
(Flame retardants) Hydrogen radicals are important to sustaining combustion reactions. Consequently, if chemical compounds that can scavenge the hydrogen radicals are introduced, the flames can be extinguished. While many reactions occur during the combustion process, we shall choose CO flames as a model system to illustrate the process (S. Senkan et al., Combustion and Flame, 69, 113). In the absence of inhibitors
The last two reactions are rapid compared to the first two. When HCl is introduced to the flame, the following additional reactions occur:
Assume that all reactions are elementary and that the PSSH holds for the O·, OH·, and Cl· radicals.
- (a) Derive a rate law for the consumption of CO when no retardant is present.
- (b) Derive an equation for the concentration of H· as a function of time, assuming constant concentration of O2, CO, and H2O for both uninhibited combustion and combustion with HCl present. Sketch H· versus time for both cases.
(a)
Interpretation:
Rate law for the consumption of
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: Rate law:
It is generally the rate equation that consists of the reaction rate with the concentration or the pressures of the reactants and constant parameters.
Explanation of Solution
Uninhibited combustion can be given as:
Reaction when
Rate law for the consumption of
(b)
Interpretation:
Equation for the concentration of
Concept Introduction:
Rate law or rate equation: Rate law:
It is generally the rate equation that consists of the reaction rate with the concentration or the pressures of the reactants and constant parameters.
Explanation of Solution
Uninhibited combustion can be given as:
Reaction when
Rate law for the consumption of
Rate of formation of active intermediates is zero. Here,
Hence,
Also,
Substitute
Therefore,
Substitute equation for
When volume is constant, concentration of
By integration factor
When
Therefore,
When
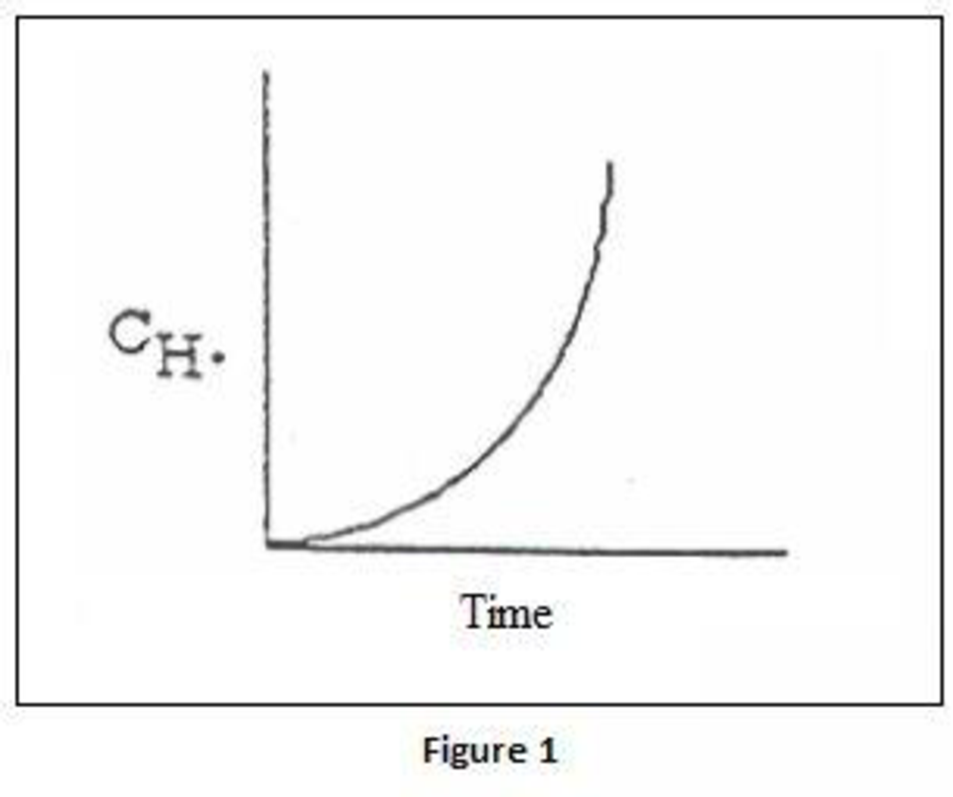
When
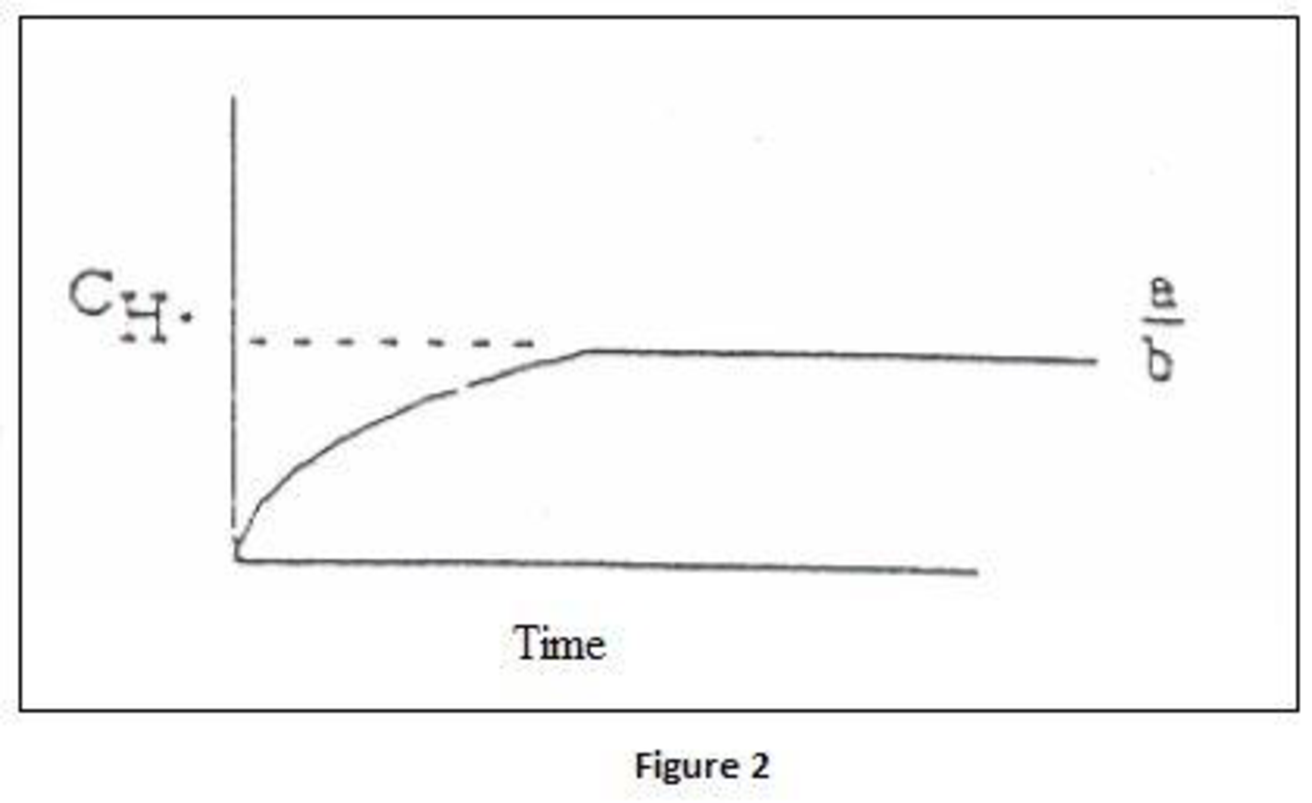
Concentration of
Where,
When
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ELEMENTS OF CHEM. REACTION ENGR
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
