which
The products that are obtained via
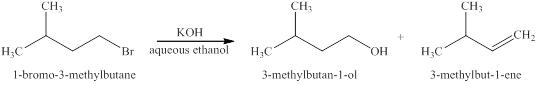
Figure 2
The
An
The products expected when
(c)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The product expected when
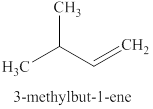
Explanation of Solution
The type of reaction which
The product that is obtained via
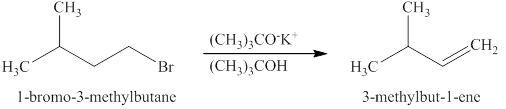
Figure 3
An
Only
The product expected when
(d)
Interpretation:
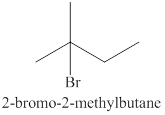
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
Concept introduction:
An
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
Explanation of Solution
Markonikov’s gave the rule purely on the basis of the observation of products received by him when performed the addition reaction on alkene.
Some reactions do not follow the rule because they follow the stability of the intermediate formed in the mechanism of that particular reaction.
The reaction of an alkene
In the reaction between the product of part (c) and
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
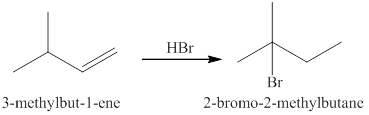
Figure 4
The products expected from the reaction of the products of part (c) and
(e)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
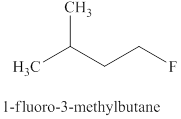
Explanation of Solution
The type of reaction which
The product for the

Figure 5
The
The fluoride ion only undergoes
The products expected when
(f)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform and potassium
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform, and potassium
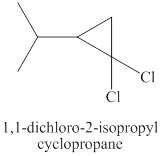
Explanation of Solution
Step-1: Take up of proton to give carbanion.
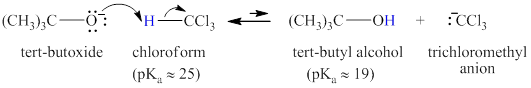
Figure 6
Step-2: Elimination of chloride ion to give carbene.
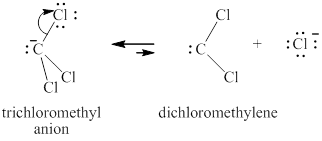
Figure 7
The carbene thus formed adds on the alkene in the leading to no change in the respective stereochemistry of substituents on alkene.
The same reaction is happening when the product of part (c) plus chloroform plus potassium
Therefore, the products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c), chloroform and potassium
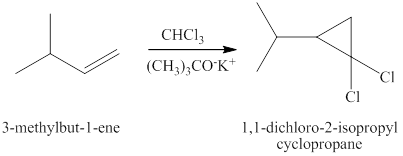
Figure 8
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) chloroform and potassium
(g)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkene with the diiodomethane in the presence of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
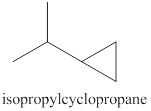
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the product of part (c) and
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
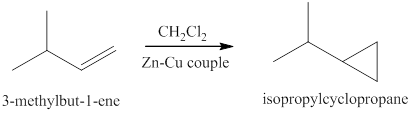
Figure 9
The products expected from the reaction of the product of part (c) and
(h)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like lithium leads to the formation of organolithium compounds (alkyllithium). These compounds are very sensitive to moisture or polar hydrogens reacts immediately leading to the formation of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of
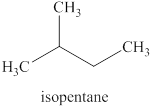
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like lithium leads to the formation of organolithium compounds (alkyllithium), which are highly susceptible to humidity or react to polar hydrogen instantly leading to the alkyl group’s formation. The same reaction is happening in this case.
The products expected from the reaction of
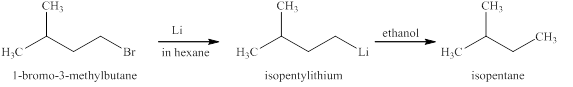
Figure 10
The products expected from the reaction of
(i)
Interpretation:
The products expected when
Concept introduction:
An alkyl halide in the presence of basic compounds undergoes multiple kinds of reaction, for example,
All these reactions take place in the presence of basic compounds but in case of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected when
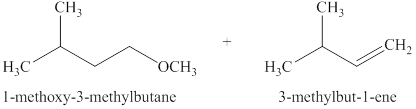
Explanation of Solution
The type of reactions that occurs when
The products that are obtained via
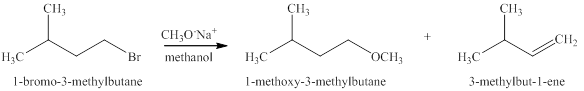
Figure 11
The
An
The products expected when
(j)
Interpretation:
The products expected from the reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like magnesium in the presence of dry ether leads to the formation of
Answer to Problem 9.45AP
The products expected from the reaction of
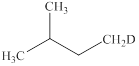
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of an alkyl halide with a metal like magnesium in the presence of dry ether results in the formation of (organometallic compounds) also known as a Grignard reagent. These compounds are very susceptible to reactions of moisture or polar hydrogen leading to the creation of alkane of the alkyl group instantly. In this case, the same reaction is occurring.
The Grignard reagent obtained in this reaction is isopentylmagnesium bromide and product obtained after treatement with heavy water is deuterated isopentane.
The products expected from the reaction of
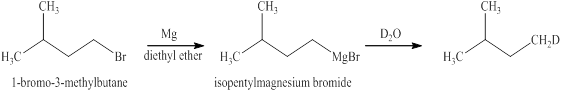
Figure 12
The products expected from the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward
- 70 Suppose the molecule below is in acidic aqueous solution. Is keto-enol tautomerization possible? • If a keto-enol tautomerization is possible, draw the mechanism for it. Be sure any extra reagents you add to the left-hand sid available in this solution. • If a keto-enol tautomerization is not possible, check the box under the drawing area. : ☐ Add/Remove step Click and drag to st drawing a structure Check Save For Late. 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe problem will not be graded for correctness, but you have to get a reasonable answer something that is either correct or very closer to the correct answer. The instructor professor wants us to do something that shows the answer but everything does not have to be correct. Ideally, yes, it has to be correct. Give it your best shot.arrow_forwardShow your steps. Hopefully, you get everything correctly or a reasonable guess that is close to the correct answer.arrow_forward
- Please give it your best shot at answering this question.arrow_forwardLook the image attaarrow_forwardPart C: Communication (/9) 17. Compare and contrast the Thomson, Rutherford and Bohr models of the atom using the chart below. You can use words and/or diagrams in your answers. (9) What was the experiment that led to the model? Where is positive charge in the atom located in the model? Where are electrons located in the molecule? Thomson Model Rutherford Model Bohr Model 2arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