- Feed mixture weighing 200 kg of unknown composition containing water, acetic acid, isopropyl ether is contacted in a single stage with 280kg mixture containing 40wt% acetic acid. 10wt% water and 50wt% isopropyl ether. The resulting raffinate layer weight 320 kg and containing 29.5wt% acetic acid, 66.5 wt% water and 4wt% isopropyl ether. Determine the composition of the original feed mixture and the extract layer Water layer Isopropyl ether layer acetic acid water Isopropyl ether acetic acid water Isopropyl ether 0 98.8 1.2 0 0.6 99.4 0.69 98.1 1.2 0.18 0.5 99.3 1.41 97.1 1.5 0.37 0.7 98.9 2.89 95.5 1.6 0.79 0.8 98.4 6.42 91.7 1.9 1.93 1 97.1 13.3 84.4 2.3 4.82 1.9 93.3 25.5 71.1 3.4 11.4 3.9 84.7 36.7 58.9 4.4 21.6 6.9 71.5 44.3 5.1 10.6 31.1 10.8 58.5 46.4 37.1 16.5 36.2 15.1 48.7arrow_forward2000 Kg/hr on an acetone water mixture containing 10% of acetone is to be extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free of acetone. If 95% recovery of acetone is desired, the equilibrium relationship is given by kg acetone/kg trichloroethane 1.65 kg acetone/kg water. Estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used when: - a- Cross-current is to be extracted. b- b- Counter-current is to be extracted.arrow_forward2/1000kg/h of an acetone - water mixture containing 20wt% by weight of acetone is to be counter currently extracted with trichloroethane. The recovered solvent to be used is free from acetone. The water and trichloroethane are insoluble. If 90% recovery of acetone is desired estimate the number of stages required if 1.5 times the minimum solvent is used. The kg acetone/kg extract=1.65 kg water/kg raffinate. a- Repeat the calculation of A if the solvent used has purity of 98.5%. b- If co-current extractor is used instead of counter-current extractor in A and B estimate the number of stages required if equal amount of solvent used in each stage.arrow_forward
- Water is pumped from a large reservoir to a point 75 feet higher than the reservoir. How many feet of head must be added by the pump if 7600 lbm/hr flows through a 6-inch pipe and the frictional head loss is 3 feet? The density of the fluid is 60 lbm/ft³ and the pump efficiency is 70%. Assume the kinetic energy correction factor equals 1.arrow_forwardA firefighter is using a large water tank to supply water for extinguishing a fire. The tank has a small hole at the bottom, and water is leaking out due to gravity. The hole is located 2.5 meters below the water surface inside the tank. a. Determine the speed at which the water exits the hole. Assume there is no air resistance and that the water flow is ideal (neglect viscosity and turbulence). b. If the hole has a diameter of 2 cm, calculate the flow rate (discharge rate) in liters per second.arrow_forwardWhat kind of boundary must a system have to undergo the stated Interaction with its surroundings if possible ( mention the 3 qualities of the boundary in each case A. WORK INTERACTIONS ONLY B. MASS AND HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY C. HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY IS THIS POSSIBLE, EXPLAIN. D. WORK AND MASS INTERACTIONS ONLY. E. WORK AND HEAT INTERACTIONS ONLY F. MASS INTERACTIONS ONLY. IS THIS POSSIBLE OR NOT. EXPLAINarrow_forward
- Answer the questionsarrow_forwardFigure below shows a portion of a fire protection system in which apump draws water at 60 F from a reservoir and delivers it to point B at the flow rate of 1500 gal/min a). Calculate the required height of the water level in the tank in order to maintain 5.0 psig pressure at point A. Answer: h = 12,6 ft b). Assuming that the pressure at A is 5.0 psig, calculate the power delivered by the pump to the water in order to maintain the pressure at point B at 85 kPa. Include energy lost due to friction but neglect any other energy losses. P₁ =19,2 hparrow_forwardWater at 60° F is being pumped from a stream to a reservoir whose surface is 210 ft above the pump. The pipe from the pump to the reservoir is an 8-in Schedule 40 steel pipe 2500 ft long. The pressure at the pump inlet is - 2,36 psig. If 4.00 ft³/s is being pumped, a). Compute the pressure at the outlet of the pump. Answer: 0,997 MPa b). Compute the power delivered by the pump to the water. Answer: 151 hp Consider the friction loss in the discharged line, but neglect other lossesarrow_forward
- 1. Consider a mixture of 2.5.0% ethane, 2.0% butane, and 1.7% n-pentane by volume.a. Estimate the LFL and UFL of the mixture. Is it flammable?b. Estimate the LOC for this mixture.arrow_forwardEstimate the LFL and UFL for propylene using Equations 6-10 and 6-11 in the textbook,and compare these to the experimental values given in the table in Appendix B.arrow_forward1. Determine the minimum compression ratio required to raise the temperature of air overhexane to its AIT. Assume an initial temperature of 20°C.2. Ethanol is kept in a storage vessel that is vented with air (at 25°C and 1 atm). Is theequilibrium mixture of vapor above the liquid and air flammable? What if the liquid isacetone instead?arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





